13.3 RNA and Gene Expression
... the instructions for making proteins from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomal (rRNA) – helps to assemble amino acids to make proteins on the ribosomes. ...
... the instructions for making proteins from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomal (rRNA) – helps to assemble amino acids to make proteins on the ribosomes. ...
Proteins - West Branch Schools
... Proteins Continued… 3. Tertiary structure of many proteins is globular, such as hemoglobin Denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the tertiary structure and secondary structure (unravel) Think of an egg! Change in temperature or pH can cause a protein to unravel and c ...
... Proteins Continued… 3. Tertiary structure of many proteins is globular, such as hemoglobin Denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the tertiary structure and secondary structure (unravel) Think of an egg! Change in temperature or pH can cause a protein to unravel and c ...
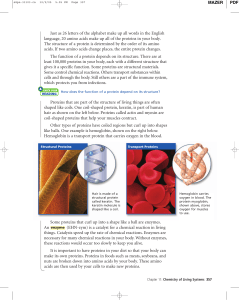
Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English
... Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein dep ...
... Just as 26 letters of the alphabet make up all words in the English language, 20 amino acids make up all of the proteins in your body. The structure of a protein is determined by the order of its amino acids. If two amino acids change places, the entire protein changes. The function of a protein dep ...
LAB SESSION 1: Bioprocessing
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
LAB SESSION 1: Bioprocessing
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
... Fractions collected as the solution passes through the column will contain differing chemicals or proteins based on their characteristics, effectively separating the different components. ...
Sections 5.3-5.5 - BridgesToLiteracy.com
... they have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions. such as enzymatic proteins, structural proteins, storage proteins, transport proteins, hormonal proteins, receptor proteins, contractile and mortor proteins, and defensive proteins. -proteins will be seen on CH.7,17,21,and 39. -on ch ...
... they have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions. such as enzymatic proteins, structural proteins, storage proteins, transport proteins, hormonal proteins, receptor proteins, contractile and mortor proteins, and defensive proteins. -proteins will be seen on CH.7,17,21,and 39. -on ch ...
A20-Protein Synthesis
... b. Function: brings instructions from DNA in nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm mRNA ...
... b. Function: brings instructions from DNA in nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm mRNA ...
Organelles: specialized subunits within a cell that have a specific
... Nucleus: “nut”. First seen in 1858. Contains DNA. Information center of the cell. Nuclear envelope: a double layer with pores that let molecules in and out ...
... Nucleus: “nut”. First seen in 1858. Contains DNA. Information center of the cell. Nuclear envelope: a double layer with pores that let molecules in and out ...
Post-transcriptional gene control
... • hnRNPs prevent formation of secondary structures within pre-mRNAs • hnRNP proteins are multidomain with one or more RNA binding domains and at least one domain for interaction with other proteins • some hnRNPs contribute to pre-mRNA recognition by RNA processing enzymes • The two most common RNA b ...
... • hnRNPs prevent formation of secondary structures within pre-mRNAs • hnRNP proteins are multidomain with one or more RNA binding domains and at least one domain for interaction with other proteins • some hnRNPs contribute to pre-mRNA recognition by RNA processing enzymes • The two most common RNA b ...
Using light as a superglue for proteins and their binding partners
... the reaction only takes place when you expose the molecules to particular wavelengths of light.” In the past such light switches, however, have not recognized precise target proteins. This has strongly limited research into specific interactions between molecules. In the current study, the scientist ...
... the reaction only takes place when you expose the molecules to particular wavelengths of light.” In the past such light switches, however, have not recognized precise target proteins. This has strongly limited research into specific interactions between molecules. In the current study, the scientist ...
The Cold Never Bothered Me Anyway Measuring the Forces at Work
... temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock proteins change their flexibility, allowing them to move about and operate at the environment temperature of the organism. ...
... temperature and is thought to help maintain protein production. It has a highly conserved structure but small differences in the amino acid sequence of extremophilic Cold Shock proteins change their flexibility, allowing them to move about and operate at the environment temperature of the organism. ...
Chapter 3
... called B cells. • Antibodies can be isolated from serum (blood) (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
... called B cells. • Antibodies can be isolated from serum (blood) (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
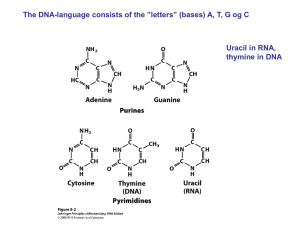
DNA to Proteins
... • Bases form the alphabet of the code • Groups of 3 bases code for an amino acid • A long string of amino acids makes a protein • Each gene is a set of instructions for making a protein ...
... • Bases form the alphabet of the code • Groups of 3 bases code for an amino acid • A long string of amino acids makes a protein • Each gene is a set of instructions for making a protein ...
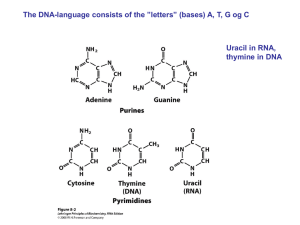
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... The amino acids in proteins are held together by covalent peptide bonds. Note that this defines the carboxyterminal and amino-terminal ends of proteins. Polymerization occurs such that the amino acid at the amino terminal end is the first to become incorporated. ...
... The amino acids in proteins are held together by covalent peptide bonds. Note that this defines the carboxyterminal and amino-terminal ends of proteins. Polymerization occurs such that the amino acid at the amino terminal end is the first to become incorporated. ...
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... The amino acids in proteins are held together by covalent peptide bonds. Note that this defines the carboxyterminal and amino-terminal ends of proteins. Polymerization occurs such that the amino acid at the amino terminal end is the first to become incorporated. ...
... The amino acids in proteins are held together by covalent peptide bonds. Note that this defines the carboxyterminal and amino-terminal ends of proteins. Polymerization occurs such that the amino acid at the amino terminal end is the first to become incorporated. ...
distinct format
... and sexual blood stages selected stages of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum to identify proteins involved in sexual stage biology. The analysis revealed 1,289 proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 ...
... and sexual blood stages selected stages of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum to identify proteins involved in sexual stage biology. The analysis revealed 1,289 proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 ...
Exam II Review: - Texas Tech University
... 1. Cleavage and Polyadenylation are coupled. 2. PAP is a template-independent RNA polymerase 3. PABPs associate with Poly (A) tails in the cytosol to organize them into nucleoprotein particles. ...
... 1. Cleavage and Polyadenylation are coupled. 2. PAP is a template-independent RNA polymerase 3. PABPs associate with Poly (A) tails in the cytosol to organize them into nucleoprotein particles. ...
A dead-end street of protein folding
... force of the structural shift induced global transformation from the original to disease related amyloid fold is expected to lie in the protein backbone, common to all proteins.(Nelson, R. et al. Nature 2005, 435, 773-778., and Wright, C. F. etal. Nature 2005, 438, 878-881.) These structures show lo ...
... force of the structural shift induced global transformation from the original to disease related amyloid fold is expected to lie in the protein backbone, common to all proteins.(Nelson, R. et al. Nature 2005, 435, 773-778., and Wright, C. F. etal. Nature 2005, 438, 878-881.) These structures show lo ...
Protein Folding and Membrane Structure
... Fluid Mosaic Model of Biological Membranes • Singer and Nicolson (1972) synthesized a variety of results that implied the unit membrane is a fluid and contains proteins as integral components • Today we recognize fluidity restrictions and local membrane domains (Domain Mosaic Model) ...
... Fluid Mosaic Model of Biological Membranes • Singer and Nicolson (1972) synthesized a variety of results that implied the unit membrane is a fluid and contains proteins as integral components • Today we recognize fluidity restrictions and local membrane domains (Domain Mosaic Model) ...
Aquaporin IDI Prelab
... a. Why are the new water channels being developed referred to as biomimetic? ...
... a. Why are the new water channels being developed referred to as biomimetic? ...
DNA RNA-Protein Synthesis Homework
... transcribing the information from the DNA in the nucleus. ...
... transcribing the information from the DNA in the nucleus. ...
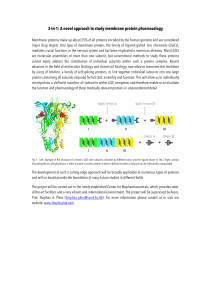
3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology
... Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nervous system and has been implicated a numerous diseases. Most LGI ...
... Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nervous system and has been implicated a numerous diseases. Most LGI ...
word
... An attenuator site is a DNA sequence where a choice is made by RNA polymerase between continued transcription and termination a) Rapid translation of the leader sequence in an mRNA favors an RNA secondary structure that terminates transcription prematurely by a Rho-independent mechanism b) Slow tran ...
... An attenuator site is a DNA sequence where a choice is made by RNA polymerase between continued transcription and termination a) Rapid translation of the leader sequence in an mRNA favors an RNA secondary structure that terminates transcription prematurely by a Rho-independent mechanism b) Slow tran ...
PDF - Available Technologies
... UC San Diego researchers have discovered an enhancer function of an approximately 30 bp DNA fragment that had been reported to function as a protein transduction domain in microbial cells. ...
... UC San Diego researchers have discovered an enhancer function of an approximately 30 bp DNA fragment that had been reported to function as a protein transduction domain in microbial cells. ...
SR protein

SR proteins are a conserved family of proteins involved in RNA splicing. SR proteins are named because they contain a protein domain with long repeats of serine and arginine amino acid residues, whose standard abbreviations are ""S"" and ""R"" respectively. SR proteins are 50-300 amino acids in length and composed of two domains, the RNA recognition motif (RRM) region and the RS binding domain. SR proteins are more commonly found in the nucleus than the cytoplasm, but several SR proteins are known to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.SR proteins were discovered in the 1990s in Drosophila and in amphibian oocytes, and later in humans. In general, metazoans appear to have SR proteins and unicellular organisms lack SR proteins.SR proteins are important in constitutive and alternative pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA export, genome stabilization, nonsense-mediated decay, and translation. SR proteins alternatively splice pre-mRNA by preferentially selecting different splice sites on the pre-mRNA strands to create multiple mRNA transcripts from one pre-mRNA transcript. Once splicing is complete the SR protein may or may not remain attached to help shuttle the mRNA strand out of the nucleus. As RNA Polymerase II is transcribing DNA into RNA, SR proteins attach to newly made pre-mRNA to prevent the pre-mRNA from binding to the coding DNA strand to increase genome stabilization. Topoisomerase I and SR proteins also interact to increase genome stabilization. SR proteins can control the concentrations of specific mRNA that is successfully translated into protein by selecting for nonsense-mediated decay codons during alternative splicing. SR proteins can alternatively splice NMD codons into its own mRNA transcript to auto-regulate the concentration of SR proteins. Through the mTOR pathway and interactions with polyribosomes, SR proteins can increase translation of mRNA.Ataxia telangiectasia, neurofibromatosis type 1, several cancers, HIV-1, and spinal muscular atrophy have all been linked to alternative splicing by SR proteins.