Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 2:Hindbrain The
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
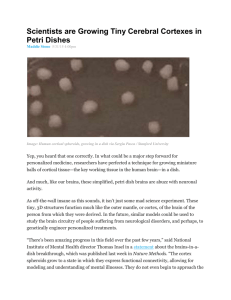
Scientists are Growing Tiny Cerebral Cortexes in Petri
... balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brains are abuzz with neuronal activity. As off-the-wall insane as this sounds, it isn’t just some mad science experiment. These tiny, 3D structures function much lik ...
... balls of cortical tissue—the key working tissue in the human brain—in a dish. And much, like our brains, these simplified, petri dish brains are abuzz with neuronal activity. As off-the-wall insane as this sounds, it isn’t just some mad science experiment. These tiny, 3D structures function much lik ...
Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron is called the SYNAPSE Synaptic gap or cleft-a tiny gap between the receiving neuron and sending neuron ...
... dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron is called the SYNAPSE Synaptic gap or cleft-a tiny gap between the receiving neuron and sending neuron ...
The Lombardi Cancer Center of Georgetown University is
... mechanisms underlying accelerated aging; and interventions to improve function. Other research includes investigations of survivorship, structures and patterns of care, and policy modeling of interventions designed to optimize outcomes of older cancer patients. The individual filling this position w ...
... mechanisms underlying accelerated aging; and interventions to improve function. Other research includes investigations of survivorship, structures and patterns of care, and policy modeling of interventions designed to optimize outcomes of older cancer patients. The individual filling this position w ...
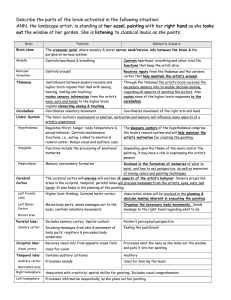
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation: ANN, the landscape artist, is standing at her easel, painting with her right hand as she looks out the window at her garden. She is listening to classical music as she paints. ...
... Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation: ANN, the landscape artist, is standing at her easel, painting with her right hand as she looks out the window at her garden. She is listening to classical music as she paints. ...
A Data Mining Survey of the Allen Brain Atlas
... Neuromodulatory systems are structures located in the sub-cortical region of the brain composed of neurons (on the order of 1,000 in a mouse and 10,000 in a human per system) that control fundamental behaviors by interacting with many areas of the brain, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and fron ...
... Neuromodulatory systems are structures located in the sub-cortical region of the brain composed of neurons (on the order of 1,000 in a mouse and 10,000 in a human per system) that control fundamental behaviors by interacting with many areas of the brain, including the amygdala, hippocampus, and fron ...
NEUROSCIENCE REVIEW
... game when his helmet flew off. Ever since the game he has been unable to speak certain words. What area of his brain was likely damaged? Broca’s area ...
... game when his helmet flew off. Ever since the game he has been unable to speak certain words. What area of his brain was likely damaged? Broca’s area ...
Nervous System
... A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region in the center called the cell body. ...
... A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region in the center called the cell body. ...
Re-examining the debate about the functional role of motor cortex
... Re-examining the debate about the functional role of motor cortex Robert Ajemian Brain and Cognitive Sciences, MIT ...
... Re-examining the debate about the functional role of motor cortex Robert Ajemian Brain and Cognitive Sciences, MIT ...
File
... when there is no food. a. they can see a pattern in it (or impose a pattern on it) b. there is repetition of the information, especially over an extended period of time c. there is a strong stimulus associated with it, including colour, light, ...
... when there is no food. a. they can see a pattern in it (or impose a pattern on it) b. there is repetition of the information, especially over an extended period of time c. there is a strong stimulus associated with it, including colour, light, ...
WARM UP 4/20
... each, write down a little note for you to remember where the part is. EX: gyri - ridges pons – bump near bottom of brain ...
... each, write down a little note for you to remember where the part is. EX: gyri - ridges pons – bump near bottom of brain ...
Chapter 2 STUDY GUIDE
... *Phineas Gage showed severe personality changes following a mining accident that damaged his prefrontal cortex (FRONTAL LOBE). *Broca’s Area is located in the frontal lobe of the left hemisphere and is responsible for speech production language production; putting words into sentences. *Wernicke’s A ...
... *Phineas Gage showed severe personality changes following a mining accident that damaged his prefrontal cortex (FRONTAL LOBE). *Broca’s Area is located in the frontal lobe of the left hemisphere and is responsible for speech production language production; putting words into sentences. *Wernicke’s A ...
hendrick
... connection (whether electrical or chemical, and if chemical, the specific neurotransmitter to which the synaptic receptor responds). As that is largely a function of the transmitting neuron, it might not need to be expressed as a property of the connection; but if it were, then estimating 100+ neuro ...
... connection (whether electrical or chemical, and if chemical, the specific neurotransmitter to which the synaptic receptor responds). As that is largely a function of the transmitting neuron, it might not need to be expressed as a property of the connection; but if it were, then estimating 100+ neuro ...
Sheep Brain Dissection
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
Nervous System
... lies deep in the central groove • The cerebrum is further divided into 5 distinct lobes ...
... lies deep in the central groove • The cerebrum is further divided into 5 distinct lobes ...
Structure of the Brain
... sulcus and the postcentral gyrus. Controls touch sensations and information from muscle stretch receptors as well as touch and body location) - Temporal lobe (locate near the temples. Controls auditory information, perception of movement and facial recognition) - Frontal lobe (contains the primary m ...
... sulcus and the postcentral gyrus. Controls touch sensations and information from muscle stretch receptors as well as touch and body location) - Temporal lobe (locate near the temples. Controls auditory information, perception of movement and facial recognition) - Frontal lobe (contains the primary m ...
The Brain
... The central nervous system (CNS) is made of the brain and the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is made of nerves. The brain is made of three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (part of the li ...
... The central nervous system (CNS) is made of the brain and the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is made of nerves. The brain is made of three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (part of the li ...
Sheep Brain Dissection - Milton
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
Chapter 3 Week 2 Day 4
... Research has been conducted on patients with brain damage to determine how well the brain can repair itself. Recovery from brain damage depends on the age of the individual and the extent of the brain damage. A. The Brain’s Plasticity and Capacity for Repair 1. Most of the human brain’s plasticity ...
... Research has been conducted on patients with brain damage to determine how well the brain can repair itself. Recovery from brain damage depends on the age of the individual and the extent of the brain damage. A. The Brain’s Plasticity and Capacity for Repair 1. Most of the human brain’s plasticity ...
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... • Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
... • Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... that transmits impulses throughout your body • 3 Types: – Sensory – Motor – Interneuron ...
... that transmits impulses throughout your body • 3 Types: – Sensory – Motor – Interneuron ...
WHY STUDY THE BRAIN IN PSYCHOLOGY?
... Contains the major centers for hearing. Some of the centers relating to speech are also located here. ...
... Contains the major centers for hearing. Some of the centers relating to speech are also located here. ...