Divisions of the Nervous System
... & Reflexes • The peripheral nervous system is also involved in reflexes. • A reflex is a quick and unconscious response to a stimulus • The brain is not involved with reflexes. ...
... & Reflexes • The peripheral nervous system is also involved in reflexes. • A reflex is a quick and unconscious response to a stimulus • The brain is not involved with reflexes. ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... Before birth, a baby’s neurons increase in number at an astonishing rate increasing the size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion n ...
... Before birth, a baby’s neurons increase in number at an astonishing rate increasing the size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion n ...
PSYB1 Revision sheet Biopsychology JM09
... Genotype never changes; phenotype can change over time. ...
... Genotype never changes; phenotype can change over time. ...
nervous_system_-_cns_and_pns_part_2_-_2015
... regulate the organs of the body without conscious control; involuntary • Control exists in the medulla • They work on smooth muscle (digestive system), cardiac muscle (heart) and glands (exocrine & endocrine) • Responsible for maintaining homeostasis during times of rest and during emergencies ...
... regulate the organs of the body without conscious control; involuntary • Control exists in the medulla • They work on smooth muscle (digestive system), cardiac muscle (heart) and glands (exocrine & endocrine) • Responsible for maintaining homeostasis during times of rest and during emergencies ...
In your journal, take notes by writing the name of
... brain stem, which is close to the center of the brain. The human thalamus can be divided into two pear-shaped halves. The thalamus is often referred to as the "relay station" of the brain. This is because the thalamus has a primary function of relaying information to other parts of the body. The tha ...
... brain stem, which is close to the center of the brain. The human thalamus can be divided into two pear-shaped halves. The thalamus is often referred to as the "relay station" of the brain. This is because the thalamus has a primary function of relaying information to other parts of the body. The tha ...
Are you your brain?
... The Right and the Good: Distributive Justice and Neural Encoding of Equity and Efficiency* Subjects making decisions re allocating meals to children in Ugandan orphanage Quandary: to share limited food equally (equity) but inadequately, or giving enough food to chosen few ...
... The Right and the Good: Distributive Justice and Neural Encoding of Equity and Efficiency* Subjects making decisions re allocating meals to children in Ugandan orphanage Quandary: to share limited food equally (equity) but inadequately, or giving enough food to chosen few ...
Chapter 4
... and environmental conditions influence the brain’s development Brain has plasticity and is context dependent https://www.youtube.c ...
... and environmental conditions influence the brain’s development Brain has plasticity and is context dependent https://www.youtube.c ...
File
... The brain goes through dynamic change during adolescence, and alcohol can seriously damage long- and short-term growth processes. Frontal lobe development and the refinement of pathways and connections continue until age 16, and a high rate of energy is used as the brain matures until age 20. Damage ...
... The brain goes through dynamic change during adolescence, and alcohol can seriously damage long- and short-term growth processes. Frontal lobe development and the refinement of pathways and connections continue until age 16, and a high rate of energy is used as the brain matures until age 20. Damage ...
Nervous System
... • Irritability – transfer impulses to the nerve cell • Conductivity – transfer impulses from the nerve cell to an organ or other nerve cell ...
... • Irritability – transfer impulses to the nerve cell • Conductivity – transfer impulses from the nerve cell to an organ or other nerve cell ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... Our Divided Brain Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. The left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. ...
... Our Divided Brain Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. The left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. ...
Document
... intermittently throughout the span of more than one year; Periodic changes in the number, frequency, type and location of the tics, and in the waxing and waning of their severity. Symptoms can sometimes disappear for weeks or months at a time; Happens before the age of 18. The range of tics or tic-l ...
... intermittently throughout the span of more than one year; Periodic changes in the number, frequency, type and location of the tics, and in the waxing and waning of their severity. Symptoms can sometimes disappear for weeks or months at a time; Happens before the age of 18. The range of tics or tic-l ...
Perception and Reality
... Do drugs really hurt you long-term? Yes. Long-term overuse of the systems of reward through drugs: Strong addiction to the drugs. Leads to less sense of reward for other activities that are actually good for you so you stop doing them. As cells die from overuse (or become habituated), you need more ...
... Do drugs really hurt you long-term? Yes. Long-term overuse of the systems of reward through drugs: Strong addiction to the drugs. Leads to less sense of reward for other activities that are actually good for you so you stop doing them. As cells die from overuse (or become habituated), you need more ...
MCDB 3650 Take Home Quiz 1 50 points (6) Describe how an
... person who has spent her entire life not using her hands. Madeline was born with cerebral palsy, and was cared for by family who did everything for her. Later in life, when her older relatives had died, she suddenly found herself needing and wanting to do things for herself. She found she was able t ...
... person who has spent her entire life not using her hands. Madeline was born with cerebral palsy, and was cared for by family who did everything for her. Later in life, when her older relatives had died, she suddenly found herself needing and wanting to do things for herself. She found she was able t ...
BRAIN RESEARCH METHODS
... It is a thin glass tube filled with salty fluid that conducts electricity ...
... It is a thin glass tube filled with salty fluid that conducts electricity ...
What is Psychology? - Weber State University
... cultural changes • Reliable differences have been found in activity of certain brain areas during some tasks – Example: MRI of language task, ...
... cultural changes • Reliable differences have been found in activity of certain brain areas during some tasks – Example: MRI of language task, ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... Biopsychology and the Foundations of Neuroscience Brain facts: --The average brain is about the size of a grapefruit --About 3 lbs in weight --100 billion nerve cells – each cells connects to up to 10,000 other nerve cells --At age 70, a person retains about 98% of their nerve cells --The brain has ...
... Biopsychology and the Foundations of Neuroscience Brain facts: --The average brain is about the size of a grapefruit --About 3 lbs in weight --100 billion nerve cells – each cells connects to up to 10,000 other nerve cells --At age 70, a person retains about 98% of their nerve cells --The brain has ...
Module 4 revised
... the brain’s sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
... the brain’s sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla ...
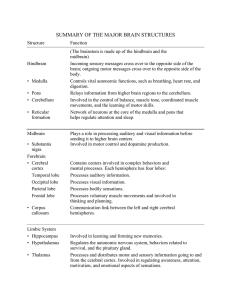
SUMMARY OF THE MAJOR BRAIN STRUCTURES
... Function (The brainstem is made up of the hindbrain and the midbrain) Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays ...
... Function (The brainstem is made up of the hindbrain and the midbrain) Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays ...
Explaining How a Thought is Formed
... problem essentially says to your brain, “You will validate this belief by creating certain experiences for me.” Whenever a triggering situation occurs, either internally or externally, your faithful servant immediately recreates the problem, i.e. the uncomfortable feelings of personal limitation. (B ...
... problem essentially says to your brain, “You will validate this belief by creating certain experiences for me.” Whenever a triggering situation occurs, either internally or externally, your faithful servant immediately recreates the problem, i.e. the uncomfortable feelings of personal limitation. (B ...
Research Methods
... Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
... Has no ill effects, unless you have a metal plate in your head Shows form and function ...
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT - Welcome to Smart Start
... Begins at birth, rapidly increases to 2-years old Continues to increase more slowly through 30years-old ...
... Begins at birth, rapidly increases to 2-years old Continues to increase more slowly through 30years-old ...
brain development - Waldorf Research Institute
... Begins at birth, rapidly increases to 2-years old Continues to increase more slowly through 30years-old ...
... Begins at birth, rapidly increases to 2-years old Continues to increase more slowly through 30years-old ...
Autonomic Nervous System Peripheral NS and Spinal Cord A
... action but it is responsible for integrating and smoothing our actions. Damage to cerebellum results in impairments in motor movement and balance. Police test cerebellums on weekends. • Pons relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. ...
... action but it is responsible for integrating and smoothing our actions. Damage to cerebellum results in impairments in motor movement and balance. Police test cerebellums on weekends. • Pons relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. ...