* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download More Principles of Relative Dating Note 2 Inclusions:
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
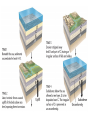
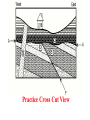
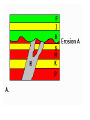
More Principles of Relative Dating Note 2 Inclusions: - pieces of one rock are contained (included ) in another - Included rock is the remains of the older rock (usually sedimentary) - rock that has included pieces is younger (usually igneous) Unconformities Unconformity– long period when deposition stops, then erodes, and then deposition starts again - (Basically a break in the rock record) Types to identify A. Angular: tilted rocks overlain by flat strata (beds); tops of tilted rocks eroded B. Nonconformity: new (igneous) rocks intrude from below and displace older one C. Disconformity:not easily identifiable - (usually shown with a wavy line) - deposition ceased then started again much later - this gives a large age gap between 2 layers Example of Principle of Original Horizontality Examples of Cross-Cutting Features (Dikes) Another Cross-Cut Feature (Dike) Practice Cross Cut View Folds: When rocks have an unconformity (time break), they are often folded by tectonic stresses within the Earth These generally take 2 shapes A. Anticline (rocks arch up) B. Syncline (rocks sink down) Examples of Anticlines Examples of Synclines