Genomics - West High School
... 3. Use High through-put methods that produce huge datasets ==> One method is a Microarray ...
... 3. Use High through-put methods that produce huge datasets ==> One method is a Microarray ...
Evidence - iPlant Pods
... – Move in 3-steps & count steps (=COUNTS) – If 3-step = (TAA or TAG or TGA), register putative TLTS – If register evaluate COUNTS (= triplets) If COUNTS < minimum discard; then go behind ATG above and start SCAN If COUNTS > maximum discard; then go behind ATG above and start SCAN If minimum ...
... – Move in 3-steps & count steps (=COUNTS) – If 3-step = (TAA or TAG or TGA), register putative TLTS – If register evaluate COUNTS (= triplets) If COUNTS < minimum discard; then go behind ATG above and start SCAN If COUNTS > maximum discard; then go behind ATG above and start SCAN If minimum ...
Study suggests common mechanism activating
... alterations of noncoding regions across cancers, integrating genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic data. The team found six super-enhancer regions that are focally amplified across different cancer types, including two that are associated with overexpression of the MYC oncogene, suggesting that th ...
... alterations of noncoding regions across cancers, integrating genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic data. The team found six super-enhancer regions that are focally amplified across different cancer types, including two that are associated with overexpression of the MYC oncogene, suggesting that th ...
Chapter 15 - jl041.k12.sd.us
... One of the best known pathways of gene recognition is the lac Operon, a regulatory pathway by which bacteria are able to produce the enzyme to digest lactose only when necessary (when lactose is present in the environment). ...
... One of the best known pathways of gene recognition is the lac Operon, a regulatory pathway by which bacteria are able to produce the enzyme to digest lactose only when necessary (when lactose is present in the environment). ...
Lecture Slides - Computer Science
... Human Genome Program, U.S. Department of Energy, Genomics and Its Impact on Medicine and Society: A 2001 Primer, 2001 ...
... Human Genome Program, U.S. Department of Energy, Genomics and Its Impact on Medicine and Society: A 2001 Primer, 2001 ...
transcription
... 1. Histones form nucleosomes on TATA boxes, blocking transcription. Promoter-binding proteins cannot disrupt the nucleosomes. Enhancer-binding proteins bind to enhancers, displacing any histones, and then cause the histones at the TATA box to free the DNA. 2. Histone Acetylation with increased trans ...
... 1. Histones form nucleosomes on TATA boxes, blocking transcription. Promoter-binding proteins cannot disrupt the nucleosomes. Enhancer-binding proteins bind to enhancers, displacing any histones, and then cause the histones at the TATA box to free the DNA. 2. Histone Acetylation with increased trans ...
Gene Regulation
... How can an operon system be imitated in eukaryotes? Suppose you have: - 3 biochemical pathways each controlled by 3 genes. - 3 enhancer sequences - 3 activator proteins How could you design a regulatory system that would turn on all the genes in a pathway at one time using 2 enhancer sequences and ...
... How can an operon system be imitated in eukaryotes? Suppose you have: - 3 biochemical pathways each controlled by 3 genes. - 3 enhancer sequences - 3 activator proteins How could you design a regulatory system that would turn on all the genes in a pathway at one time using 2 enhancer sequences and ...
Bioinformatics: A New Frontier for Computer - People
... (eye color, number of limbs, etc.); controlled by interaction of many genes ...
... (eye color, number of limbs, etc.); controlled by interaction of many genes ...
Primer Design Considerations for Adding a T7 Promoter
... Required: • T7 promoter sequence (5′-TAA TAC GAC TCA CTA TAG GG-3′). Required for transcription of the DNA template. • ATG start codon (5′-ATG-3′) if not present in the sequence being amplified. Needed for translation initiation. • Gene-specific sequence. Needed to allow priming of the ta ...
... Required: • T7 promoter sequence (5′-TAA TAC GAC TCA CTA TAG GG-3′). Required for transcription of the DNA template. • ATG start codon (5′-ATG-3′) if not present in the sequence being amplified. Needed for translation initiation. • Gene-specific sequence. Needed to allow priming of the ta ...
What is some basic information about DNA?
... 4 nucleotides make Up DNA: Nucleotides can be thought of as building blocks. These building blocks can be arranged in sequences. The human genome contains about 3 billion of these building blocks. Some sequences of the building blocks encode genes. Some sequences are related to the regulation of gen ...
... 4 nucleotides make Up DNA: Nucleotides can be thought of as building blocks. These building blocks can be arranged in sequences. The human genome contains about 3 billion of these building blocks. Some sequences of the building blocks encode genes. Some sequences are related to the regulation of gen ...
Topic 4 Genetics
... pathways, you have the same genes. [Allele: one specific form of a gene differing from other alleles by one or a few bases only and occupying the same gene locus as other alleles of the gene.] You get one set of alleles from your mom, and one from your dad. Which allele that gets expressed depends u ...
... pathways, you have the same genes. [Allele: one specific form of a gene differing from other alleles by one or a few bases only and occupying the same gene locus as other alleles of the gene.] You get one set of alleles from your mom, and one from your dad. Which allele that gets expressed depends u ...
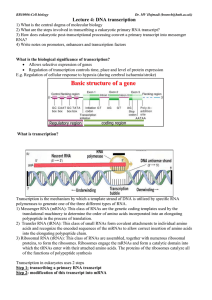
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Step 1 – Transcribing a primary RNA transcript - An overview of the 3 steps involved A) Initiation by RNA polymerase holoenzyme (an agglomeration of many different factors that together direct the synthesis of mRNA on a DNA template and which has a natural affinity for DNA) binding to specific DNA s ...
... Step 1 – Transcribing a primary RNA transcript - An overview of the 3 steps involved A) Initiation by RNA polymerase holoenzyme (an agglomeration of many different factors that together direct the synthesis of mRNA on a DNA template and which has a natural affinity for DNA) binding to specific DNA s ...
amino acids
... 4 only ~1.5% of the human genome encodes proteins and ~80% is not related to genes or their regulation. ...
... 4 only ~1.5% of the human genome encodes proteins and ~80% is not related to genes or their regulation. ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Considered to have two parts: – Core promoter - attracts general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II at a basal level and sets the transcription start site and direction of transcription – Proximal promoter - helps attract general transcription factors and RNA polymerase and includes promo ...
... • Considered to have two parts: – Core promoter - attracts general transcription factors and RNA polymerase II at a basal level and sets the transcription start site and direction of transcription – Proximal promoter - helps attract general transcription factors and RNA polymerase and includes promo ...
here - VCU
... a strand of mRNA is based on the sequence of a complementary strand of DNA. Murine: of or relating to rats/mice nt = nucleotide A nucleotide consists of a base (one of four chemicals: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid. Dinucleotide: A sequen ...
... a strand of mRNA is based on the sequence of a complementary strand of DNA. Murine: of or relating to rats/mice nt = nucleotide A nucleotide consists of a base (one of four chemicals: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid. Dinucleotide: A sequen ...
Chapter 17 Transcriptional Regulation In Eukaryotes
... Action at a distance: loops and insulators -how do enhancers affect (영향을 주다) transcription from a distance, even tens or hundreds kb apart ? -in prokaryotes, for example, IHF(integration host factor) induce DNA bending -In Drosophila, Chip help DNA form multiple mini-loops -insulator: control act ...
... Action at a distance: loops and insulators -how do enhancers affect (영향을 주다) transcription from a distance, even tens or hundreds kb apart ? -in prokaryotes, for example, IHF(integration host factor) induce DNA bending -In Drosophila, Chip help DNA form multiple mini-loops -insulator: control act ...
Lecture 5
... When there is enough methyl groups attached, it turns the gene off and makes it difficult to transcribe Some (but not all) methylations are reversible Abnormal methylation can lead to problems - Ex: FMR1 – hypermethylation leads to Fragile X syndrome; which is the leading Mendelian (single gen ...
... When there is enough methyl groups attached, it turns the gene off and makes it difficult to transcribe Some (but not all) methylations are reversible Abnormal methylation can lead to problems - Ex: FMR1 – hypermethylation leads to Fragile X syndrome; which is the leading Mendelian (single gen ...
October 3, 2016 Worksheet
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
Chapter 16 Gene Regulation Levels of Gene Regulation Bacterial
... – DNA regulatory elements which are bound by transcriptional activator proteins. • Example: Metallothionein – Response elements to heavy metals • Eukaryotic Genes may be activated by several different response elements ...
... – DNA regulatory elements which are bound by transcriptional activator proteins. • Example: Metallothionein – Response elements to heavy metals • Eukaryotic Genes may be activated by several different response elements ...
Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to
... Explain negative control over gene expression exhibited by repressible operons. ...
... Explain negative control over gene expression exhibited by repressible operons. ...
Notes
... Both alleles of BRCA1 or both alleles of BRCA2 must be mutant for cancer to develop. Why would in follow a dominant inheritance pattern? ...
... Both alleles of BRCA1 or both alleles of BRCA2 must be mutant for cancer to develop. Why would in follow a dominant inheritance pattern? ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.