Sedimentary Textures
... • Well sorted, rounded, medium grain size has good pore spaces and will allow water to fall through quickly • Poorly sorted, angular sediments have small pore spaces and trap water reducing permeability ...
... • Well sorted, rounded, medium grain size has good pore spaces and will allow water to fall through quickly • Poorly sorted, angular sediments have small pore spaces and trap water reducing permeability ...
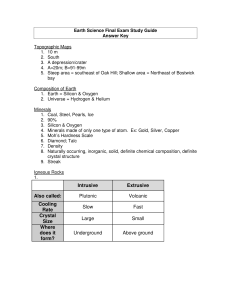
Final Exam Study Guide Answer Key
... 4. Carbonic acid (chemical weathering) draw a profile 5. Quartz 6. Type of cement holding together 7. Rich organic material in soil from decayed organic matter 8. Type of rock & climate Surface Water 1. High land that separates two watersheds 2. The material that a river carries; solution, suspensio ...
... 4. Carbonic acid (chemical weathering) draw a profile 5. Quartz 6. Type of cement holding together 7. Rich organic material in soil from decayed organic matter 8. Type of rock & climate Surface Water 1. High land that separates two watersheds 2. The material that a river carries; solution, suspensio ...
More Principles of Relative Dating Note 2 Inclusions:
... - pieces of one rock are contained (included ) in another - Included rock is the remains of the older rock (usually sedimentary) - rock that has included pieces is younger (usually igneous) ...
... - pieces of one rock are contained (included ) in another - Included rock is the remains of the older rock (usually sedimentary) - rock that has included pieces is younger (usually igneous) ...
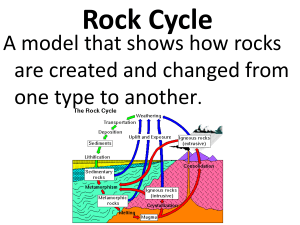
The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
... The Rock Cycle Rock – a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic material Rock cycle – the continual process by which new rock forms from old rock material Erosion – the process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity moves soil and sediment from one location to another Dep ...
Book F Ch. 2 L4 NOTES
... Foliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are arranged in planes or bands Nonfoliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are not arranged in planes or bands Metamorphism: Rocks undergo the process of metamorphism when exposed to high heat (temp ...
... Foliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are arranged in planes or bands Nonfoliated: the texture of metamorphic rock in which the mineral grains are not arranged in planes or bands Metamorphism: Rocks undergo the process of metamorphism when exposed to high heat (temp ...
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary
... 7. detrital rocks – sedimentary rocks that are made from erosion & deposition of sediments in layers that are cemented (glued)together by dissolved minerals in water and compacted(squeezed) together 8. chemical rocks – sedimentary rocks that form when mineral-filled water evaporates 9. organic rocks ...
... 7. detrital rocks – sedimentary rocks that are made from erosion & deposition of sediments in layers that are cemented (glued)together by dissolved minerals in water and compacted(squeezed) together 8. chemical rocks – sedimentary rocks that form when mineral-filled water evaporates 9. organic rocks ...
3 Types of Rocks – PowerPoint Igneous Rocks are formed by: They
... Clastic are made of ____________ of other ______________ that have been ______________________ or ___________________. How are they grouped? Mudrock has Sandstone has Conglomerates have Biochemical rocks form from Chemical precipitates form in What conditions show sedimentary rock formation? Sedimen ...
... Clastic are made of ____________ of other ______________ that have been ______________________ or ___________________. How are they grouped? Mudrock has Sandstone has Conglomerates have Biochemical rocks form from Chemical precipitates form in What conditions show sedimentary rock formation? Sedimen ...
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth
... 7. detrital rocks – sedimentary rocks that are made from erosion & deposition of sediments in layers that are cemented (glued)together by dissolved minerals in water and compacted(squeezed) together 8. chemical rocks – sedimentary rocks that form when mineral-filled water evaporates 9. organic rocks ...
... 7. detrital rocks – sedimentary rocks that are made from erosion & deposition of sediments in layers that are cemented (glued)together by dissolved minerals in water and compacted(squeezed) together 8. chemical rocks – sedimentary rocks that form when mineral-filled water evaporates 9. organic rocks ...
GEOLOGY 335 LAB -- SEDIMENTARY PROCESSES
... water may be concentrated and precipitated as beds of gypsum, halite, and more complex salts. Organic Reef. An organic reef is a structure built of the shells and secretions of marine organisms. The framework of geologically young reefs typically is built by corals and algae, but the reef community ...
... water may be concentrated and precipitated as beds of gypsum, halite, and more complex salts. Organic Reef. An organic reef is a structure built of the shells and secretions of marine organisms. The framework of geologically young reefs typically is built by corals and algae, but the reef community ...
Categorization of pores in sedimentary rocks II
... of intergranular cement Primary intragranular porosity ...
... of intergranular cement Primary intragranular porosity ...
Section 7.3 Student note
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
rocks - Mrs. DiLorenzo Earth Science
... How do Sedimentary Rocks form? 1. Cementation: occurs when clasts are cemented together. – Calcite, quartz, & hematite are common cements. – Clastic Sedimentary Rocks: mainly composed of solid sediments ...
... How do Sedimentary Rocks form? 1. Cementation: occurs when clasts are cemented together. – Calcite, quartz, & hematite are common cements. – Clastic Sedimentary Rocks: mainly composed of solid sediments ...
Rock Cycle
... Metamorphic Rock Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
... Metamorphic Rock Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
NTW-Minerals and rocks
... __________ (breaking down) and erosion _______ (the moving around) of rock particles 2) compaction __________- pressure that squeezes out the air and water 3) cementation ___________- water that is dissolved with minerals “glues particles together and then they hardens ...
... __________ (breaking down) and erosion _______ (the moving around) of rock particles 2) compaction __________- pressure that squeezes out the air and water 3) cementation ___________- water that is dissolved with minerals “glues particles together and then they hardens ...
Unit 3 Geochemical Cycles in the Earth`s System
... Form within cooling ________ Form from _________metamorphism _______ – mineral solutions in cracks ________ – large number of veins ______ deposits – concentrated at bottom of stream beds due to water mv’t ...
... Form within cooling ________ Form from _________metamorphism _______ – mineral solutions in cracks ________ – large number of veins ______ deposits – concentrated at bottom of stream beds due to water mv’t ...
Name
... the transporting medium. The single most characteristic feature of sedimentary rocks is __________. The common name for sediment consisting of particles between 1/16 mm and 2 mm is __________. The presence of abundant feldspar in a sedimentary rock suggests that advanced stages of chemical weatherin ...
... the transporting medium. The single most characteristic feature of sedimentary rocks is __________. The common name for sediment consisting of particles between 1/16 mm and 2 mm is __________. The presence of abundant feldspar in a sedimentary rock suggests that advanced stages of chemical weatherin ...
Rock Cycle
... 1. Go to www.phschool.com 2. Enter cfp-1056 into the Web Code area on the top left hand side of the web page. 3. Press the yellow circle to the right of the area where you entered the web code. 4. Press the orange start button. 5. Read the description at the top of the page titled “The Rock cycle” a ...
... 1. Go to www.phschool.com 2. Enter cfp-1056 into the Web Code area on the top left hand side of the web page. 3. Press the yellow circle to the right of the area where you entered the web code. 4. Press the orange start button. 5. Read the description at the top of the page titled “The Rock cycle” a ...
Changing Earth*s Surface
... mechanical and chemical processes that change Earth’s surface over time. (wind, water, sun, acid rain) ...
... mechanical and chemical processes that change Earth’s surface over time. (wind, water, sun, acid rain) ...
Geology Part II: Rocks
... Geology Part II • The Rock Cycle • Rocks: – Igneous – Sedimentary – Metamorphic ...
... Geology Part II • The Rock Cycle • Rocks: – Igneous – Sedimentary – Metamorphic ...
Sedimentary Rocks Answers Explained
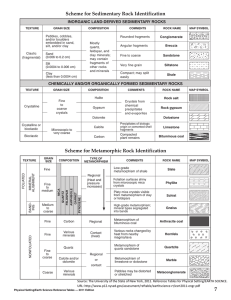
... 1. (2) Looking at the Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification on Page 7 of the ESRT under grain size, particles less than 0.006 would be both silt and clay, which turn into the sedimentary rocks siltstone and shale. 2. (1) Fragments held together by natural cement only occurs with sedimentary roc ...
... 1. (2) Looking at the Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification on Page 7 of the ESRT under grain size, particles less than 0.006 would be both silt and clay, which turn into the sedimentary rocks siltstone and shale. 2. (1) Fragments held together by natural cement only occurs with sedimentary roc ...
sedmentary rocks 1
... Deposited grains of rocks and minerals derived intact from source, transported by gravity, water, wind, ice. Organic Shells, shell fragments, bones, reefs, etc. May be transported or precipitated in situ. Inorganic Chemical Chemical precipitates due to precipitation of dissolved constituents. Transp ...
... Deposited grains of rocks and minerals derived intact from source, transported by gravity, water, wind, ice. Organic Shells, shell fragments, bones, reefs, etc. May be transported or precipitated in situ. Inorganic Chemical Chemical precipitates due to precipitation of dissolved constituents. Transp ...
File
... ____10. Oceanic J. Having to do with volcanoes, having to do with something angry or violent Part II: How to use our vocabulary words (all words will be used, no words will be repeated). 1-3. Sedimentary rocks often occur in layers because of the processes that form them like, _____________, when se ...
... ____10. Oceanic J. Having to do with volcanoes, having to do with something angry or violent Part II: How to use our vocabulary words (all words will be used, no words will be repeated). 1-3. Sedimentary rocks often occur in layers because of the processes that form them like, _____________, when se ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.