Lecture 2 - Computer Science
... •When you move your eyes, the image moves. How do you know the world is not moving? ...
... •When you move your eyes, the image moves. How do you know the world is not moving? ...
In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
unit 3b brain
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
EXC 7770 Psychoneurological & Medical Issues in Special Education
... Part of the basal ganglia Emotional processing Emotional memory ...
... Part of the basal ganglia Emotional processing Emotional memory ...
Pituitary malfunctions
... Left side functions: The left hemisphere controls touch and movement of the right side of the body, vision in the right half of the visual field, comprehension and production of speech, reading ability, mathematical reasoning, and a host of other abilities. Right side functions: The right hemisphere ...
... Left side functions: The left hemisphere controls touch and movement of the right side of the body, vision in the right half of the visual field, comprehension and production of speech, reading ability, mathematical reasoning, and a host of other abilities. Right side functions: The right hemisphere ...
Video Review
... Responsible for the most complex aspects of perception, emotion, movement, and thought. ...
... Responsible for the most complex aspects of perception, emotion, movement, and thought. ...
Module 4 Notes
... processes body sensations. The occipital lobes at the back of the head receive input from the eyes. An auditory area of the temporal lobes receives information from the ears. ...
... processes body sensations. The occipital lobes at the back of the head receive input from the eyes. An auditory area of the temporal lobes receives information from the ears. ...
Sensation & Perception
... the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take informati ...
... the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take informati ...
Unit 3ABC Reading and Study Guide
... What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmitters? What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? How does the endoc ...
... What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmitters? What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? How does the endoc ...
Consciousness, biology and quantum hypotheses
... B.J. Baars, D.B. Edelman / Physics of Life Reviews 9 (2012) 285–294 ...
... B.J. Baars, D.B. Edelman / Physics of Life Reviews 9 (2012) 285–294 ...
The Brain: Your Crowning Glory
... We begin our tour of the brain at the lowest level, the hindbrain — the part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull and widens. We then work our way upward, first to the midbrain, which lies above the hindbrain, and then to the forebrain, which lies in the highest part of the brain. Con ...
... We begin our tour of the brain at the lowest level, the hindbrain — the part of the brain where the spinal cord enters the skull and widens. We then work our way upward, first to the midbrain, which lies above the hindbrain, and then to the forebrain, which lies in the highest part of the brain. Con ...
Figure 3B.23 Testing the divided brain
... Figure 3B.13 Left hemisphere tissue devoted to each body part in the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sens ...
... Figure 3B.13 Left hemisphere tissue devoted to each body part in the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sens ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... A. Split brains: A house divided 1. Corpus callosum, which connects the cerebral hemispheres in normal brains, is severed 2. This surgery has been performed in animal studies and for some human conditions such as severe epilepsy 3. Effects a. Split-brain patients are able to lead normal lives b. Eff ...
... A. Split brains: A house divided 1. Corpus callosum, which connects the cerebral hemispheres in normal brains, is severed 2. This surgery has been performed in animal studies and for some human conditions such as severe epilepsy 3. Effects a. Split-brain patients are able to lead normal lives b. Eff ...
Slide ()
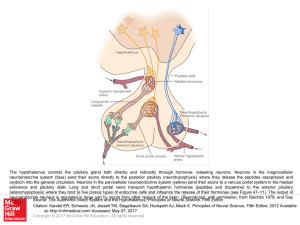
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
Latest Findings in the Mechanisms of Cortical `Arousal`: `Enabling
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
CNS - Misericordia University
... time and are in stage 4 more than adults); Elderly have about the same total sleep time as adults but broken into smaller episodes, also spend less time in REM. Time spent in Stage 4 declines with age. • Person consistently deprived of REM may become moody or depressed; may exhibit other personality ...
... time and are in stage 4 more than adults); Elderly have about the same total sleep time as adults but broken into smaller episodes, also spend less time in REM. Time spent in Stage 4 declines with age. • Person consistently deprived of REM may become moody or depressed; may exhibit other personality ...
A.1 Neural Development
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
PETER SOMOGYI University of Oxford, United Kingdom Peter
... areas and contribute to the coordination of network activity such as theta rhythmicity and high frequency ripple oscillations (SWR). Some of them exclusively innervate local cortical GABAergic interneurons. Individual MSDB neurons show a wide range of activity patterns, which may be related to their ...
... areas and contribute to the coordination of network activity such as theta rhythmicity and high frequency ripple oscillations (SWR). Some of them exclusively innervate local cortical GABAergic interneurons. Individual MSDB neurons show a wide range of activity patterns, which may be related to their ...
doc psych 100 review summary
... According to Hebb “set” occurs when two stimuli are presented one after the other and the response to the second is controlled or modified by the first. o The cell assembly theory explains set: The mechanism of thought is a recurrent neural loop that received sensory input from another loop but that ...
... According to Hebb “set” occurs when two stimuli are presented one after the other and the response to the second is controlled or modified by the first. o The cell assembly theory explains set: The mechanism of thought is a recurrent neural loop that received sensory input from another loop but that ...
Slide 1
... Occipital lobe - section of the brain located at the rear and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain. Primary visual cortex – processes visual information from the eyes. Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. Parieta ...
... Occipital lobe - section of the brain located at the rear and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain. Primary visual cortex – processes visual information from the eyes. Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. Parieta ...
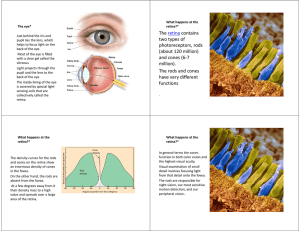
The retina contains two types of photoreceptors, rods (about 120
... • Now the next step is to reassemble this fragmented information and integrate it so that we see an image, a colour, a face, a movement etc. • This occurs via two main neural streams that go to particular parts of the brain termed visual association areas where visual signals are further inter ...
... • Now the next step is to reassemble this fragmented information and integrate it so that we see an image, a colour, a face, a movement etc. • This occurs via two main neural streams that go to particular parts of the brain termed visual association areas where visual signals are further inter ...
File
... Scientists can map which parts of the brain control various parts of the body. The mapping is done by stimulating the sensory or motor cortex with a weak electric current. The stimulation often produces tingling or movement in part of the body. Humans put great emphasis on speech and manipulation of ...
... Scientists can map which parts of the brain control various parts of the body. The mapping is done by stimulating the sensory or motor cortex with a weak electric current. The stimulation often produces tingling or movement in part of the body. Humans put great emphasis on speech and manipulation of ...
Artificial Intelligence and Artificial Consciousness: Continuum or
... • Another possible source of discontinuity between cognitive and phenomenological? • Perhaps any genuine AC would have to be considered as having its own intrinsic experiential point of view, and hence an intrinsic moral worth; • i.e. it would deserve consideration for its own sake; • this would be ...
... • Another possible source of discontinuity between cognitive and phenomenological? • Perhaps any genuine AC would have to be considered as having its own intrinsic experiential point of view, and hence an intrinsic moral worth; • i.e. it would deserve consideration for its own sake; • this would be ...
Myers AP - Unit 03B
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.