CH3
... The bulges in cortex are termed gyri The cortex is primarily composed of cells, giving it a ...
... The bulges in cortex are termed gyri The cortex is primarily composed of cells, giving it a ...
Answers to Test Your Understanding of Concepts
... 9. Damage to Broca’s area of the cortex produces speech difficulty without causing impairment in verbal comprehension (Broca’s aphasia). This evidence suggests that Broca’s area is involved in the motor control of speech. Damage to Wernicke’s area impairs language understanding, but not motor abili ...
... 9. Damage to Broca’s area of the cortex produces speech difficulty without causing impairment in verbal comprehension (Broca’s aphasia). This evidence suggests that Broca’s area is involved in the motor control of speech. Damage to Wernicke’s area impairs language understanding, but not motor abili ...
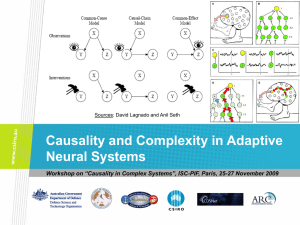
Mirror neurons and the 8 parallel consciousnesses
... loss of consciousness of sensorial information on the left. It is usually caused by unilateral lesion in the right part of the brain, in even just one of the different areas with specular counterparts in the left hemisphere. Only the lesion on the right is capable of causing the disease, because it ...
... loss of consciousness of sensorial information on the left. It is usually caused by unilateral lesion in the right part of the brain, in even just one of the different areas with specular counterparts in the left hemisphere. Only the lesion on the right is capable of causing the disease, because it ...
Understanding Teenagers
... mood & behavior (I feel this way, so I will do this or not do this. It can be very dangerous if teens just rely on their feelings to determine their actions. Their impulse control is immature. -> Risky behaviors…increased incidence of unintentional injuries, violence, substance abuse, unintended pre ...
... mood & behavior (I feel this way, so I will do this or not do this. It can be very dangerous if teens just rely on their feelings to determine their actions. Their impulse control is immature. -> Risky behaviors…increased incidence of unintentional injuries, violence, substance abuse, unintended pre ...
Attention and Consciousness
... Another example is conscious and unconscious pain in which unconscious pain barely reached cortex and conscious one engaged large brain areas. While learning new tasks (like walking or simple games) children are very conscious of actions, but after they master it and action becomes more automati ...
... Another example is conscious and unconscious pain in which unconscious pain barely reached cortex and conscious one engaged large brain areas. While learning new tasks (like walking or simple games) children are very conscious of actions, but after they master it and action becomes more automati ...
What” and ”where” – dynamic parallel processing of sound
... • Similar network of cerebral structures (e.g., premotor cortex) is activated when normal control subjects execute physically or imagine a sequence of up-down foot movements mental practice with motor imagery can be used as a therapeutic approach to keep active the neural circuits involved in loco ...
... • Similar network of cerebral structures (e.g., premotor cortex) is activated when normal control subjects execute physically or imagine a sequence of up-down foot movements mental practice with motor imagery can be used as a therapeutic approach to keep active the neural circuits involved in loco ...
Sensory organs and perception
... After they left the isolation chamber, the perceptions of many were temporarily distorted, and their brain-wave patterns, which had slowed down during the experiment, took several hours to return to normal. ...
... After they left the isolation chamber, the perceptions of many were temporarily distorted, and their brain-wave patterns, which had slowed down during the experiment, took several hours to return to normal. ...
psych mod 4 terms
... measures how these signals interact with brain cells and transforms this interaction into an incredibly detailed image of the brain (or body).MRIs are used to study the structure of the brain. 7. PET Scan- involves injecting a lightly radioactive solution into the blood and then measuring the amount ...
... measures how these signals interact with brain cells and transforms this interaction into an incredibly detailed image of the brain (or body).MRIs are used to study the structure of the brain. 7. PET Scan- involves injecting a lightly radioactive solution into the blood and then measuring the amount ...
The Nervous System
... the skull and several layers of sheathing; spinal cord by the vertebrae; peripheral nerves by layers of sheathing ...
... the skull and several layers of sheathing; spinal cord by the vertebrae; peripheral nerves by layers of sheathing ...
CIN_W4_Presentation_Thu_Batten
... Question 8 – Changing our minds? • When we change our mind about something, how does it change the physical structure of our brains? • Could the mental process of “changing one’s mind” correspond to the physical process of switching between attractors in our brain? • Is brain dynamics governed by a ...
... Question 8 – Changing our minds? • When we change our mind about something, how does it change the physical structure of our brains? • Could the mental process of “changing one’s mind” correspond to the physical process of switching between attractors in our brain? • Is brain dynamics governed by a ...
Chapter 1 - Center for Advanced Brain Imaging
... show recovery. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
... show recovery. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
What a Frog s Eye tells the Frog s brain
... These operations are independent of the general level of illumination 1. Local sharp edges and contrast 2. the curvature of edge of a dark contrast 3. the movement of edges 4. the local dimming produced by movement or rapid general darkening Each group of fibers serving one operation maps the re ...
... These operations are independent of the general level of illumination 1. Local sharp edges and contrast 2. the curvature of edge of a dark contrast 3. the movement of edges 4. the local dimming produced by movement or rapid general darkening Each group of fibers serving one operation maps the re ...
Lecture notes for Chapter 12
... Communication between cerebral areas, and between cortex and lower CNS Association fibers— horizontal; connect different parts of same hemisphere Commissural fibers— horizontal; connect gray matter of two hemispheres Projection fibers— vertical; connect hemispheres with lower brain or ...
... Communication between cerebral areas, and between cortex and lower CNS Association fibers— horizontal; connect different parts of same hemisphere Commissural fibers— horizontal; connect gray matter of two hemispheres Projection fibers— vertical; connect hemispheres with lower brain or ...
File - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
... A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges runs along the inside of the Axon. Energy (ATP) is needed to cause these changes Diagram 34.6 pg 322 ...
... A chain reaction is set up & a movement of +ive charges runs along the inside of the Axon. Energy (ATP) is needed to cause these changes Diagram 34.6 pg 322 ...
Organization of Nervous System
... transmit information to another neuron are called neurotransmitters. There are several kinds of neurotransmitters, which we will discuss in later lectures. ...
... transmit information to another neuron are called neurotransmitters. There are several kinds of neurotransmitters, which we will discuss in later lectures. ...
Chapter 6
... Channels sensory information pain, taste, temperature, audition, vision Integrates sensorimotor information From Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum, and Cortex Regulates function of association cortex and cortically mediated speech, language, and cognitive functions. ...
... Channels sensory information pain, taste, temperature, audition, vision Integrates sensorimotor information From Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum, and Cortex Regulates function of association cortex and cortically mediated speech, language, and cognitive functions. ...
Rexed`s Lamina
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
Hippocampus+and+Neurons+Final+Draft
... The Hippocampus and Neurons are parts of the brain that fascinate me. This is an amazing organ in which electricity (synapses) coupled with this organ’s ability to control every function in the human body make this organ a never-ending source of research. I narrowed this project to the hippocampus a ...
... The Hippocampus and Neurons are parts of the brain that fascinate me. This is an amazing organ in which electricity (synapses) coupled with this organ’s ability to control every function in the human body make this organ a never-ending source of research. I narrowed this project to the hippocampus a ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... • PET and fMRI = minutes and seconds Spatial resolution: Measure where an event is occurring • Lesion and functional imaging = millimetre • Single-cell recordings = level of the neuron ...
... • PET and fMRI = minutes and seconds Spatial resolution: Measure where an event is occurring • Lesion and functional imaging = millimetre • Single-cell recordings = level of the neuron ...
The language of the brain
... When it comes to laying down memories, the relative timing of spikes seems to be as important as the rate of firing. In particular, the synchronized firing of spikes in the cortex is important for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is s ...
... When it comes to laying down memories, the relative timing of spikes seems to be as important as the rate of firing. In particular, the synchronized firing of spikes in the cortex is important for increasing the strengths of synapses—an important process in forming long-term memories. A synapse is s ...
outline unit III
... 2. brain lateralization (hemispheric specialization) 1. the specialization of function in each hemisphere 3. split brain patients 1. the corpus collosum has been cut to treat severe epilepsy 2. can’t orally report information presented to only the right hemisphere of the brain 3. Association area 1. ...
... 2. brain lateralization (hemispheric specialization) 1. the specialization of function in each hemisphere 3. split brain patients 1. the corpus collosum has been cut to treat severe epilepsy 2. can’t orally report information presented to only the right hemisphere of the brain 3. Association area 1. ...
From Nerve Cells to Cognition: The Internal
... developments. First, in the 1960s and 1970s techniques were developed by Robert Wurtz and Edward Evarts at the National Institutes of Health for studying the activity of single cells in the brains of animals, including primates, engaged in controlled behavior in the laboratory. This allowed investig ...
... developments. First, in the 1960s and 1970s techniques were developed by Robert Wurtz and Edward Evarts at the National Institutes of Health for studying the activity of single cells in the brains of animals, including primates, engaged in controlled behavior in the laboratory. This allowed investig ...
Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
... Composed of distinctive cell groups: e.g. Caudate & lentiform Play a role in motor control, may be involved with attention and cognition. Disorders of the basal nuclei show up as too much or too little movement such as Huntington’s or Parkinson’s diseases. ...
... Composed of distinctive cell groups: e.g. Caudate & lentiform Play a role in motor control, may be involved with attention and cognition. Disorders of the basal nuclei show up as too much or too little movement such as Huntington’s or Parkinson’s diseases. ...
Temporal Aspects of Visual Extinction
... can show recovery. • Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
... can show recovery. • Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and modify functions and adapt to internal and external changes – Important for learning – Important for rehabilitation – Younger brains tend to be more plastic ...
Neural correlates of consciousness

The neural correlates of consciousness (NCC) constitute the minimal set of neuronal events and mechanisms sufficient for a specific conscious percept. Neuroscientists use empirical approaches to discover neural correlates of subjective phenomena. The set should be minimal because, under the assumption that the brain is sufficient to give rise to any given conscious experience, the question is which of its components is necessary to produce it.