The Review
... 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrain? What is the function? 10. What makes up the forebrain? What is the function of each part? 11. What does the limbic system control? ...
... 7. Who is Phineas Gage, what happen to him, what were the effects? 8. What parts make up the hindbrain? What is the function of each part? 9. What makes up the midbrain? What is the function? 10. What makes up the forebrain? What is the function of each part? 11. What does the limbic system control? ...
Brain and Behavior
... Aggregate field view A reaction against strict materialism (mind not completely biological). ...
... Aggregate field view A reaction against strict materialism (mind not completely biological). ...
Introductory Psychology
... The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. It is the body’s ultimate control and information processing center. ...
... The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. It is the body’s ultimate control and information processing center. ...
The Teenage Brain
... • Attention • Concentration • Awareness of abilities • Self-control • “do the right thing” ...
... • Attention • Concentration • Awareness of abilities • Self-control • “do the right thing” ...
1244509Health Nervous System 2012
... 2% soluble organics, 1% inorganic salt. The brain can stay alive for 4 to 6 minutes without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
... 2% soluble organics, 1% inorganic salt. The brain can stay alive for 4 to 6 minutes without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
TOC - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
The Journal of Neuroscience Journal Club SYMPOSIUM
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
Video Review
... Video Review What does this case tell us about the structure and function of the human brain? ...
... Video Review What does this case tell us about the structure and function of the human brain? ...
The Brain
... • The crowing glory of the brain! • Only in human beings does the cerebrum make up such a large part of the brain. • The surface of the cerebrum is made up of wrinkled ridges and valleys called the ...
... • The crowing glory of the brain! • Only in human beings does the cerebrum make up such a large part of the brain. • The surface of the cerebrum is made up of wrinkled ridges and valleys called the ...
Psychology Unit 2 over Chapters 3 and 4 Chapter 3 “Biological
... Clarify how the autonomic nervous system works in emergency and everyday situations Describe what hormones are and how they affect behavior Distinguish the parts of neurons and what they do Describe electrical responses of neurons and what makes them possible Explain how neurons use neurot ...
... Clarify how the autonomic nervous system works in emergency and everyday situations Describe what hormones are and how they affect behavior Distinguish the parts of neurons and what they do Describe electrical responses of neurons and what makes them possible Explain how neurons use neurot ...
Theory of Vision: What We Can Easily See
... complex conjunction patterns are found farther up the “What” processing pathway. ...
... complex conjunction patterns are found farther up the “What” processing pathway. ...
Chapter 2
... 31. Which of the following would contribute to the negative resting membrane potential of a neuron? (p 17) 32. Which of the following states is true regarding the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (45) 33. When the membrane potential becomes positive, this is called __________. (p 46) 34. Wha ...
... 31. Which of the following would contribute to the negative resting membrane potential of a neuron? (p 17) 32. Which of the following states is true regarding the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (45) 33. When the membrane potential becomes positive, this is called __________. (p 46) 34. Wha ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: D ...
... A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: D ...
Visual Brain
... – Fovea has more cortical space than expected • Fovea accounts for .01% of retina • Signals from fovea account for 8% to 10% of the visual cortex • This provides extra processing for highacuity tasks. ...
... – Fovea has more cortical space than expected • Fovea accounts for .01% of retina • Signals from fovea account for 8% to 10% of the visual cortex • This provides extra processing for highacuity tasks. ...
Secrets of the Teen Brain
... Research Outcomes • The Cerebellum which coordinates both physical and mental activities maybe responsive to experience. • Development of brain generally proceeds from back to front. • 1st sensory functions, 2nd coordination of those sensory functions, 3rd prefrontal cortex. ...
... Research Outcomes • The Cerebellum which coordinates both physical and mental activities maybe responsive to experience. • Development of brain generally proceeds from back to front. • 1st sensory functions, 2nd coordination of those sensory functions, 3rd prefrontal cortex. ...
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... Occipital lobe: Dedicated entirely to vision and visual perception; shape, color, motion perception Functions of the Cortex The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and ...
... Occipital lobe: Dedicated entirely to vision and visual perception; shape, color, motion perception Functions of the Cortex The Motor Cortex is the area at the rear of the frontal lobes that control voluntary movements. The Sensory Cortex (parietal cortex) receives information from skin surface and ...
Study Guide 3
... 41. What is the most common cause of color blindness? Why is color blindness more common in males than in females? 42. What is meant by color constancy? Object constancy? 43. What are the main principles (or "laws") of perceptual organization according to Gestalt theory? 44. What are some cues that ...
... 41. What is the most common cause of color blindness? Why is color blindness more common in males than in females? 42. What is meant by color constancy? Object constancy? 43. What are the main principles (or "laws") of perceptual organization according to Gestalt theory? 44. What are some cues that ...
connectome - LjcdsNeuro2011
... Timeline of brain research • 450BC The Greek physician Alcmaeon concludes that the brain is the central organ for sensation and not the heart as previously believed by Pythagorian thinkers. • 300BC The first detailed account of the structure of the brain is completed by the Alexandrian biologists H ...
... Timeline of brain research • 450BC The Greek physician Alcmaeon concludes that the brain is the central organ for sensation and not the heart as previously believed by Pythagorian thinkers. • 300BC The first detailed account of the structure of the brain is completed by the Alexandrian biologists H ...
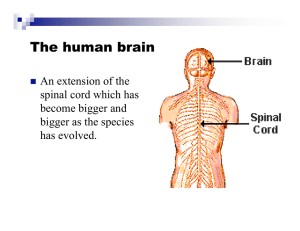
The human brain
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
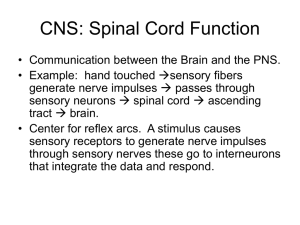
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information from the cerebral cortex as to where those part ...
... input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information from the cerebral cortex as to where those part ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the synapse are called neurotransmitters Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the c ...
... and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the synapse are called neurotransmitters Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the c ...
brain drain answers
... and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the synapse are called neurotransmitters Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the c ...
... and the part that sends the message is called the axon. The sending part of the nerve cell is often covered in myelin which speeds up the rate of transmission. Chemicals that cross the synapse are called neurotransmitters Schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease are both caused by an imbalance of the c ...
The Great Brain Drain Review - Reeths
... from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimer’s. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory. GABA is an example of an inhibitory neurotransmitter. The neural impuls ...
... from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory because decreased amounts of it in the brain are associated with the disease, Alzheimer’s. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory or inhibitory. GABA is an example of an inhibitory neurotransmitter. The neural impuls ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.