DNA Polymerase
... sequence in which they are linked together determines the proteins function. Change the sequence, type, or number of amino acids in a protein you change the function. Amino Acids without water sensitive R-groups ...
... sequence in which they are linked together determines the proteins function. Change the sequence, type, or number of amino acids in a protein you change the function. Amino Acids without water sensitive R-groups ...
Core promoter
... complexity during evolution Simple yeast promoter majority contains a single UAS located within a few hundred bps of TATA ...
... complexity during evolution Simple yeast promoter majority contains a single UAS located within a few hundred bps of TATA ...
DNA Fill in the blank notes.
... __________gathers nucleotides and makes a strand called ________ (__________ _______). ...
... __________gathers nucleotides and makes a strand called ________ (__________ _______). ...
Genetics
... transmission of genetic information. They are a set of instructions encoded in the nucleotide sequence of each organism. Genes code for the specific sequences of amino acids that comprise the proteins characteristic to that organism. • 3.2 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it rel ...
... transmission of genetic information. They are a set of instructions encoded in the nucleotide sequence of each organism. Genes code for the specific sequences of amino acids that comprise the proteins characteristic to that organism. • 3.2 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it rel ...
Reduction: For and Against Chapter 7
... The law of independent assortment reduced to molecular level ...
... The law of independent assortment reduced to molecular level ...
AP Bio Molecular Genetics Review Sheet
... What is a phage, transformation, DNA, Griffith, and Avery? (What do they have to do with each other?) What was determined directly from X-Ray diffraction photographs of DNA? What is required when replicating the Lagging strand of DNA? What is the primary transcript of eukaryotic genes? Can you use a ...
... What is a phage, transformation, DNA, Griffith, and Avery? (What do they have to do with each other?) What was determined directly from X-Ray diffraction photographs of DNA? What is required when replicating the Lagging strand of DNA? What is the primary transcript of eukaryotic genes? Can you use a ...
Ch 17 Protein Synthesis
... polymerase II bind to promoter upstream from gene 2. Promoter region contains a TATA box which indicates non-template strand ...
... polymerase II bind to promoter upstream from gene 2. Promoter region contains a TATA box which indicates non-template strand ...
Eat to Regulate Your Genes?
... messenger RNA, which then is (or may be) “translated” into protein. The entire process is broadly known as “gene expression.” However, one of the hottest fields of research in molecular biology over the past decade or two has to do with DNA regions that produce a wide assortment of nonprotein-coding ...
... messenger RNA, which then is (or may be) “translated” into protein. The entire process is broadly known as “gene expression.” However, one of the hottest fields of research in molecular biology over the past decade or two has to do with DNA regions that produce a wide assortment of nonprotein-coding ...
Scheme of work for Chapter 7, Nucleic acids and proteins
... four examples and their functions; explain the significance of polar and non-polar amino acids in ...
... four examples and their functions; explain the significance of polar and non-polar amino acids in ...
AP Biology Discussion Notes
... through a stimulatory protein, such as catabolite activator protein (CAP), an activator of transcription • When glucose (a preferred food source of E. coli) is scarce, CAP is activated by binding with cyclic ...
... through a stimulatory protein, such as catabolite activator protein (CAP), an activator of transcription • When glucose (a preferred food source of E. coli) is scarce, CAP is activated by binding with cyclic ...
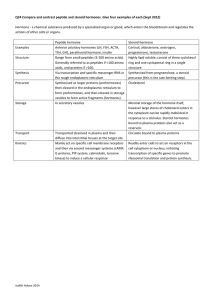
Q24 Compare and contrast peptide and steroid hormones. Give four
... however large stores of cholesterol esters in the cytoplasm can be rapidly mobilized in response to a stimulus. Steroid hormones bound to plasma proteins also act as a reservoir. Transport Transported ...
... however large stores of cholesterol esters in the cytoplasm can be rapidly mobilized in response to a stimulus. Steroid hormones bound to plasma proteins also act as a reservoir. Transport Transported ...
Show It
... ribosome to assemble proteins Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – a structural component of ribosomes ...
... ribosome to assemble proteins Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – a structural component of ribosomes ...
File - Georgetown ISD
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
Gene Regulation Prokaryoperon_RD_MP
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
... • Promoter-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with RNA polymerase to start transcription. This sequence also contains the operator region. • Operator-The nucleotide sequence that can bind with repressor protein to inhibit transcription. ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... reactions are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reaction) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
... reactions are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reaction) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
DNA Handout KEY - Iowa State University
... 4. What are Chargraff’s rules? If a segment of DNA is composed of 30% C, what is the % of A? A=T and C=G 20% (C=30%=G, A+G=C+T, A=T) 5. A always pairs with _T__, forming _2__ H-bonds. C always pairs with _G__, forming _3_Hbonds. 6. What is the important relationship between structure and function re ...
... 4. What are Chargraff’s rules? If a segment of DNA is composed of 30% C, what is the % of A? A=T and C=G 20% (C=30%=G, A+G=C+T, A=T) 5. A always pairs with _T__, forming _2__ H-bonds. C always pairs with _G__, forming _3_Hbonds. 6. What is the important relationship between structure and function re ...
Making RNA in other ways
... the existence of introns • Introns may become copied into DNA or directly inserted into DNA as RNA – The insertion is sequence specific – So if cells fuse (as during fertilization) a retrotransposon can copy an intron from a gene on one chromosome and insert it into the same gene at the same place o ...
... the existence of introns • Introns may become copied into DNA or directly inserted into DNA as RNA – The insertion is sequence specific – So if cells fuse (as during fertilization) a retrotransposon can copy an intron from a gene on one chromosome and insert it into the same gene at the same place o ...
DNA to Protein Synthesis Internet Quest
... 8. What happens to the mRNA molecule when protein production is complete? ...
... 8. What happens to the mRNA molecule when protein production is complete? ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... When replication is complete, 2 complete double helixes of DNA exist BUT each one contains 1 old strand and 1 new strand of DNA. It is only after replication that chromatin can condense around histone proteins to form chromosomes and complete the cell cycle. Unfortunately, if copying errors were mad ...
... When replication is complete, 2 complete double helixes of DNA exist BUT each one contains 1 old strand and 1 new strand of DNA. It is only after replication that chromatin can condense around histone proteins to form chromosomes and complete the cell cycle. Unfortunately, if copying errors were mad ...
Repressilator
... Experimental setting in more detail. Tunning out to the correct parameters. The repressilator in the language of BioBricks and MIT´s abstraction hierarchy. ...
... Experimental setting in more detail. Tunning out to the correct parameters. The repressilator in the language of BioBricks and MIT´s abstraction hierarchy. ...
Protein Synthesis Test Review
... 7. What is a frameshift mutation? _The whole sequence is altered due to an insertion or deletion resulting in large scale changes to the genetic code.____________________ 8. Will the protein be the same if a mutation occurs? Why or why not? ___ If there are any gene alterations the protein will be d ...
... 7. What is a frameshift mutation? _The whole sequence is altered due to an insertion or deletion resulting in large scale changes to the genetic code.____________________ 8. Will the protein be the same if a mutation occurs? Why or why not? ___ If there are any gene alterations the protein will be d ...
LS1a Fall 09
... o Step 1: The incoming aminoacyl-tRNA binds to the A-site. o Step 2: The bond between the C-terminus of the amino acid chain and the tRNA in the P-site is broken as the amino acid chain makes a new bond to the amino-group of the amino acid in the A-site. The mRNA advances by three nucleotides, placi ...
... o Step 1: The incoming aminoacyl-tRNA binds to the A-site. o Step 2: The bond between the C-terminus of the amino acid chain and the tRNA in the P-site is broken as the amino acid chain makes a new bond to the amino-group of the amino acid in the A-site. The mRNA advances by three nucleotides, placi ...
Exons and Introns
... 1.DNA In eukaryotes, the genome is divided into : •Non-coding areas... between genes. •Genes : Each gene is divided into several exons, separated by non coding sequences, •Introns (not coding) •Exons (coding) •Promoters, and regulation sequences. 2.RNA polymerases RNA polymerases are enzymes that wi ...
... 1.DNA In eukaryotes, the genome is divided into : •Non-coding areas... between genes. •Genes : Each gene is divided into several exons, separated by non coding sequences, •Introns (not coding) •Exons (coding) •Promoters, and regulation sequences. 2.RNA polymerases RNA polymerases are enzymes that wi ...