How Does the Brain Work?
... The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most evolved part of the brain is divided into lobes specialized to regulate sensory experience, language and memory, and our sense of space. The frontal lobe is the most distinctive ...
... The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most evolved part of the brain is divided into lobes specialized to regulate sensory experience, language and memory, and our sense of space. The frontal lobe is the most distinctive ...
669790507205MyersMod_LG_12
... Visual Information Processing 2. Discuss the different levels of visual information processing. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones is received and transmitted by the million or so ganglion cells whose fibers make ...
... Visual Information Processing 2. Discuss the different levels of visual information processing. We process information at progressively more abstract levels. The information from the retina’s 130 million rods and cones is received and transmitted by the million or so ganglion cells whose fibers make ...
Biopsychology - WordPress.com
... Emotions, stress, illness (schizophrenia, anxiety, etc) Language and cognition Lateralization of function ...
... Emotions, stress, illness (schizophrenia, anxiety, etc) Language and cognition Lateralization of function ...
Five basic concepts illustrate the usefulness of neuroscience to
... particularly helpful in mitigating depression. If clients are sad, encourage them to walk or run. Not only will they feel better, but their brains will be expanding as well. 3) The importance of attention and focus: Our basic concepts of attending behavior and attention — required for the learning p ...
... particularly helpful in mitigating depression. If clients are sad, encourage them to walk or run. Not only will they feel better, but their brains will be expanding as well. 3) The importance of attention and focus: Our basic concepts of attending behavior and attention — required for the learning p ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
chapter 4 note sheet
... - blindness involves the failure to see fully visible objects or events in a visual display Feature detection theory - bottom-up processing Form perception - top-down processing Subjective contours - a phenomenon whereby contours are perceived where none actually exist, attributed to top-down proces ...
... - blindness involves the failure to see fully visible objects or events in a visual display Feature detection theory - bottom-up processing Form perception - top-down processing Subjective contours - a phenomenon whereby contours are perceived where none actually exist, attributed to top-down proces ...
Slide ()
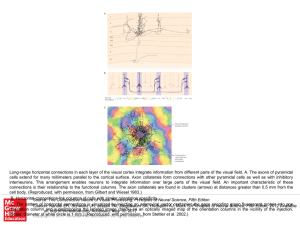
... cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as with inhibitory interneurons. This arrangement enables neurons to integrate information over large parts of the visual field. An important characteristic of the ...
... cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as with inhibitory interneurons. This arrangement enables neurons to integrate information over large parts of the visual field. An important characteristic of the ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... The Limbic System • Amygdala –two almondshaped neural clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotion and fear ...
... The Limbic System • Amygdala –two almondshaped neural clusters that are components of the limbic system and are linked to emotion and fear ...
Computational vision --- a window to our brain
... Focus on segmentation problem in vision --- region segmentation ...
... Focus on segmentation problem in vision --- region segmentation ...
Computational vision --- a window to our brain
... Focus on segmentation problem in vision --- region segmentation ...
... Focus on segmentation problem in vision --- region segmentation ...
MIND: The Cognitive Side of Mind and Brain
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
Document
... hippocampal subdivisions that also receive input directly from the cIPL. (2) To the posterior parahippocampal cortex (areas TF, TH and TFO), which projects in turn to the CA1/prosubicular subdivisions of the ...
... hippocampal subdivisions that also receive input directly from the cIPL. (2) To the posterior parahippocampal cortex (areas TF, TH and TFO), which projects in turn to the CA1/prosubicular subdivisions of the ...
Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
... _______ 11. pathway for neural fibers traveling to and from brain; controls simple reflexes. _______ 12. a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. _______ 13. axon fibers connecting two cerebral hemispheres _______ 14. two almond-shaped neural clusters that are linked to emotion ...
... _______ 11. pathway for neural fibers traveling to and from brain; controls simple reflexes. _______ 12. a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. _______ 13. axon fibers connecting two cerebral hemispheres _______ 14. two almond-shaped neural clusters that are linked to emotion ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
... - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
Brain Structure and Functioning in Relation to Outdoor Space
... Bonner 1998). They have also shown ...
... Bonner 1998). They have also shown ...
Overview and Integration
... Eight Phases in Embryonic and Fetal Development at a Cellular Level 1. Mitosis/Proliferation 2. Migration 3. Differentiation 4. Aggregation 5. Synaptogenesis ...
... Eight Phases in Embryonic and Fetal Development at a Cellular Level 1. Mitosis/Proliferation 2. Migration 3. Differentiation 4. Aggregation 5. Synaptogenesis ...
46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
... is the ability of the brain to reorganize and compensate for brain damage. 19. The branchlike extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons are called the 20. The is a set of inheritance rules in which the presence of a single dominant gene causes a trait to be expressed but two gen ...
... is the ability of the brain to reorganize and compensate for brain damage. 19. The branchlike extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons are called the 20. The is a set of inheritance rules in which the presence of a single dominant gene causes a trait to be expressed but two gen ...
Exam - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the retinas “cross over” and ascend to the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. Thus, each hemi ...
... pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the retinas “cross over” and ascend to the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. Thus, each hemi ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
Myers Module Six
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
CS 160 * Comparative Cognition * Spring 02
... - e.g. “Blindsight” Human w/damage to higher visual areas is “blind” but can point to moving stim. - Inferior Colliculus = Processes auditory info (esp location), & integrate with motor output - Together, Colliculi coord their “maps” of motion in vis & auditory world, so thing seen = thing heard - N ...
... - e.g. “Blindsight” Human w/damage to higher visual areas is “blind” but can point to moving stim. - Inferior Colliculus = Processes auditory info (esp location), & integrate with motor output - Together, Colliculi coord their “maps” of motion in vis & auditory world, so thing seen = thing heard - N ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
... a point-to-point transmission of light intensity, as is the case for shaping a pixelated picture on a television or computer screen. Instead, analytical processing of the visual information, both in the retina and in the brain, occurs in such a way that only information about selected characteristic ...
... a point-to-point transmission of light intensity, as is the case for shaping a pixelated picture on a television or computer screen. Instead, analytical processing of the visual information, both in the retina and in the brain, occurs in such a way that only information about selected characteristic ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
The Brain for Not-So
... The provided no nourishment, but was soft and warm Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
... The provided no nourishment, but was soft and warm Infants greatly preferred the “cloth mother” Retreated to the soft mother when anxious Were more outgoing, adventurous, able to meet new monkeys in presence of “cloth mother” Touch (e.g., “skin to skin”) now an important part of ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.