General Psychology - K-Dub
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
the central nervous system
... moving up the neurons of the spinal cord. The spinal cord does, however, perform many reflex reactions. Both the brain and spinal cord are made up of both myelinated and unmyelinated neurons. ...
... moving up the neurons of the spinal cord. The spinal cord does, however, perform many reflex reactions. Both the brain and spinal cord are made up of both myelinated and unmyelinated neurons. ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the chemical, dopamine in the brain. When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. ...
... Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the chemical, dopamine in the brain. When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. ...
Brain Structure - Updated 14
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
... Goal: gain a hands-on idea of how electrical information is passed along an axon for neural transmission to occur. ...
Module 6 PowerPoint
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
Module 6 Powerpoint
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
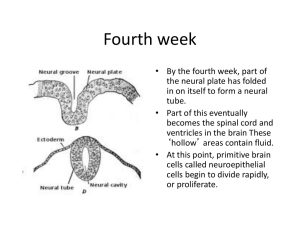
Fourth week
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
vocab - sociallyconsciousbird.com
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
sensationandperception_PP_Vision_Mods 18 and 19
... With the exception of pain, all the senses taps a different form of stimulus, and each sends the information it gathers to a different part of the brain. The senses all operate in much the same way, but each extracts different information and sends it to its own specialized processing region of the ...
... With the exception of pain, all the senses taps a different form of stimulus, and each sends the information it gathers to a different part of the brain. The senses all operate in much the same way, but each extracts different information and sends it to its own specialized processing region of the ...
Vision - Ms. Fahey
... 18-2. Discuss the different levels of processing that occur as information travels from the retina to the brain’s cortex. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones travels to our bipolar cells, then to our million or so ...
... 18-2. Discuss the different levels of processing that occur as information travels from the retina to the brain’s cortex. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones travels to our bipolar cells, then to our million or so ...
Brain Advanced 2
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
... • The ability of the brain to reorganize neural pathways based on new experiences • Persistent functional changes in the brain represent new knowledge • Age dependent component • Brain injuries ...
Chapter Two Part Three - K-Dub
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
... outer grey “bark” structure that is wrinkled in order to create more surface area for 20+ billion neurons. inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
Major Brain Structures and Functions
... receives info from all senses (except smell) and routes them to higher brain regions; “gateway” to the cortex; also involved in sleep (helps us tune out during deep sleep) ...
... receives info from all senses (except smell) and routes them to higher brain regions; “gateway” to the cortex; also involved in sleep (helps us tune out during deep sleep) ...
Crisis Response 101
... What happens when a person experiences inescapable, repeated, life-threatening, overwhelming stress ...
... What happens when a person experiences inescapable, repeated, life-threatening, overwhelming stress ...
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
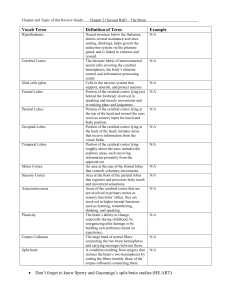
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... and binge eating, may stem from a reward deficiency syndrome. ...
... and binge eating, may stem from a reward deficiency syndrome. ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... Molecules that are similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor sites on a dendrite and block that neurotransmitter's effects are called what? a. antagonists b. endocrines c. action potentials d. endorphins e. agonists Ellen volunteers during her AP psychology class to try to balance ...
... Molecules that are similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor sites on a dendrite and block that neurotransmitter's effects are called what? a. antagonists b. endocrines c. action potentials d. endorphins e. agonists Ellen volunteers during her AP psychology class to try to balance ...
Studying the Brain
... EEG – records the electrical activity of the brain Shows the different levels of activity in the brain when a person is awake, drowsy, or asleep Stimulation Electrodes are used to stimulate the brain & record the activity Used with terminal cancer patients to relieve pain Can be used to ...
... EEG – records the electrical activity of the brain Shows the different levels of activity in the brain when a person is awake, drowsy, or asleep Stimulation Electrodes are used to stimulate the brain & record the activity Used with terminal cancer patients to relieve pain Can be used to ...
PsychSim5: Neural Messages 1 PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES
... This activity describes what researchers have learned about the special abilities of the left and right sides of the brain. You will learn how information is transmitted to these two hemispheres and about the unique function of each. Hemispheric Connections What is the name of the band of fibers c ...
... This activity describes what researchers have learned about the special abilities of the left and right sides of the brain. You will learn how information is transmitted to these two hemispheres and about the unique function of each. Hemispheric Connections What is the name of the band of fibers c ...
Temprana Reflex Therapy Info
... Temprana Reflex therapy is a Brain-Based concept Temprana Reflex Therapy is brain-based concept based in the latest in specific analyzing and treatment. Temprana Reflex Therapy can increase the body's ability to heal itself by specifically analyzing and reversing neurological impairment. Treatments ...
... Temprana Reflex therapy is a Brain-Based concept Temprana Reflex Therapy is brain-based concept based in the latest in specific analyzing and treatment. Temprana Reflex Therapy can increase the body's ability to heal itself by specifically analyzing and reversing neurological impairment. Treatments ...
Studying the Living Human Brain
... The Cerebral Cortex The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. It is the body’s ultimate control and information processing center. ...
... The Cerebral Cortex The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. It is the body’s ultimate control and information processing center. ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.