power point presentation
... Substituting 1 base seems to be perfectly fine as the data in blue boxes lies perfectly on the prediction line. Substitution of 2 bases seems to be ok, but then about half of the data points lie distinctively far away from the line. ...
... Substituting 1 base seems to be perfectly fine as the data in blue boxes lies perfectly on the prediction line. Substitution of 2 bases seems to be ok, but then about half of the data points lie distinctively far away from the line. ...
APh 162 – Cellular Decision Making Measuring Gene Expression
... eaten by the cells, we use the inducer IPTG. This small molecule interacts with Lac repressor in much the same way that the real sugar does except that it cannot be cleaved by the enzyme beta-galactosidase, making it a useful experimental substrate. In the absence of lactose or IPTG, Lac repressor b ...
... eaten by the cells, we use the inducer IPTG. This small molecule interacts with Lac repressor in much the same way that the real sugar does except that it cannot be cleaved by the enzyme beta-galactosidase, making it a useful experimental substrate. In the absence of lactose or IPTG, Lac repressor b ...
Large Scale Gene Expression Analysis
... sequences • Enhancer elements regulate genes in distance ...
... sequences • Enhancer elements regulate genes in distance ...
- ISpatula
... RNA polymerase initiates transcription at promoter site polycistronic mRNA(3 sets of start and stop codons) its translation produces 3 proteins for lactose use in energy ...
... RNA polymerase initiates transcription at promoter site polycistronic mRNA(3 sets of start and stop codons) its translation produces 3 proteins for lactose use in energy ...
Molecular genetics of gene expression
... Eukaryotic genes contain introns which are spliced to form mature mRNA ...
... Eukaryotic genes contain introns which are spliced to form mature mRNA ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Dissociate fairly easily from polymerase Found in substoichiometric quantities Might shuttle from one polymerase II to another Rpb4 may help anchor Rpb7 to the enzyme Mutants without Rpb4 and Rpb7 transcribes well, but cannot initiate at a real promoter ...
... Dissociate fairly easily from polymerase Found in substoichiometric quantities Might shuttle from one polymerase II to another Rpb4 may help anchor Rpb7 to the enzyme Mutants without Rpb4 and Rpb7 transcribes well, but cannot initiate at a real promoter ...
Practice Exam II
... T The mutation could be induced by a base analog or an alkylating agent. F The mutation could be reverted by treatment with ICR 170 or ethidium bromide. ...
... T The mutation could be induced by a base analog or an alkylating agent. F The mutation could be reverted by treatment with ICR 170 or ethidium bromide. ...
Biology 105: Biology Science for Life with Physiology, 3rd Ed., Belk
... 34 nitrogenous bases with double rings of carbon and nitrogen atoms, e.g. adenine & guanine 35 nitrogenous bases with a single ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms, e.g. thymine & cytosine 36 the triplet groupings of mRNA nucleotides 37 cow’s growth factor protein genetically engineered to be produced ...
... 34 nitrogenous bases with double rings of carbon and nitrogen atoms, e.g. adenine & guanine 35 nitrogenous bases with a single ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms, e.g. thymine & cytosine 36 the triplet groupings of mRNA nucleotides 37 cow’s growth factor protein genetically engineered to be produced ...
Biology Packet 7: DNA & RNA
... Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of DNA replication. Describe how errors are corrected during DNA replication. Rel ...
... Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of DNA replication. Describe how errors are corrected during DNA replication. Rel ...
Promoters
... Sirolimus is a macrocyclic lactone produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. The chemical name of sirolimus (also known as rapamycin) is (3S,6R,7E,9R,10R,12R,14S,15E,17E,19E,21S,23S,26R,27R,34aS)9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-hexadecahydro-9,27-dihydroxy-3[(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy ...
... Sirolimus is a macrocyclic lactone produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. The chemical name of sirolimus (also known as rapamycin) is (3S,6R,7E,9R,10R,12R,14S,15E,17E,19E,21S,23S,26R,27R,34aS)9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-hexadecahydro-9,27-dihydroxy-3[(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy ...
Chapter 11 - Evangel University
... four different types of subunits: _____________________ the _____________ enzyme is 2’ the _____________ is 2’s the role of the s subunit is recognition of the ______________; the s subunit is released after ________________ • of the two DNA strands, the one that serves as the template for RNA ...
... four different types of subunits: _____________________ the _____________ enzyme is 2’ the _____________ is 2’s the role of the s subunit is recognition of the ______________; the s subunit is released after ________________ • of the two DNA strands, the one that serves as the template for RNA ...
Gene Regulation - Marblehead High School
... Lactose – a sugar that, if present binds to the repressor causing it to move from the gene so RNA polymerase can bind and the lac gene is expressed ...
... Lactose – a sugar that, if present binds to the repressor causing it to move from the gene so RNA polymerase can bind and the lac gene is expressed ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... is the use of transgenic farm animals to produce pharmaceuticals; genes that code for therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are incorporated into an animal’s DNA, and the proteins appear in the animal’s milk. 26.3 Gene Therapy Gene Therapy Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human c ...
... is the use of transgenic farm animals to produce pharmaceuticals; genes that code for therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are incorporated into an animal’s DNA, and the proteins appear in the animal’s milk. 26.3 Gene Therapy Gene Therapy Gene therapy is the insertion of genetic material into human c ...
Slide 1
... eve is expressed in stripe 2. The distributions of these proteins were visualized by staining a developing Drosophila embryo with antibodies directed against each of the four proteins (see Figures 7-52 and 7-53). The expression of eve in stripe 2 occurs only at the position where the two activators ...
... eve is expressed in stripe 2. The distributions of these proteins were visualized by staining a developing Drosophila embryo with antibodies directed against each of the four proteins (see Figures 7-52 and 7-53). The expression of eve in stripe 2 occurs only at the position where the two activators ...
No Slide Title
... – regions that are actively being transcribed into RNA or easily available for transcription are more extended (10%) – active chromatin [30-nm fiber or 300nm] • transcription (RNA polymerase) and replication (DNA polymerase are not obstructed by histones. It is thought that the DNA partially detache ...
... – regions that are actively being transcribed into RNA or easily available for transcription are more extended (10%) – active chromatin [30-nm fiber or 300nm] • transcription (RNA polymerase) and replication (DNA polymerase are not obstructed by histones. It is thought that the DNA partially detache ...
Final spring 2016
... 55. Suppose that part of an amino acid sequence of a protein changed from tyrosine-proline-glycine-alanine to tyrosine-histidine-glycine-alanine. This change was most likely caused by a point mutation called a(an) ____________________. 56. A point mutation will cause the cell to make an incomplete p ...
... 55. Suppose that part of an amino acid sequence of a protein changed from tyrosine-proline-glycine-alanine to tyrosine-histidine-glycine-alanine. This change was most likely caused by a point mutation called a(an) ____________________. 56. A point mutation will cause the cell to make an incomplete p ...
regulation-2013
... 8-Regulation by protein stability •Ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Cyclins control of cell cycle. • Protein molecule is tagged for degradation by attachment of a 20 kDa protein, ubiquitin ...
... 8-Regulation by protein stability •Ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Cyclins control of cell cycle. • Protein molecule is tagged for degradation by attachment of a 20 kDa protein, ubiquitin ...
Genomics and Behavior “Central Dogma” Outline
... • RNA polymerase begins to move down the strand of DNA and transcribe it into RNA. It unwinds the DNA as it moves down the strand. RNA RNA polymerase ...
... • RNA polymerase begins to move down the strand of DNA and transcribe it into RNA. It unwinds the DNA as it moves down the strand. RNA RNA polymerase ...
258927_Fx_DNA-RNA
... 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of our studies at this point. I will add, though, that it ...
... 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of our studies at this point. I will add, though, that it ...
Name:
... 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of our studies at this point. I will add, though, that it ...
... 16. What must be done to this string of amino acids in order to turn it into a functional protein? 17. The rest of this process isn’t really about transcription or translation, but rather about enzymatic activity and is thus beyond the scope of our studies at this point. I will add, though, that it ...
Transcription
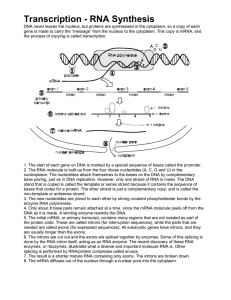
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
Unit 4 - University of Colorado Boulder
... The central dogma is a cellular “chain of command.” 7. Define the “central dogma” in one sentence 8. List the major steps in the process of transcription in the order in which they happen; describe the roles played by the main molecules or DNA regions that are involved (RNA polymerase, transcription ...
... The central dogma is a cellular “chain of command.” 7. Define the “central dogma” in one sentence 8. List the major steps in the process of transcription in the order in which they happen; describe the roles played by the main molecules or DNA regions that are involved (RNA polymerase, transcription ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.