* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Ore genesis wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
Igneous rock wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
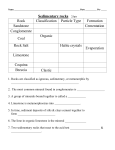
Name: ____________________________ Class Period: ______________ Vocabulary Homework: -posit-,-ic, -ion, com-posit- = place with / -ion = action or process/ -ic = having to do with or related to/ com=with, together Composition Deposition Organic Clastic Compaction Communication Cementation Metamorphic Oceanic Volcanic Part I: Definitions (match the vocabulary word to its definition) ____1 Compaction A. The chemical makeup of a substance like a rock or the atmosphere ____2. Communication B. The process by which sediments moved by erosion are dropped off and placed with other sediments ____3. Deposition C. The process by which a message becomes public or shared with others ____4. Cementation D. The process by which sediments are squeezed together and made solid with other sediments ____5.Composition quartz or calcite E. The process by which sediments are " glued/ cemented together" by minerals dissolved in water like ____6. Volcanic F. Having to do with something that comes from living things ____7. CLastic G. Having to do with existing rock that has been changed in form by heat and pressure ____8. Organic H. Having to do with sedimentary rocks formed when fragments of other rocks are cemented together ____9. Metamorphic I. Having to do with the ocean ____10. Oceanic J. Having to do with volcanoes, having to do with something angry or violent Part II: How to use our vocabulary words (all words will be used, no words will be repeated). 1-3. Sedimentary rocks often occur in layers because of the processes that form them like, _____________, when sediments are dropped off, ________________, from sediments pressing on sediments below, and finally, _____________, when sediments are glued together by minerals . 4. All rocks are classified by both their texture and ________________ that is determined by the substances that make them up. 5. Teachers use Google classroom as a _______________________ tool to share information about class and work with students. 6. Sedimentary rocks that form from the remains of living things are called ______________ . 7. Sedimentary rocks that form when sediments or fragments of other rocks are cemented together are called _________________. 8. The noise from the explosion of Krakatoa, a _____________ island in Indonesia that blew up in 1883, was so loud that it was heard 3000 miles away. 9. Japan is made up of a volcanic island chain where two ______________ plates converge or come together on the ocean floor. 10. We study ________________________ rocks after igneous and sedimentary rocks because they form when existing rock is changed in form by exposure to heat and pressure. Part III: True/False (if false, change the statement to make it true). ___1. Igneous rocks are formed from existing rocks that change into new rock after being exposed to extreme heat and pressure. ___2. Clastic sedimentary rocks are different from the other types of sedimentary rocks because they are formed from the remains of living things. ___3. Clear communication is important between countries to maintain peace. ___4. Oceanic crust that is made mostly of basalt is more dense than continental crust that is mostly granite. We Part IV: Using the words yourself ● Pick four words from the chart, identify the part of speech, and use it correctly in a sentence (you may change the tense or make it plural). 1) Word: Part of Speech: Sentence: 2) Word: Part of Speech: Sentence: 3) Word: Part of Speech: Sentence: 4) Word: Sentence: Part of Speech: