BIOLOGY 110
... What type of reaction is used to string A.A.s into proteins? What is the name applied to a covalent bond that is formed between two A.A.s in a protein? 5. Characterize the difference between primary, secondary, tertiary, and quatenary structure in proteins. 6. Explain protein denaturation and give a ...
... What type of reaction is used to string A.A.s into proteins? What is the name applied to a covalent bond that is formed between two A.A.s in a protein? 5. Characterize the difference between primary, secondary, tertiary, and quatenary structure in proteins. 6. Explain protein denaturation and give a ...
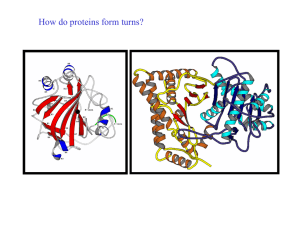
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
BioCore II lecture6
... easily maintained at high concentrations within organelles. b. Chemical reactions that are incompatible can be segregated in different organelles. c. DNA is transcribed and translated at significantly higher rates because all of the machinery is inside a single, membrane-bound nucleus. d. When the p ...
... easily maintained at high concentrations within organelles. b. Chemical reactions that are incompatible can be segregated in different organelles. c. DNA is transcribed and translated at significantly higher rates because all of the machinery is inside a single, membrane-bound nucleus. d. When the p ...
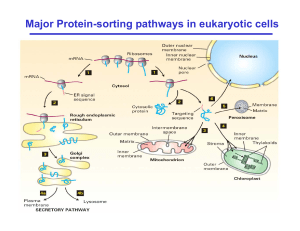
Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
About Proteins
... The order of the AAs determines the function If even one AA is out of order by mistake, the protein will not function (work) This is because proteins fold in a specific way ...
... The order of the AAs determines the function If even one AA is out of order by mistake, the protein will not function (work) This is because proteins fold in a specific way ...
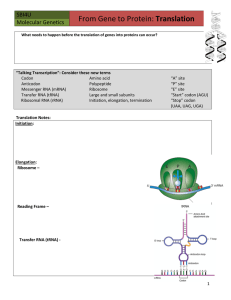
Protein Synthesis PPT
... Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), but RNA can leave the nucleus (single stranded). ...
... Why? DNA has the genetic code for the protein that needs to be made, but proteins are made by the ribosomes—ribosomes are outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. DNA is too large to leave the nucleus (double stranded), but RNA can leave the nucleus (single stranded). ...
The Mac Daddies of Molecules
... Lipids are used for storing energy (why it pays to have some fat on you!) Made of carbon & hydrogen ...
... Lipids are used for storing energy (why it pays to have some fat on you!) Made of carbon & hydrogen ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
Cell Transport Notes Learning Targets 8. Explain the significance of
... 8. Explain the significance of the selectively permeable membrane to the transport of molecules. ...
... 8. Explain the significance of the selectively permeable membrane to the transport of molecules. ...
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius
... TESS The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius ...
... TESS The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius ...
The basis of specific ligand recognition by proteins
... general problem of mobility will be addressed by specifically looking at interfaces between proteins and DNA, where the protein binds specifically to a certain DNA sequence (“reading” of DNA). Available experimental data from the PDB database [1] will be collected and compared (sequence and structur ...
... general problem of mobility will be addressed by specifically looking at interfaces between proteins and DNA, where the protein binds specifically to a certain DNA sequence (“reading” of DNA). Available experimental data from the PDB database [1] will be collected and compared (sequence and structur ...
custom protein production service
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
Amoeba Shines Light on Photosynthetic Evolution The major
... from Carnegie's Eva Nowack and Arthur Grossman has opened a window into the early stages of chloroplast evolution. Their work is published online by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in the week of February 27-March 2. It is widely accepted that chloroplasts originated from photosy ...
... from Carnegie's Eva Nowack and Arthur Grossman has opened a window into the early stages of chloroplast evolution. Their work is published online by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in the week of February 27-March 2. It is widely accepted that chloroplasts originated from photosy ...
CRYSTAL 24 Abstract Submission Form
... substrates, -naphthyl acetate and p-nitrophenyl acetate. In terms of steady state kinetics, the mutations caused a drop in the Km for the hydrolysis reaction with these two substrates. For the best mutant, there was a 5.6 fold increase in kcat/Km for the hydrolysis of -naphthyl acetate and a 3.5 f ...
... substrates, -naphthyl acetate and p-nitrophenyl acetate. In terms of steady state kinetics, the mutations caused a drop in the Km for the hydrolysis reaction with these two substrates. For the best mutant, there was a 5.6 fold increase in kcat/Km for the hydrolysis of -naphthyl acetate and a 3.5 f ...
docx - BeanBeetles.org
... cells and thus multicellular organisms. The information for building proteins expressed in a cell is coded for in the DNA of the cell. This relationship between proteins and DNA is well understood and has been called the “central dogma” of biology. However, though the DNA of an individual remains re ...
... cells and thus multicellular organisms. The information for building proteins expressed in a cell is coded for in the DNA of the cell. This relationship between proteins and DNA is well understood and has been called the “central dogma” of biology. However, though the DNA of an individual remains re ...
What are some other organic molecules?
... 1)The sequence (order) of amino acids in a protein determine its shape 2) The shape of a protein determines its activity ...
... 1)The sequence (order) of amino acids in a protein determine its shape 2) The shape of a protein determines its activity ...
„Biochemical reconstitution of protein complexes involved in
... mutated proteins lost the ability to interact with each other and therefore were not able to regulate ...
... mutated proteins lost the ability to interact with each other and therefore were not able to regulate ...
The Mac Daddies of Molecules
... Proteins are just chains of amino acids, like a beaded necklace, that sometimes fold into weird shapes Their functions are VAST!!!!! ...
... Proteins are just chains of amino acids, like a beaded necklace, that sometimes fold into weird shapes Their functions are VAST!!!!! ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;9)(p34;q34) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... (protein tyrosine kinase 6, also called BRK) play a role downstream of the EGF receptor (EGFR). SFPQ and NONO form complexes with the androgen receptor (AR) and modulate its transcriptional activity (Huret, ...
... (protein tyrosine kinase 6, also called BRK) play a role downstream of the EGF receptor (EGFR). SFPQ and NONO form complexes with the androgen receptor (AR) and modulate its transcriptional activity (Huret, ...
Normal Protein Trafficking and the Unfolded Protein Response
... protein response is triggered. During the unfolded protein response cells may respond by: • destroying the proteins • trying to refold the proteins • commit apoptosis (cell suicide) ...
... protein response is triggered. During the unfolded protein response cells may respond by: • destroying the proteins • trying to refold the proteins • commit apoptosis (cell suicide) ...
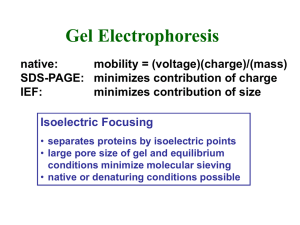
No Slide Title
... • dry gel and expose to X-ray film • use intensifying screens for high energy isotopes • use fluors impregnated in gel for low and medium energy isotopes ...
... • dry gel and expose to X-ray film • use intensifying screens for high energy isotopes • use fluors impregnated in gel for low and medium energy isotopes ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.