video slide - Geneva High School
... • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into am ...
... • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into am ...
Hereditary Myopathy with Lactic Acidosis
... disease was caused by malfunctions in either the transportation, assembly or processing of Fe-S clusters. The aim of my thesis was to identify the disease causing gene of HML and to investigate the underlying disease-mechanisms. In paper I we identified a diseasecritical region on chromosome 12; a r ...
... disease was caused by malfunctions in either the transportation, assembly or processing of Fe-S clusters. The aim of my thesis was to identify the disease causing gene of HML and to investigate the underlying disease-mechanisms. In paper I we identified a diseasecritical region on chromosome 12; a r ...
Translation
... • One difference between prokaryote and eukaryote ribosomes is: – 1. Their function – 2. Prokaryotes do not have ribosomes because they do not have organelles – 3. Their size – 4. How they work ...
... • One difference between prokaryote and eukaryote ribosomes is: – 1. Their function – 2. Prokaryotes do not have ribosomes because they do not have organelles – 3. Their size – 4. How they work ...
and related proteins three-dimensional structure in a large family of
... (Siezen et al., 1991). Greer (1990) coined the term “structurally conserved regions,” or SCRs, to describe common regions of proteins belonging to the same family, based on the superposition of their 3D structures. Similarly, he used the term “variable regions,” or VRs, to describe those regions whe ...
... (Siezen et al., 1991). Greer (1990) coined the term “structurally conserved regions,” or SCRs, to describe common regions of proteins belonging to the same family, based on the superposition of their 3D structures. Similarly, he used the term “variable regions,” or VRs, to describe those regions whe ...
BCH 101- 5 Amino acids
... important is the ability of histidines in hemoglobin to buffer the H + ions from carbonic acid ionization in red blood cells. It is this property of hemoglobin that allows it to exchange O 2 and CO2 at the tissues or lungs, respectively. The primary alcohol of serine and threonine as well as the thi ...
... important is the ability of histidines in hemoglobin to buffer the H + ions from carbonic acid ionization in red blood cells. It is this property of hemoglobin that allows it to exchange O 2 and CO2 at the tissues or lungs, respectively. The primary alcohol of serine and threonine as well as the thi ...
Separation of nuclear protein complexes by blue native
... complexes such as pyruvate dehydrogenase complex [4] or virus particles [9]. The procedure has several advantages that make the BN-PAGE suitable also for separation of nuclear protein complexes. The most important is the neutral pH ensuring physiological stability of protein complexes during separat ...
... complexes such as pyruvate dehydrogenase complex [4] or virus particles [9]. The procedure has several advantages that make the BN-PAGE suitable also for separation of nuclear protein complexes. The most important is the neutral pH ensuring physiological stability of protein complexes during separat ...
figure 1 - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
... atoms in their side chain (figure 2). Furthermore, compared with other intracellular compounds, nucleotides are highly nutrient rich with a carbon : nitrogen ratio (C : N) between 1 and 2.5 (Sterner & Elser 2002). Therefore, riboproteic complexes are an extremely nutrient-rich pool in the cell due b ...
... atoms in their side chain (figure 2). Furthermore, compared with other intracellular compounds, nucleotides are highly nutrient rich with a carbon : nitrogen ratio (C : N) between 1 and 2.5 (Sterner & Elser 2002). Therefore, riboproteic complexes are an extremely nutrient-rich pool in the cell due b ...
Signatures of nitrogen limitation in the elemental composition of the
... atoms in their side chain (figure 2). Furthermore, compared with other intracellular compounds, nucleotides are highly nutrient rich with a carbon : nitrogen ratio (C : N) between 1 and 2.5 (Sterner & Elser 2002). Therefore, riboproteic complexes are an extremely nutrient-rich pool in the cell due b ...
... atoms in their side chain (figure 2). Furthermore, compared with other intracellular compounds, nucleotides are highly nutrient rich with a carbon : nitrogen ratio (C : N) between 1 and 2.5 (Sterner & Elser 2002). Therefore, riboproteic complexes are an extremely nutrient-rich pool in the cell due b ...
Subviral-Particle Biogenesis Hepatitis B Virus Small Surface
... additional functions during SVP morphogenesis, e.g., by establishing lateral interactions in the membrane bilayer. ...
... additional functions during SVP morphogenesis, e.g., by establishing lateral interactions in the membrane bilayer. ...
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids Table of a
... important is the ability of histidines in hemoglobin to buffer the H+ ions from carbonic acid ionization in red blood cells. It is this property of hemoglobin that allows it to exchange O2 and CO2 at the tissues or lungs, respectively. The primary alcohol of serine and threonine as well as the thiol ...
... important is the ability of histidines in hemoglobin to buffer the H+ ions from carbonic acid ionization in red blood cells. It is this property of hemoglobin that allows it to exchange O2 and CO2 at the tissues or lungs, respectively. The primary alcohol of serine and threonine as well as the thiol ...
Small AnDsense RNAs and RNA Interference
... In an organism like C. elegans, dsRNA (with a sequence which is complementary to a target mRNA of interest) can be used to downregulate that mRNA experimentally. ...
... In an organism like C. elegans, dsRNA (with a sequence which is complementary to a target mRNA of interest) can be used to downregulate that mRNA experimentally. ...
Overcoming stalled translation in human mitochondria
... essential binding partner SmpB, which with tmRNA rescues ribosomes stalled on RNA templates that either lack a stop codon or have stalled during the elongation phase for other reasons. Alternative rescue pathways identified in Escherichia coli require the activity of protein factors ArfA or ArfB (Yae ...
... essential binding partner SmpB, which with tmRNA rescues ribosomes stalled on RNA templates that either lack a stop codon or have stalled during the elongation phase for other reasons. Alternative rescue pathways identified in Escherichia coli require the activity of protein factors ArfA or ArfB (Yae ...
Capabilities and limitations of gel electrophoresis for elemental
... preserved. Hence, it is often applied if an enzyme has to retain its activity after separation. This is why it is a possible separation technique for metal–protein complexes, which would be disturbed in the presence of denaturing chemicals. Unfortunately, the state-of-the-art 2DE protocols rely on t ...
... preserved. Hence, it is often applied if an enzyme has to retain its activity after separation. This is why it is a possible separation technique for metal–protein complexes, which would be disturbed in the presence of denaturing chemicals. Unfortunately, the state-of-the-art 2DE protocols rely on t ...
Free amino acids and proteins dynamics in somatic embryogenesis
... a particular advantage which consists to yield new plants with more stable genome (Roja Rani et al., 2005). This technique is an alternative pathway for the propagation of African pearwood (Sanonne et al., 2012). Somatic embryo development reposed on biochemical and physiological principles that are ...
... a particular advantage which consists to yield new plants with more stable genome (Roja Rani et al., 2005). This technique is an alternative pathway for the propagation of African pearwood (Sanonne et al., 2012). Somatic embryo development reposed on biochemical and physiological principles that are ...
Some psychrophiles Abstract
... The lower temperature limit for psychrophiles is not clearly defined, although a limit of 12°C for reproduction and 20°C for metabolic function has been proposed [9]. Photosynthesis in the Antarctic lichen Umbilicaria aprina has been reported to occur at 17°C [10], and the yeast Rhodotolura glutinis ...
... The lower temperature limit for psychrophiles is not clearly defined, although a limit of 12°C for reproduction and 20°C for metabolic function has been proposed [9]. Photosynthesis in the Antarctic lichen Umbilicaria aprina has been reported to occur at 17°C [10], and the yeast Rhodotolura glutinis ...
What is transcription
... Encoded by rpoB gene. The catalytic center of the RNA polymerase Rifampicin (used for anti-tuberculosis): bind to the β subunit (12A away from active site), and inhibit transcription initiation. Blocking the path for extending RNA chain beyond 2-3 nts. Mutation in rpoB gene can result in rifampicin ...
... Encoded by rpoB gene. The catalytic center of the RNA polymerase Rifampicin (used for anti-tuberculosis): bind to the β subunit (12A away from active site), and inhibit transcription initiation. Blocking the path for extending RNA chain beyond 2-3 nts. Mutation in rpoB gene can result in rifampicin ...
Genetics Class- Ch. 10 Notes
... RNA processing Translation - production of protein using mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA ...
... RNA processing Translation - production of protein using mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA ...
Optimizing bacterial expression and purifica- Biomedical laboratory science,
... consisting of optimizing temperature, time and testing the solubility of the fusion proteins and 3. Optimizing the purification of the two fragments of Phactr4 protein. The cloning process was successfully performed after some optimization and change of vector. The optimal combination of temperature ...
... consisting of optimizing temperature, time and testing the solubility of the fusion proteins and 3. Optimizing the purification of the two fragments of Phactr4 protein. The cloning process was successfully performed after some optimization and change of vector. The optimal combination of temperature ...
ch9 FA 11 - Cal State LA
... – Beta subunit is a GTPase • Assembly – Polymer grows by addition of units at the “plus” end – GTP-bound tubulin can add – GTP form hydrolyzes to GDP form – GDP-bound tubulin cannot add – GDP-bound tubulin can release only from “plus” end – GDP-bound tubulin cannot release from “minus” end or from c ...
... – Beta subunit is a GTPase • Assembly – Polymer grows by addition of units at the “plus” end – GTP-bound tubulin can add – GTP form hydrolyzes to GDP form – GDP-bound tubulin cannot add – GDP-bound tubulin can release only from “plus” end – GDP-bound tubulin cannot release from “minus” end or from c ...
Protein Targeting to the Nuclear Pore. What Can
... Harley M.S. Smith and Natasha V. Raikhel* Department of Energy Plant Research Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan 48824–1312 Characteristic of eukaryotic cells are the numerous types of membrane-bound organelles or compartments found in the cytoplasm, with each type carryin ...
... Harley M.S. Smith and Natasha V. Raikhel* Department of Energy Plant Research Laboratory, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan 48824–1312 Characteristic of eukaryotic cells are the numerous types of membrane-bound organelles or compartments found in the cytoplasm, with each type carryin ...
Stages of Translation (Biol 200 Sp2015): KEY Initiation
... 2. Based on the figures, list two things that happen after release factor binds to the ribosome: i. ________The new protein is separated from the last tRNA_________________ ii. __ The large and small ribosomal subunits separate and fall off the mRNA___ 3. What is the sequence of the codon that indic ...
... 2. Based on the figures, list two things that happen after release factor binds to the ribosome: i. ________The new protein is separated from the last tRNA_________________ ii. __ The large and small ribosomal subunits separate and fall off the mRNA___ 3. What is the sequence of the codon that indic ...
Biogenesis of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoproteins
... signal(s) present in this complex are responsible for this subcellular localization. The presence of a retention signal was first demonstrated for E2 by Cocquerel et al. (1998). Indeed, E2 expressed in the absence of E1 can fold properly and is retained in the ER, as shown by the lack of complex gly ...
... signal(s) present in this complex are responsible for this subcellular localization. The presence of a retention signal was first demonstrated for E2 by Cocquerel et al. (1998). Indeed, E2 expressed in the absence of E1 can fold properly and is retained in the ER, as shown by the lack of complex gly ...
What are enzymes and how do they work
... Cell 3: About a third of all new proteins in a mutated cell are not doing their jobs correctly. When you compared to proteins in a healthy cell, these proteins appear much larger overall. Some tRNA has changed it’s anticodon to recognize one of the three STOP codons, so this is erroneously continuin ...
... Cell 3: About a third of all new proteins in a mutated cell are not doing their jobs correctly. When you compared to proteins in a healthy cell, these proteins appear much larger overall. Some tRNA has changed it’s anticodon to recognize one of the three STOP codons, so this is erroneously continuin ...
Handout 14, 15 - U of L Class Index
... The 40S ribosomal subunit, alongside with factors, tRNAi Met and GTP recognize the m7G cap at the 5’-end of an mRNA and allow the ribosomal subunit to bind at the end of the mRNA. The 40S subunit is scanning the mRNA toward the 3’-end, searching for the initiation codon, melting the stem loop struct ...
... The 40S ribosomal subunit, alongside with factors, tRNAi Met and GTP recognize the m7G cap at the 5’-end of an mRNA and allow the ribosomal subunit to bind at the end of the mRNA. The 40S subunit is scanning the mRNA toward the 3’-end, searching for the initiation codon, melting the stem loop struct ...
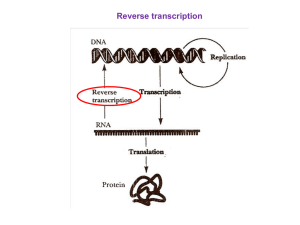
Reverse transcriptase
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.