Ms. Setzer-The Brain!
... left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). ...
... left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
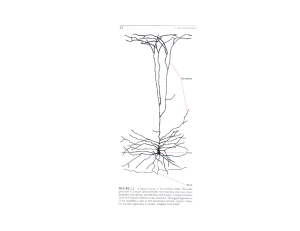
... The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tu ...
... The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tu ...
Chapter 7 part two
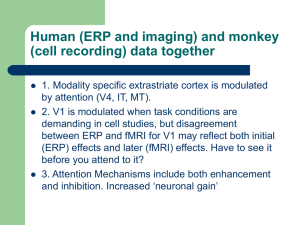
... suppressed processing in the neural populations representing features of different objects. Therefore, as a ‘winner’ emerges in one system, the same object becomes dominant across the distributed network. Last, the competition can be biased not only by bottom-up factors (for example, stimulus intens ...
... suppressed processing in the neural populations representing features of different objects. Therefore, as a ‘winner’ emerges in one system, the same object becomes dominant across the distributed network. Last, the competition can be biased not only by bottom-up factors (for example, stimulus intens ...
Brain Development
... including growth of spines on the branches • Increases capacity of dendrites to form connections with other neurons ...
... including growth of spines on the branches • Increases capacity of dendrites to form connections with other neurons ...
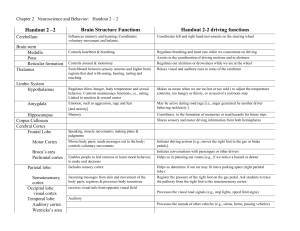
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...
WebQuest * Human Senses
... Or you can type inhttp://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/3d/index.html Explore the brain by function and answer the following questions. 1. Vision. a. In terms of vision, nerve impulses travel along the retina through the to the brains visual processing centers in the ...
... Or you can type inhttp://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/3d/index.html Explore the brain by function and answer the following questions. 1. Vision. a. In terms of vision, nerve impulses travel along the retina through the to the brains visual processing centers in the ...
chapter 3 study guide
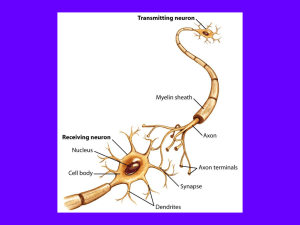
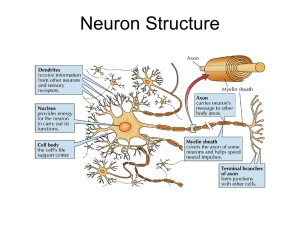
... Neurons: Identify and locate the fundamental components and functions that form the biological bases of communication and behavior within the nervous system, including: ...
... Neurons: Identify and locate the fundamental components and functions that form the biological bases of communication and behavior within the nervous system, including: ...
Abstract n Bio - Prof Arto Nurmikko
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
... electrical microcircuits in the brain has been a central research topic of modern neuroscience for at least a century. More recently, engineers, physicists, and mathematicians have been bringing their tools of trade to both experimental and theoretical research in brain science. Pursu ...
Lecture 5 - TeachLine
... What do we mean by “why” in science? What is the primary goal of neuroscience? ...
... What do we mean by “why” in science? What is the primary goal of neuroscience? ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
... 14. Please explain the difference between the ontogeny and phylogeny of the brain. 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, an ...
... 14. Please explain the difference between the ontogeny and phylogeny of the brain. 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, an ...
Bolt ModEP7e LG11.39-42B
... to the visual cortex. In the cortex, individual neurons (feature detectors) respond to specific features of a visual stimulus. The visual cortex passes this information along to other areas of the cortex, which includes higher-level brain cells that respond to specific visual scenes. Other supercell ...
... to the visual cortex. In the cortex, individual neurons (feature detectors) respond to specific features of a visual stimulus. The visual cortex passes this information along to other areas of the cortex, which includes higher-level brain cells that respond to specific visual scenes. Other supercell ...
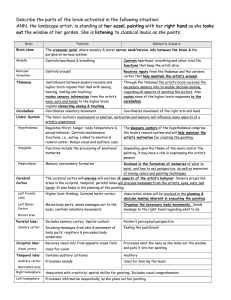
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... The pleasure centers of the hypothalamus comprise the brain’s reward system and will help maintain the artist’s motivation for creating the painting. ...
... The pleasure centers of the hypothalamus comprise the brain’s reward system and will help maintain the artist’s motivation for creating the painting. ...
Artificial Eye.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... contact with the nerve fiber layer retinal ganglion cells. The information in this approach must be captured by a camera system before transmitting data and energy to the implant. The "Sub retinal" approach involves the electrical stimulation of the inner retina from the sub retinal space by implant ...
... contact with the nerve fiber layer retinal ganglion cells. The information in this approach must be captured by a camera system before transmitting data and energy to the implant. The "Sub retinal" approach involves the electrical stimulation of the inner retina from the sub retinal space by implant ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... Two other ways of assessing brain function are through studying people with brain damage or well-known changes in function (e.g., the elderly) ...
... Two other ways of assessing brain function are through studying people with brain damage or well-known changes in function (e.g., the elderly) ...
Chapter 2
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
specimen jar craft - National Wildlife Federation
... jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. I ...
... jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. I ...
Slide ()
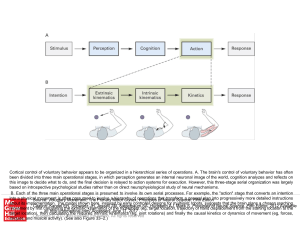
... Cortical control of voluntary behavior appears to be organized in a hierarchical series of operations. A. The brain's control of voluntary behavior has often been divided into three main operational stages, in which perception generates an internal neuronal image of the world, cognition analyzes and ...
... Cortical control of voluntary behavior appears to be organized in a hierarchical series of operations. A. The brain's control of voluntary behavior has often been divided into three main operational stages, in which perception generates an internal neuronal image of the world, cognition analyzes and ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. ...
... The brain is one of the few organs that can only use glucose to get ATP as its energy source. Therefore, without some sugar in our bloodstream, the brain will die. ...
Vision
... The entire range of electromagnetic energy Wavelength- the distance between the crest of two successive ...
... The entire range of electromagnetic energy Wavelength- the distance between the crest of two successive ...
INC-IEM Neuroengineering Seminar - 13-11-04
... device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of neuroprostheses is now emerging that aims to combine neural recording, signal processing, and microstimulation functionalities for closed-loop operation. These devices might use information extract ...
... device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of neuroprostheses is now emerging that aims to combine neural recording, signal processing, and microstimulation functionalities for closed-loop operation. These devices might use information extract ...
Neuroesthetics

Neuroesthetics (or neuroaesthetics) is a relatively recent sub-discipline of empirical aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic perceptions of art and music. Neuroesthetics received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, and psychologists.