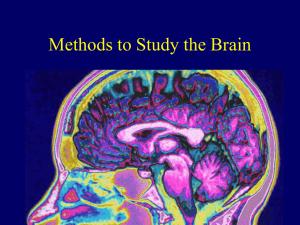
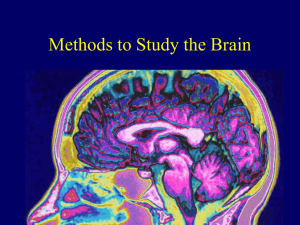
Chapter
... and focused by the lens. The lens' job is to make sure the rays come to a sharp focus on the retina. The resulting image on the retina is upside-down. • Here at the retina, the light rays are converted to electrical ...
... and focused by the lens. The lens' job is to make sure the rays come to a sharp focus on the retina. The resulting image on the retina is upside-down. • Here at the retina, the light rays are converted to electrical ...
Brain anatomy - Psycholosphere
... Many fine folds; large surface area Muscle movement & muscle tone Balance Some learning & memory ...
... Many fine folds; large surface area Muscle movement & muscle tone Balance Some learning & memory ...
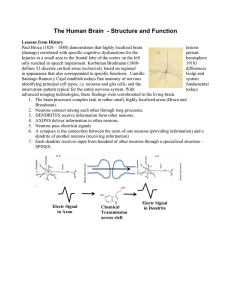
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... The Cerebrum is the largest and “newest” part of the human brain and is made up of the cortex. Major regions of the cortext are responsible for the processing of our sensations, how we receive the world. The Frontal Lobe is implicated in motor control, complex thoughts, associations, and social thin ...
... The Cerebrum is the largest and “newest” part of the human brain and is made up of the cortex. Major regions of the cortext are responsible for the processing of our sensations, how we receive the world. The Frontal Lobe is implicated in motor control, complex thoughts, associations, and social thin ...
brain09.3
... 2009 – An interdisciplinary team of scientists at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem has developed a new analytical tool to answer the question of how our brain cells record outside stimuli and react to them. Although much progress has been made in understanding the brain in recent decades, scientis ...
... 2009 – An interdisciplinary team of scientists at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem has developed a new analytical tool to answer the question of how our brain cells record outside stimuli and react to them. Although much progress has been made in understanding the brain in recent decades, scientis ...
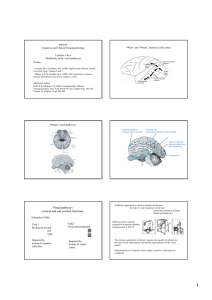
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... The visual brain areas of monkeys and humans are remarkably similar the coordination of saccadic movements, pursuit eye movements, grasping with the hand and body locomotion is computationally complex if carried out by a single central system - As such different specialised circuits may have evolved ...
... The visual brain areas of monkeys and humans are remarkably similar the coordination of saccadic movements, pursuit eye movements, grasping with the hand and body locomotion is computationally complex if carried out by a single central system - As such different specialised circuits may have evolved ...
International Baccalaureate Biology Option
... Damage to this area results in the person knowing what they want to say but they can only make sounds and are unable to make meaningful words and sentences. ...
... Damage to this area results in the person knowing what they want to say but they can only make sounds and are unable to make meaningful words and sentences. ...
From science to arts
... "The scientist does not study nature because it is useful to do so. He studies it because he takes pleasure in it; and he takes pleasure in it because it is beautiful. If nature were not beautiful, it would not be worth knowing..." Many physicists (Dirac, Einstein...) seem to hold a similar view, th ...
... "The scientist does not study nature because it is useful to do so. He studies it because he takes pleasure in it; and he takes pleasure in it because it is beautiful. If nature were not beautiful, it would not be worth knowing..." Many physicists (Dirac, Einstein...) seem to hold a similar view, th ...
January 23, set B
... But if you elaborated on the information in some meaningful way, you would be more likely to recall it. For example, you could think about the limbic system’s involvement in emotions, memory, and motivation by constructing a simple story. • “I knew it was lunchtime because my hypothalamus told me I ...
... But if you elaborated on the information in some meaningful way, you would be more likely to recall it. For example, you could think about the limbic system’s involvement in emotions, memory, and motivation by constructing a simple story. • “I knew it was lunchtime because my hypothalamus told me I ...
Sensation and Perception
... • Protecting the surface of the eye • Transmitting vibrations received by the eardrum to the hammer, anvil, and stirrup • Transforming vibrations into neural signals • Coordinating impulses from the rods and cones in the retina • Sending messages to the brain about orientation of the head and body ...
... • Protecting the surface of the eye • Transmitting vibrations received by the eardrum to the hammer, anvil, and stirrup • Transforming vibrations into neural signals • Coordinating impulses from the rods and cones in the retina • Sending messages to the brain about orientation of the head and body ...
The outer layer of the cerebral cortex is divided into different areas
... (3). Similarly, a facial expression, even if not consciously perceived, modifies the perception of emotion in the voice of the speaker (4). Our experience tells us that in nature, simultaneous signals from different sensory organs are the rule rather than the exception. But, in fact, most connection ...
... (3). Similarly, a facial expression, even if not consciously perceived, modifies the perception of emotion in the voice of the speaker (4). Our experience tells us that in nature, simultaneous signals from different sensory organs are the rule rather than the exception. But, in fact, most connection ...
demystified Vedic Vision
... Optic nerve transmits this image to a screen in the brain (visual cortex). V.S. Ramachandran from UCSD: “Inside the brain there really is no replica of the external world. Rather, there is an abstract symbolic description of that world.” ...
... Optic nerve transmits this image to a screen in the brain (visual cortex). V.S. Ramachandran from UCSD: “Inside the brain there really is no replica of the external world. Rather, there is an abstract symbolic description of that world.” ...
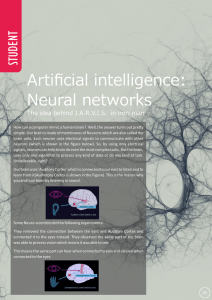
Artificial intelligence: Neural networks
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
... brain uses to process any kind of data. It has an input layer, one or more hidden layers and an output layer. In machine learning and deep learning problems, a neural network is one of the most widely used algorithms which is used to process data that helps a machine learn different things (like a hu ...
Consciousness and Awareness
... • Z Torey: Constructing a virtual world of vision, more real, more intense • S Tenberken: Creating an artistic/novelistic world of vision, via synesthesia ...
... • Z Torey: Constructing a virtual world of vision, more real, more intense • S Tenberken: Creating an artistic/novelistic world of vision, via synesthesia ...
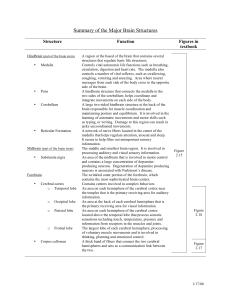
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
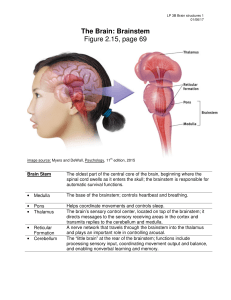
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
... A region at the based of the brain that contains several structures that regulate basic life structures. Controls vital autonomic life functions such as breathing, circulation, digestion and heart rate. The medulla also controls a number of vital reflexes, such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting and ...
The Structures of the Brain
... brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them. ...
... brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) between them. ...
Document
... • Parietal Lobe: • Can be divided into two functional regions. • The first function integrates sensory information to form a single perception (cognition). • The second function constructs a spatial coordinate system to represent the world around us. ...
... • Parietal Lobe: • Can be divided into two functional regions. • The first function integrates sensory information to form a single perception (cognition). • The second function constructs a spatial coordinate system to represent the world around us. ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... measured by amount of radioactivity present • This technique shows the pattern of neural activation is Figure 15.10 These molecules have the same related to both chemical chemical formula, but the molecular group at the structure and to perception bottom is rotated to a different position. The black ...
... measured by amount of radioactivity present • This technique shows the pattern of neural activation is Figure 15.10 These molecules have the same related to both chemical chemical formula, but the molecular group at the structure and to perception bottom is rotated to a different position. The black ...
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception
... •Inattentional blindness •Feature detection theory - bottom-up processing •Form perception - top-down processing •Subjective contours •Gestalt psychologists: the whole is more than the sum of its parts ...
... •Inattentional blindness •Feature detection theory - bottom-up processing •Form perception - top-down processing •Subjective contours •Gestalt psychologists: the whole is more than the sum of its parts ...
Slide ()
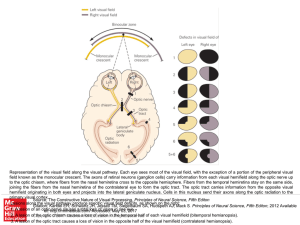
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
... Representation of the visual field along the visual pathway. Each eye sees most of the visual field, with the exception of a portion of the peripheral visual field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the op ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.