Central Nervous System
... Some cognitive function in predicting motor movements Fine coordination: 3 main functions ____________________________________ ____________________________________ Flocculonodular lobe= _________________________ Hemispheres separated by falx cerebelli Cerebellar cortex – gray ...
... Some cognitive function in predicting motor movements Fine coordination: 3 main functions ____________________________________ ____________________________________ Flocculonodular lobe= _________________________ Hemispheres separated by falx cerebelli Cerebellar cortex – gray ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... Gray matter is the cell bodies; found on surface or cortex and center of spinal cord. White matter is b/c of myelin—axons of neurons (send info); inside cortex and on outside of spinal cord. Central sulcus: divides brain in half from anterior to posterior. Pre-central gyrus: anterior to central ...
... Gray matter is the cell bodies; found on surface or cortex and center of spinal cord. White matter is b/c of myelin—axons of neurons (send info); inside cortex and on outside of spinal cord. Central sulcus: divides brain in half from anterior to posterior. Pre-central gyrus: anterior to central ...
Why light
... Kittens raised in vertical environments ignored the horizontally oriented parts of their environments. Kittens raised in horizontal environments ignored the vertically oriented parts of their environments. ...
... Kittens raised in vertical environments ignored the horizontally oriented parts of their environments. Kittens raised in horizontal environments ignored the vertically oriented parts of their environments. ...
The Biological Perspective - Klicks-IBPsychology-Wiki
... • Some used to excite (Trigger activation) others used to inhibit (Prevent neuron firing) still more are used to block or clear away these exciters and inhibitors • If neurons are constantly stimulated they reduce their ...
... • Some used to excite (Trigger activation) others used to inhibit (Prevent neuron firing) still more are used to block or clear away these exciters and inhibitors • If neurons are constantly stimulated they reduce their ...
PNS and CNS Nervous System Organization Peripheral Nervous
... • Single motor neuron cell leading from the CNS directly to the muscle • Cell body of motor neurons located in CNS ...
... • Single motor neuron cell leading from the CNS directly to the muscle • Cell body of motor neurons located in CNS ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
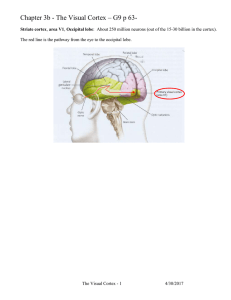
... • Occipital Lobe – processing of visual information – visual cortex • interpretation of visual images • motor activity of eyes • correlation of images with previous visual experiences ...
... • Occipital Lobe – processing of visual information – visual cortex • interpretation of visual images • motor activity of eyes • correlation of images with previous visual experiences ...
Introduction to Psychology: Final Exam
... C27. The brain’s activating system, or “alarm clock,” thatdirects attention and alertness. A 28. This structure in the brainstem directs vital life functions such as heartbeat and breathing. E 29. A peanut-sized structure that is part of the forebrain’s limbic system regulates behaviors related to s ...
... C27. The brain’s activating system, or “alarm clock,” thatdirects attention and alertness. A 28. This structure in the brainstem directs vital life functions such as heartbeat and breathing. E 29. A peanut-sized structure that is part of the forebrain’s limbic system regulates behaviors related to s ...
THE VISUAL SYSTEM
... daylight vision and color vision • Fovea: tiny spot in center of retina; contains only cones • Rods: play key role in night vision and peripheral vision ...
... daylight vision and color vision • Fovea: tiny spot in center of retina; contains only cones • Rods: play key role in night vision and peripheral vision ...
Thought translation, tennis and Turing tests in the vegetative state
... midbrain, is the state of coma, which is characterized by a complete loss of consciousness and wakefulness. More specifically, individuals in a comatose brain state are no longer conscious of themselves or their surroundings, and they are unable to produce willed movements. But coma is hardly ever a ...
... midbrain, is the state of coma, which is characterized by a complete loss of consciousness and wakefulness. More specifically, individuals in a comatose brain state are no longer conscious of themselves or their surroundings, and they are unable to produce willed movements. But coma is hardly ever a ...
Chapter 2
... Location of function – brain areas for particular functions • Brain stem – top of spinal cord ; pons & medulla • Pons – sleeping; waking & dreaming; left-right body coordination; arousal • Medulla – some automatic functions; breathing, swallowing & heart rate functions that are not consciously wille ...
... Location of function – brain areas for particular functions • Brain stem – top of spinal cord ; pons & medulla • Pons – sleeping; waking & dreaming; left-right body coordination; arousal • Medulla – some automatic functions; breathing, swallowing & heart rate functions that are not consciously wille ...
Slide 1
... • 85 billion (85,000,000,000) neurons in the human brain. • 3,000 years one cell/second • 1 neuron cell body = 10 microns wide 85,000,000,000 neurons = 850 km • If you use a basketball (diameter = ~24 cm) as the cell body, then your axon would have to be 240,000 cm (2.4 kilometers) in length! ...
... • 85 billion (85,000,000,000) neurons in the human brain. • 3,000 years one cell/second • 1 neuron cell body = 10 microns wide 85,000,000,000 neurons = 850 km • If you use a basketball (diameter = ~24 cm) as the cell body, then your axon would have to be 240,000 cm (2.4 kilometers) in length! ...
Neuroscience 14b – Organisation of the Cerebral Cortex
... o Their stimulation does not lead to simple reproducible effects. o Can be divided into polymodal and supramodal. There has also been a third proposed type of cortical area – the higher order areas which carry out further processing of information from primary modalities. They supplement the primary ...
... o Their stimulation does not lead to simple reproducible effects. o Can be divided into polymodal and supramodal. There has also been a third proposed type of cortical area – the higher order areas which carry out further processing of information from primary modalities. They supplement the primary ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amount of generalization is normal, over generalizing to the CS+ has been implicated as a marker ...
... fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amount of generalization is normal, over generalizing to the CS+ has been implicated as a marker ...
NOTE
... an area of the left frontal lobe that directs the muscle movements involved in speech ...
... an area of the left frontal lobe that directs the muscle movements involved in speech ...
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System - dr
... b. Precentral gyrus (what is its function) c. Postcentral gyrus (what is its function) 12. Describe the path of motor control from the brain to skeletal muscle. Be sure to include the basal ganglia and cerebellum’s role in addition to the primary motor and premotor cortex. Be able to locate upper an ...
... b. Precentral gyrus (what is its function) c. Postcentral gyrus (what is its function) 12. Describe the path of motor control from the brain to skeletal muscle. Be sure to include the basal ganglia and cerebellum’s role in addition to the primary motor and premotor cortex. Be able to locate upper an ...
Development of the Brain
... Figure 5.3 Human brain at five stages of development The brain already shows an adult structure at birth, although it continues to grow during the first year or so. Video ...
... Figure 5.3 Human brain at five stages of development The brain already shows an adult structure at birth, although it continues to grow during the first year or so. Video ...
Neuroscience, Genetics, and Behavior
... Close-Up: Left-Handedness—Is Being a Lefty All Right? • Thinking Critically About Left Brain/Right Brain • Summing Up Myers 5e ...
... Close-Up: Left-Handedness—Is Being a Lefty All Right? • Thinking Critically About Left Brain/Right Brain • Summing Up Myers 5e ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam1_050117_final_solution
... PÁZMÁNY PÉTER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND BIONICS DEPARTMENT OF NEUROSCIENCE ...
... PÁZMÁNY PÉTER CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND BIONICS DEPARTMENT OF NEUROSCIENCE ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... combinations of features. Maintained in separate global and detailed maps. ...
... combinations of features. Maintained in separate global and detailed maps. ...
Biology Option Review Section E
... Animal responses can be affected by natural selection in regards to higher rates of survival, as is the case with the Loggerhead turtles who are, after birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and ...
... Animal responses can be affected by natural selection in regards to higher rates of survival, as is the case with the Loggerhead turtles who are, after birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and ...
Myers AP - Unit 3B
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
Introduction to the Brain
... – Damaged region’s function is taken over by another area, or areas, of the brain ...
... – Damaged region’s function is taken over by another area, or areas, of the brain ...
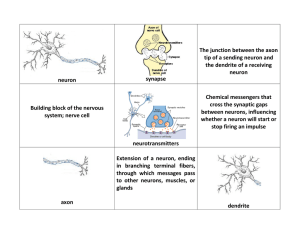
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
PPT File - Holden R
... – Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons – Tracts • Rubrospinal • Vestibulospinal • Reticulospinal ...
... – Synapse in some intermediate nucleus rather than directly with lower motor neurons – Tracts • Rubrospinal • Vestibulospinal • Reticulospinal ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.