Slide ()
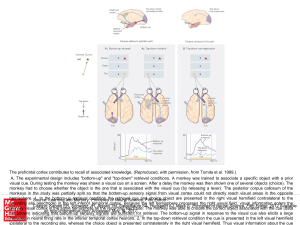
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
Slide ()
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
neurobiological-basis-of-behavior
... neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types of Neurons 1. Sensory neuron (afferent neuron) – carry information from the senses to the spinal cord 2. Interneuron – makes connections to oth ...
... neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types of Neurons 1. Sensory neuron (afferent neuron) – carry information from the senses to the spinal cord 2. Interneuron – makes connections to oth ...
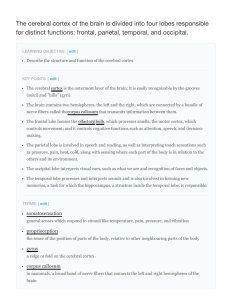
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
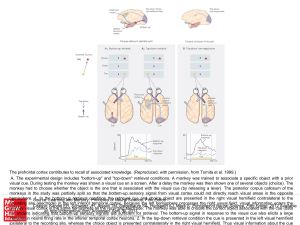
... patients' left visual fields, they may be unable to verbally name the object (and may claim not to have seen an object at all). This is because the visual input from the left visual field crosses and enters the right hemisphere and is unable to signal to the speech center, which generally is found i ...
... patients' left visual fields, they may be unable to verbally name the object (and may claim not to have seen an object at all). This is because the visual input from the left visual field crosses and enters the right hemisphere and is unable to signal to the speech center, which generally is found i ...
456 ss 96 final - People Server at UNCW
... 12. The primary somatosensory cortex is found at the: a) frontal lobe b) parietal lobe c) Occipital lobe d) longitudinal fissure 13. The normal role for the Striato-pallidal pathway in motor behavior seems to be mainly a) inhibitory b) excitatory c) to initiate voluntary behaviors d) to project to t ...
... 12. The primary somatosensory cortex is found at the: a) frontal lobe b) parietal lobe c) Occipital lobe d) longitudinal fissure 13. The normal role for the Striato-pallidal pathway in motor behavior seems to be mainly a) inhibitory b) excitatory c) to initiate voluntary behaviors d) to project to t ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
Chapter 02
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
Slide ()
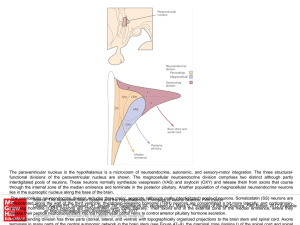
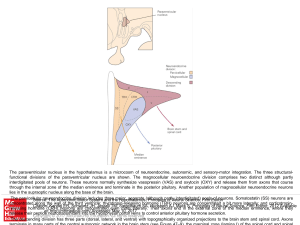
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
Inside the BRAIN: Neurons and Neural Networks
... The limbic system is involved in emotions, memory, and learning • The limbic system is a functional group of integrating centers in the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus • It is involved in emotions, memory (short-term and long-term), and learning – The amygdala is central to the formatio ...
... The limbic system is involved in emotions, memory, and learning • The limbic system is a functional group of integrating centers in the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus • It is involved in emotions, memory (short-term and long-term), and learning – The amygdala is central to the formatio ...
Slide ()
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
... concentrated along the wall of the third ventricle; thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neurons are concentrated a bit more laterally; and corticotropinCitation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available releasi ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 07 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System, Part 3
... • Important fact. On the whole, the right side of the brain processes sensory information from the left side of the body and issues motor commands to the left side of the body. Likewise, the left side of the brain processes sensory information from the right side of the body and issues motor command ...
... • Important fact. On the whole, the right side of the brain processes sensory information from the left side of the body and issues motor commands to the left side of the body. Likewise, the left side of the brain processes sensory information from the right side of the body and issues motor command ...
Mind-brain identity and functionalism
... 1. Since 1980, dramatic progress has been made in providing neural explanations for many mental processes. ...
... 1. Since 1980, dramatic progress has been made in providing neural explanations for many mental processes. ...
Final - Center for Neural Science
... b) is the only frequency to which the nerve fiber responds. c) changes with the frequency of the stimulus. d) is the frequency to which the neuron is most responsive. 12) A pure tone one octave above another tone has a frequency ______ of the lower tone. a) four times that b) two times that c) that ...
... b) is the only frequency to which the nerve fiber responds. c) changes with the frequency of the stimulus. d) is the frequency to which the neuron is most responsive. 12) A pure tone one octave above another tone has a frequency ______ of the lower tone. a) four times that b) two times that c) that ...
Chapter 02_Quiz - Biloxi Public Schools
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
... 16. In order for you to experience the pain of being stuck with a pin, ___ must first relay messages from your ankle to your ...
Introduction to Neuroscience
... Cells of the nervous system • Nerve cells (neurons) – specialised cells – convey sensory information into the brain – transmit commands from the brain to control organs and muscles, – thought, feeling, action – form complex circuits ...
... Cells of the nervous system • Nerve cells (neurons) – specialised cells – convey sensory information into the brain – transmit commands from the brain to control organs and muscles, – thought, feeling, action – form complex circuits ...
Latest Findings in the Mechanisms of Cortical `Arousal`: `Enabling
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
... to be states of consciousness in the phenomenal sense of having conscious experiences; but to bestow that title to only waking states in the medical sense of being conscious of ones surroundings. While REM and waking states share some commonalities in terms of "phenomenal" experiences – "The dream s ...
Module 07_lecture
... • The strip of brain tissue at the rear of the frontal lobes • Controls voluntary movement • Different parts of the cortex control different parts of the body. • The motor cortex in the left hemisphere controls the right side of the body and ...
... • The strip of brain tissue at the rear of the frontal lobes • Controls voluntary movement • Different parts of the cortex control different parts of the body. • The motor cortex in the left hemisphere controls the right side of the body and ...
Problems with Imbalance
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
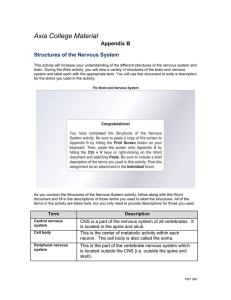
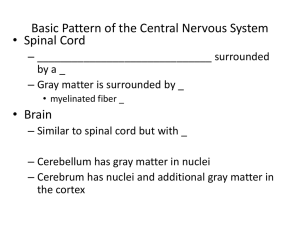
Basic Pattern of the Central Nervous System
... _____________________________ (controls the opposite side of the body) • Hemispheres are not equal in function • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior involves the entire cortex ...
... _____________________________ (controls the opposite side of the body) • Hemispheres are not equal in function • No functional area acts alone; conscious behavior involves the entire cortex ...
Document
... • Gate-control Theory: An explanation for pain control that proposes we have a neural “gate” that can, under some circumstances, block incoming pain signals. • Placebos: Substances that appear to be drugs but are not • Placebo effect: A response to a placebo caused by subjects’ belief that they are ...
... • Gate-control Theory: An explanation for pain control that proposes we have a neural “gate” that can, under some circumstances, block incoming pain signals. • Placebos: Substances that appear to be drugs but are not • Placebo effect: A response to a placebo caused by subjects’ belief that they are ...
Slide ()
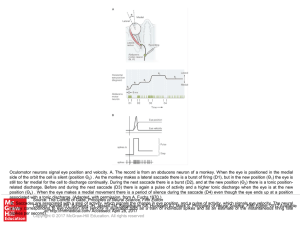
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
Physiological-clinical importance of the eye.
... ganglion cells translate these into action potentials that propagates along the primary optic pathway to visual centers in the brain. ...
... ganglion cells translate these into action potentials that propagates along the primary optic pathway to visual centers in the brain. ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.