Genome Control - University of California, Los Angeles
... • Engineered E. Coli cells only synthesizes carboyxl terminal of β galactosidase protein • pUC8 plasmid contains gene for amino terminal • If pUC8 transforms cells, gene is fully functional ...
... • Engineered E. Coli cells only synthesizes carboyxl terminal of β galactosidase protein • pUC8 plasmid contains gene for amino terminal • If pUC8 transforms cells, gene is fully functional ...
Steps in gene expression: comparison of
... Low fidelity compared to DNA polymerase: errors 1/104-105. RNA polymerase incorporates ~30 nt/s (much slower than DNA polymerase). ...
... Low fidelity compared to DNA polymerase: errors 1/104-105. RNA polymerase incorporates ~30 nt/s (much slower than DNA polymerase). ...
4.3 DNA Control Mechanisms
... 1. Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod discovered this control mechanism.(1961) 2. Operon “operator” controls RNA Polymerase access to the DNA strand. 3. Operon is part of the promoter sequence. It is located between the TATA box and Start codon. 4. Repressor and co-repressor - These molecules act as a ...
... 1. Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod discovered this control mechanism.(1961) 2. Operon “operator” controls RNA Polymerase access to the DNA strand. 3. Operon is part of the promoter sequence. It is located between the TATA box and Start codon. 4. Repressor and co-repressor - These molecules act as a ...
DNA Code problerm
... B. instability of the DNA molecule C. the ability of the same tRNA anticodon to recognize different codons D. the high mutability of certain genes 9. If you wanted to block transcription of a group of functionally related genes in a prokaryote, you could place an obstacle A. upstream of both the pro ...
... B. instability of the DNA molecule C. the ability of the same tRNA anticodon to recognize different codons D. the high mutability of certain genes 9. If you wanted to block transcription of a group of functionally related genes in a prokaryote, you could place an obstacle A. upstream of both the pro ...
Advanced Biology\Stem Cells, histones, etc
... When chromatin (DNA plus histone complex) is open (loose), transcription can occur because promoter regions are accessible. When chromatin is tightly coiled, no access to promoters so no transcription. Methyl groups (CH3) attach to cytosine in DNA (often at promoter region), coiling the DNA/histone ...
... When chromatin (DNA plus histone complex) is open (loose), transcription can occur because promoter regions are accessible. When chromatin is tightly coiled, no access to promoters so no transcription. Methyl groups (CH3) attach to cytosine in DNA (often at promoter region), coiling the DNA/histone ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • ChIP-chip analysis can be used to identify DNAbinding sites for activators and other proteins • Small genome organisms - all of the intergenic regions can be included in the microarray • If genome is large, that is not practical • To narrow areas of interest can use CpG islands – These are associa ...
... • ChIP-chip analysis can be used to identify DNAbinding sites for activators and other proteins • Small genome organisms - all of the intergenic regions can be included in the microarray • If genome is large, that is not practical • To narrow areas of interest can use CpG islands – These are associa ...
BIO 103 - Genes
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
EE150a – Genomic Signal and Information Processing
... Types of Microarrays • “Traditionally”, there are two formats: – probe cDNA immobilized to a solid surface using robot spotting and exposed to a set of targets, and – an array of oligonucleotide probes synthesized on chip (via, ...
... Types of Microarrays • “Traditionally”, there are two formats: – probe cDNA immobilized to a solid surface using robot spotting and exposed to a set of targets, and – an array of oligonucleotide probes synthesized on chip (via, ...
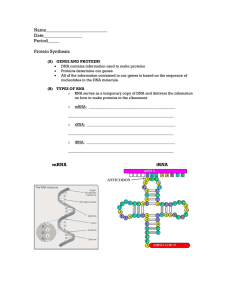
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Dissociate fairly easily from polymerase Found in substoichiometric quantities Might shuttle from one polymerase II to another Rpb4 may help anchor Rpb7 to the enzyme Mutants without Rpb4 and Rpb7 transcribes well, but cannot initiate at a real promoter ...
... Dissociate fairly easily from polymerase Found in substoichiometric quantities Might shuttle from one polymerase II to another Rpb4 may help anchor Rpb7 to the enzyme Mutants without Rpb4 and Rpb7 transcribes well, but cannot initiate at a real promoter ...
PotuS!977m - BioMedSearch
... versus -) have been generated. These vectors were designed to facilitate rapid mapping of DNA inserts. The mapping technique, based on a strategy described by Wahl at at (ref. 1), requires the presence of unique restriction sites flanking both the DNA insert arnd two DNA hybridization target sequenc ...
... versus -) have been generated. These vectors were designed to facilitate rapid mapping of DNA inserts. The mapping technique, based on a strategy described by Wahl at at (ref. 1), requires the presence of unique restriction sites flanking both the DNA insert arnd two DNA hybridization target sequenc ...
DNA, RNA, Genes, Chromosomes
... hair and eye color, as well as more subtle characteristics, such as the oxygencarrying ability of the blood. Complex traits, such as IQ and physical strength, may be shaped by the interaction of a number of different genes along with environmental influences. It is estimated that humans have 100,000 ...
... hair and eye color, as well as more subtle characteristics, such as the oxygencarrying ability of the blood. Complex traits, such as IQ and physical strength, may be shaped by the interaction of a number of different genes along with environmental influences. It is estimated that humans have 100,000 ...
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... the RNA from the degradation. RNA is spliced by a ____________ made of snRNA, removing noncoding sections called _______, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be use ...
... the RNA from the degradation. RNA is spliced by a ____________ made of snRNA, removing noncoding sections called _______, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be use ...
Note 7.4 - Controlling Gene Expression
... The regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes is very complex. Eukaryotes use a control system consisting of for parts; Transcriptional (as mRNA is being synthesized) Post-transcriptional (as mRNA is being processed) Translational (as the protein is being synthesized) Post-translational (after the ...
... The regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes is very complex. Eukaryotes use a control system consisting of for parts; Transcriptional (as mRNA is being synthesized) Post-transcriptional (as mRNA is being processed) Translational (as the protein is being synthesized) Post-translational (after the ...
分子生物學小考(一) 範圍ch3~ch7
... (E) transport to cytoplasm, addition of 5’ cap, addition of poly(A) tail, splicing, initiation of transcription 14. Which one of the following definition of terminology is not correct? (A) "Transcription Factor" is a protein that assists RNA polymerase to recognize promoters (B) "Transcription Repre ...
... (E) transport to cytoplasm, addition of 5’ cap, addition of poly(A) tail, splicing, initiation of transcription 14. Which one of the following definition of terminology is not correct? (A) "Transcription Factor" is a protein that assists RNA polymerase to recognize promoters (B) "Transcription Repre ...
Trnascription in eucaryotes
... defined tissues. Nevertheless in nearly all cell types the DNA is the same. • Some genes are present in nearly all cells – these are housekeeping genes. ...
... defined tissues. Nevertheless in nearly all cell types the DNA is the same. • Some genes are present in nearly all cells – these are housekeeping genes. ...
Gene Expression
... upon cellular conditions, this may enable gene to turn on (promote) or off (repress). Eukaryotes have multiple switches. – Induction- If proteins from neighboring cells are present, gene may turn on (ex: retina) – Hormones and other molecules may attach to enhancer sequence to turn on genes. ...
... upon cellular conditions, this may enable gene to turn on (promote) or off (repress). Eukaryotes have multiple switches. – Induction- If proteins from neighboring cells are present, gene may turn on (ex: retina) – Hormones and other molecules may attach to enhancer sequence to turn on genes. ...
Ch17_note_summary
... spliceosome made of snRNA, removing noncoding sections called introns, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called alternative RNA splicing. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
... spliceosome made of snRNA, removing noncoding sections called introns, and leaving exons. Some genes can produce multiple polypeptides depending on what is spliced; this is called alternative RNA splicing. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in evolution. ...
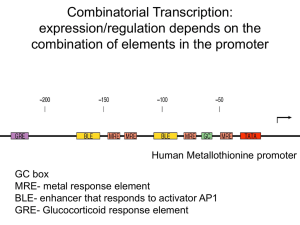
Combinatorial Transcription: expression/regulation depends on the
... • Addition of H1 further represses transcription (by binding to the linker DNA), but this can be overcome by activators such as Sp1. • There are regulatory proteins, such as the glucocorticoid-receptor complex, that can remove histones from certain promoters. ...
... • Addition of H1 further represses transcription (by binding to the linker DNA), but this can be overcome by activators such as Sp1. • There are regulatory proteins, such as the glucocorticoid-receptor complex, that can remove histones from certain promoters. ...
Tuesday5/10
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
Chapter 16
... is absent. If operator is bound, promoter region is partially blocked-genes can not be transcribed. • This two switch control mechanism thus causes the cell to produce only what the cell needs, when it needs it. ...
... is absent. If operator is bound, promoter region is partially blocked-genes can not be transcribed. • This two switch control mechanism thus causes the cell to produce only what the cell needs, when it needs it. ...
F4-6 Gene Regulation and Mutation Ch12,13
... 2. Lac (tose) Operon – contains a promoter, an operator, a regulatory gene and 3 enzyme genes to control lac digestion 3. When lactose is present: a. Regulatory gene’s repressor protein inactivated b. RNA then allowed to begin transcription c. Enzymes are created to digest lactose 4. When lactose go ...
... 2. Lac (tose) Operon – contains a promoter, an operator, a regulatory gene and 3 enzyme genes to control lac digestion 3. When lactose is present: a. Regulatory gene’s repressor protein inactivated b. RNA then allowed to begin transcription c. Enzymes are created to digest lactose 4. When lactose go ...
Epigenetic regulators as novel treatments
... Some definitions: Epigenetics-the study of heritable changes in gene expression without changing the DNA sequence; this occurs at 3 levels of organization: 1) methylation of cytosine nucleotides within coding sequences and at promoter sites that alter transcription rates 2) changes in chromatin pro ...
... Some definitions: Epigenetics-the study of heritable changes in gene expression without changing the DNA sequence; this occurs at 3 levels of organization: 1) methylation of cytosine nucleotides within coding sequences and at promoter sites that alter transcription rates 2) changes in chromatin pro ...
You Light Up My Life
... of a multicelled organism rarely use more than 5-10 percent of their genes at any given time ...
... of a multicelled organism rarely use more than 5-10 percent of their genes at any given time ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.