RNA and Translation notes
... •Transcription and translation are coupled in prokaryotes: translation occurs while the mRNA is being made. ...
... •Transcription and translation are coupled in prokaryotes: translation occurs while the mRNA is being made. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... The lac Operon How does an organism “know” whether to turn a gene on or off? The common bacterium E. coli provides us with a perfect example of how gene expression can be regulated. The 4288 proteinencoding genes in this bacterium include a cluster of three genes that are turned on or off together. ...
... The lac Operon How does an organism “know” whether to turn a gene on or off? The common bacterium E. coli provides us with a perfect example of how gene expression can be regulated. The 4288 proteinencoding genes in this bacterium include a cluster of three genes that are turned on or off together. ...
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
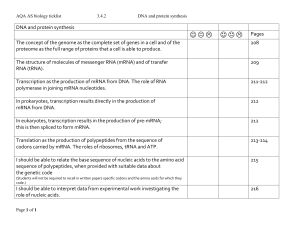
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
UTACCEL 2010
... molecule and one nucleotide molecule. There are four types of nucleotides (or 'bases') in the DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The two strands of DNA are structured in such a way that an adenine on one strand is always attached to a thymine on the other strand, and the gu ...
... molecule and one nucleotide molecule. There are four types of nucleotides (or 'bases') in the DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The two strands of DNA are structured in such a way that an adenine on one strand is always attached to a thymine on the other strand, and the gu ...
Ch 18 Notes - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... General transcription factors are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes. In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific transcription factors. Enhances & Specific TF’s Proximal control elements are located cl ...
... General transcription factors are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes. In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific transcription factors. Enhances & Specific TF’s Proximal control elements are located cl ...
Biology 340 Molecular Biology
... Globin genes: CCAAT box Muscle specific genes: E box, CANNTG --Elements such as the TATA box and Sp1 sites are found in close proximity to the start site of the gene and are often referred to as proximal promoter elements. --Some regulatory elements are found at thousands of base pairs upstream of t ...
... Globin genes: CCAAT box Muscle specific genes: E box, CANNTG --Elements such as the TATA box and Sp1 sites are found in close proximity to the start site of the gene and are often referred to as proximal promoter elements. --Some regulatory elements are found at thousands of base pairs upstream of t ...
The genetic engineers toolkit
... out the function of a gene by creating a non functioning one in an organism so you can see its effects. Gene knockdown A way of making the mRNA non functional ...
... out the function of a gene by creating a non functioning one in an organism so you can see its effects. Gene knockdown A way of making the mRNA non functional ...
Lecture 15 POWERPOINT here
... We could perform alternative splicing as we saw in the last lecture. We could control how much of the mRNA was transported to the cytoplasm. We could control how much protein was made by the ribosomes. We could even regulate which proteins were activated once they have been made. ...
... We could perform alternative splicing as we saw in the last lecture. We could control how much of the mRNA was transported to the cytoplasm. We could control how much protein was made by the ribosomes. We could even regulate which proteins were activated once they have been made. ...
Previously in Bio308
... How would a neuropeptide get made (in general terms)? What are the basic parts of DNA, RNA, and proteins? What is the difference between hnRNA, mRNA and tRNA? ...
... How would a neuropeptide get made (in general terms)? What are the basic parts of DNA, RNA, and proteins? What is the difference between hnRNA, mRNA and tRNA? ...
siRNA expression vector pRNAT-H1
... Description: GenScript pDream2.1/LIC vector is a protein expression vector for both efficient cloning and highlevel expression of any target genes. The gene of interest can be efficiently cloned into the vector using Ligation Independent Cloning (LIC) method, and can be expressed directly without an ...
... Description: GenScript pDream2.1/LIC vector is a protein expression vector for both efficient cloning and highlevel expression of any target genes. The gene of interest can be efficiently cloned into the vector using Ligation Independent Cloning (LIC) method, and can be expressed directly without an ...
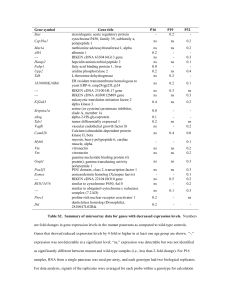
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
... “Present” in at least one array out of a total of 4 arrays were selected for further analyses, and those with ratios ≤ 0.5 or ≥ 2.0 were considered as differentially expressed genes at a significant level. For P19 and P32 experiments, cDNA sample was similarly generated from total pancreatic RNA (10 ...
Gene Expression/Mutations
... - Operon: promoter, operator, structural (functional) genes - Promoter: control sequence, site where replication starts - Operator: DNA sequence between promoter and enzyme genes, acts as on/off switch for genes - Functional genes: coding sections - Inducer: protein that initiates gene expression, m ...
... - Operon: promoter, operator, structural (functional) genes - Promoter: control sequence, site where replication starts - Operator: DNA sequence between promoter and enzyme genes, acts as on/off switch for genes - Functional genes: coding sections - Inducer: protein that initiates gene expression, m ...
Genotyping of Mice to Study Role of Krüppel
... The β-globin locus contains CACCC binding sites in the promoters of the β-like genes, which could serve as targets for KLF2 binding ...
... The β-globin locus contains CACCC binding sites in the promoters of the β-like genes, which could serve as targets for KLF2 binding ...
Nucleic Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
Prostate cancer stem cells Ongoing Projects 3
... sequences. This can lead to genes being gained or lost or being under the control of the wrong elements. Increased expression of oncogenes or decreseed expression of tumour suppressor genes can lead to cancer. We use a method called FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridisa-on) ...
... sequences. This can lead to genes being gained or lost or being under the control of the wrong elements. Increased expression of oncogenes or decreseed expression of tumour suppressor genes can lead to cancer. We use a method called FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridisa-on) ...
The genotype is the plan / blueprint for creating an organism
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the coding region is part of the transcription unit. The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary ami ...
... transcription unit - the part of a gene that gets copied (transcribed) by RNA polymerase coding region – For genes that make (encode) proteins, the coding region is part of the transcription unit. The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary ami ...
Feb 26
... 5’-TATAAT-3’ determines exact start site: bound by s factor 2)” -35 region” : 5’-TTGACA-3’ : bound by s factor 3) UP element : -57: bound by a factor ...
... 5’-TATAAT-3’ determines exact start site: bound by s factor 2)” -35 region” : 5’-TTGACA-3’ : bound by s factor 3) UP element : -57: bound by a factor ...
Transcription
... The structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase. Two depictions of the three-dimensional structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase, with the DNA and RNA modeled in. This RNA polymerase is formed from four different subunits, indicated by different colors (right). The DNA strand used as a template is red, ...
... The structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase. Two depictions of the three-dimensional structure of a bacterial RNA polymerase, with the DNA and RNA modeled in. This RNA polymerase is formed from four different subunits, indicated by different colors (right). The DNA strand used as a template is red, ...
“Bill Nye: Genes” Video Worksheet
... passed down from Parent to child. In the process, of course, the genetic material is recombined in new ways, which is why some people bear resemblance to their Parents and Grandparents without looking like any one relative in particular. 13. What analogy does Bill use to describe the human set of ch ...
... passed down from Parent to child. In the process, of course, the genetic material is recombined in new ways, which is why some people bear resemblance to their Parents and Grandparents without looking like any one relative in particular. 13. What analogy does Bill use to describe the human set of ch ...
Part 4 Transcription
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
... 9. Understand transcription and the role that RNA polymerase plays in it. ...
EpigEnEtiCS: A pRiMER
... molecular level. In humans, they include the parent-of-origin specific expression of genes (imprinting) and the shutting-down of almost all genes on one of the two X chromosomes in females (X-chromosome inactivation). All these epigenetic phenomena are characterized by chemical modifications to DNA ...
... molecular level. In humans, they include the parent-of-origin specific expression of genes (imprinting) and the shutting-down of almost all genes on one of the two X chromosomes in females (X-chromosome inactivation). All these epigenetic phenomena are characterized by chemical modifications to DNA ...
Slide 1
... •Gene prediction a very difficult problem in pattern recognition •Coding regions generally do not have conserved sequences •Much progress made with prokaryotic gene prediction •Eukaryotic genes more difficult to predict correctly ...
... •Gene prediction a very difficult problem in pattern recognition •Coding regions generally do not have conserved sequences •Much progress made with prokaryotic gene prediction •Eukaryotic genes more difficult to predict correctly ...
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand).Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.