Study Guide
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
Unit II: Body and Mind
... – Result of damage to the parietal lobe association areas on one side of the cortex, usually the right side – Person ignores information from opposite side of body or visual field ...
... – Result of damage to the parietal lobe association areas on one side of the cortex, usually the right side – Person ignores information from opposite side of body or visual field ...
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... 2. Manipulating the brain a. Lesions – purposely destroying a part of the brain and observing the results. b. Brain Stimulation (Show at :40-:50 sec) ...
... 2. Manipulating the brain a. Lesions – purposely destroying a part of the brain and observing the results. b. Brain Stimulation (Show at :40-:50 sec) ...
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... 2. Manipulating the brain a. Lesions – purposely destroying a part of the brain and observing the results. b. Brain Stimulation (Show at :40-:50 sec) ...
... 2. Manipulating the brain a. Lesions – purposely destroying a part of the brain and observing the results. b. Brain Stimulation (Show at :40-:50 sec) ...
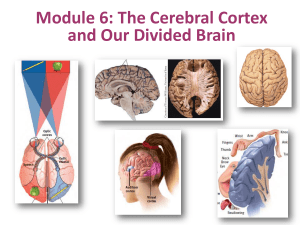
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
Biological foundations of psychology
... brain’s electrical activity, recorded from electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
... brain’s electrical activity, recorded from electrodes placed on the scalp. ...
Emotional control system and centers of our personalities Extremely
... • Involved with the sensory and motor tracts, the cardiac and respiratory center, swallowing and coughing, and cranial nerves •Certain neurons in the medulla control respiration and heart rate. •Damage to the medulla results in dilated pupils, abnormal breathing, inability to control movement, or pa ...
... • Involved with the sensory and motor tracts, the cardiac and respiratory center, swallowing and coughing, and cranial nerves •Certain neurons in the medulla control respiration and heart rate. •Damage to the medulla results in dilated pupils, abnormal breathing, inability to control movement, or pa ...
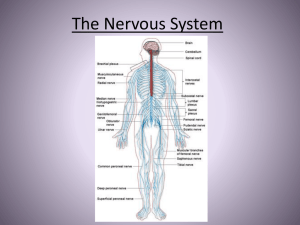
The Nervous System
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
A New Source for New Neurons : TheologyPlus : http://www
... That may be the goal, but it's hard to imagine this research will be limited to therapy. In fact it may turn out to be easier to use it to enhance the cognitive capacity of normal or healthy aging brains than it is to treat disease. Anything that stimulates the growth of new neurons is likely to be ...
... That may be the goal, but it's hard to imagine this research will be limited to therapy. In fact it may turn out to be easier to use it to enhance the cognitive capacity of normal or healthy aging brains than it is to treat disease. Anything that stimulates the growth of new neurons is likely to be ...
Aotearoa Neuroscience Postdoctoral Fellow Projects
... Preterm born infants have very high rates of neurological disability, including deficits in learning, memory and cognition that persist into adolescence and adulthood. These deficits are strongly associated impaired growth of grey matter structures of the brain, including the cerebral cortex. In a p ...
... Preterm born infants have very high rates of neurological disability, including deficits in learning, memory and cognition that persist into adolescence and adulthood. These deficits are strongly associated impaired growth of grey matter structures of the brain, including the cerebral cortex. In a p ...
Brain-Computer Interface
... Directed at assisting, augmenting, or repairing human cognitive or sensory-motor functions. ...
... Directed at assisting, augmenting, or repairing human cognitive or sensory-motor functions. ...
Major Brain Structures and Functions
... Brain (Neural) Plasticity • The brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Severed neurons do not usually regenerate • Instead, the brain’s neural tissue can reorganize itself • One brain area can take on functions not normally “assigned” to that area • Brain’s are most plastic w ...
... Brain (Neural) Plasticity • The brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Severed neurons do not usually regenerate • Instead, the brain’s neural tissue can reorganize itself • One brain area can take on functions not normally “assigned” to that area • Brain’s are most plastic w ...
Verlamde man bestuurt computer via gedachten
... The device can tap into a hundred neurons at a time, and is the most sophisticated such implant tested in humans so far. Many paralysed people control computers with their eyes or tongue. But muscle function limits these techniques, and they require a lot of training. For over a decade researchers h ...
... The device can tap into a hundred neurons at a time, and is the most sophisticated such implant tested in humans so far. Many paralysed people control computers with their eyes or tongue. But muscle function limits these techniques, and they require a lot of training. For over a decade researchers h ...
Studying the Brain
... Controls hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior Controls the body’s reaction to temperature ...
... Controls hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior Controls the body’s reaction to temperature ...
J. Claude Hemphill III
... localized more diffusely throughout the cerebral cortex. The reticular formation is distinguished from other brain structures associated with induction of sleep. (Netter illustration from www.netterimages.com. © Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.) Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... localized more diffusely throughout the cerebral cortex. The reticular formation is distinguished from other brain structures associated with induction of sleep. (Netter illustration from www.netterimages.com. © Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.) Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Nervous System
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
... It begins in the dendrites, moves rapidly towards the neurons cells body, and then down the axon until it reaches the axon tips. It travels along the neuron in the form of electricity. ...
SRCD Abstract 01 - University of Illinois Archives
... environment. By looking at this process in the brain and behavior, we can see how genes and experience interact. The initial development of the basic pattern of organization of the brain, positioning cells and forming initial connections, occurs under substantial control of orchestrated patterns of ...
... environment. By looking at this process in the brain and behavior, we can see how genes and experience interact. The initial development of the basic pattern of organization of the brain, positioning cells and forming initial connections, occurs under substantial control of orchestrated patterns of ...