One Gene -One polypeptide
... 11.4 One Gene One Polypeptide Each gene codes for a polypeptide (protein). A polypeptide is made up of amino acids (monomer) Proteins can have 1,2,3,or 4 polypeptides, Human traits can have more than 1 gene. ...
... 11.4 One Gene One Polypeptide Each gene codes for a polypeptide (protein). A polypeptide is made up of amino acids (monomer) Proteins can have 1,2,3,or 4 polypeptides, Human traits can have more than 1 gene. ...
Brief overview of Bio backgound
... Store [sequence,structure] pairs in a database Find ways to score similarity of residue sequences Given a new sequence, find closest matches ...
... Store [sequence,structure] pairs in a database Find ways to score similarity of residue sequences Given a new sequence, find closest matches ...
Viruses (4)
... Proximal control elements are located close to the promoter Distal control elements, groupings of which are called enhancers, may be far away from a gene or even located in an intron Some transcription factors function as repressors, inhibiting expression of a particular gene by a variety of me ...
... Proximal control elements are located close to the promoter Distal control elements, groupings of which are called enhancers, may be far away from a gene or even located in an intron Some transcription factors function as repressors, inhibiting expression of a particular gene by a variety of me ...
Slide ()
... Proposed genetic rearrangement of chromosome 11 in a subset of sporadic parathyroid adenomas. An inversion of DNA sequence near the centromere of chromosome 11 places the 5′-regulatory region of the PTH gene (also on chromosome 11) adjacent to the PRAD1 gene, whose product is involved in cell cycle ...
... Proposed genetic rearrangement of chromosome 11 in a subset of sporadic parathyroid adenomas. An inversion of DNA sequence near the centromere of chromosome 11 places the 5′-regulatory region of the PTH gene (also on chromosome 11) adjacent to the PRAD1 gene, whose product is involved in cell cycle ...
DNA structure and protein synthesis
... • The stretch of DNA that is transcribed is called a transcription unit • Transcription factors (sigma) – initiate the binding of the RNA polymerase • The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II bound to a promoter is called a transcription initiation complex • A promoter c ...
... • The stretch of DNA that is transcribed is called a transcription unit • Transcription factors (sigma) – initiate the binding of the RNA polymerase • The completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II bound to a promoter is called a transcription initiation complex • A promoter c ...
Human Genetics
... • Why do some people not like the idea? The plasmid also needs a “marker gene” This is usually an antibiotic resistance gene Some people fear that the insulin which is extracted from the bacteria would also contain a gene product to make anyone who uses the insulin resistant to antibiotics! ...
... • Why do some people not like the idea? The plasmid also needs a “marker gene” This is usually an antibiotic resistance gene Some people fear that the insulin which is extracted from the bacteria would also contain a gene product to make anyone who uses the insulin resistant to antibiotics! ...
Nerve activates contraction - Jackson County School District
... reminder of the kinship that bonds all life on Earth. ...
... reminder of the kinship that bonds all life on Earth. ...
reduce usage of proper splice site
... • Initiation of transcription, promoter structure, RNA polymerase structure and function ...
... • Initiation of transcription, promoter structure, RNA polymerase structure and function ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
... • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
New Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentation
... which are called anticodons, and one amino acid. The tRNA reads the code and carries the amino acid to be incorporated into the developing protein. ...
... which are called anticodons, and one amino acid. The tRNA reads the code and carries the amino acid to be incorporated into the developing protein. ...
mRNA - Decatur ISD
... – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
... – binding site before beginning of gene – Generally referred to as a TATA box because it is a repeating sequence of T and A – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors ...
Study Questions for Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biological and/or evolutionary importance. List 3 potential functions of introns. 1. Increase opportunity fo ...
... spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biological and/or evolutionary importance. List 3 potential functions of introns. 1. Increase opportunity fo ...
Activities for Bioengineering
... reading of the mRNA when it should not. • What is the name of this type of mutation nonsense • What other types of mutation exist that may cause drastic problems to the cell? Missense ...
... reading of the mRNA when it should not. • What is the name of this type of mutation nonsense • What other types of mutation exist that may cause drastic problems to the cell? Missense ...
RNA nucleotides
... 5. tRNA will keep matching it’s anticodon with mRNA’s codon and leaving behind amino acids until it comes to one of the stop codons. (UAG, UGA, UAA) 6. Once tRNA comes to a stop codon, it will stop translating mRNA and the long chain of amino acids will break off and become a protein (polypeptide). ...
... 5. tRNA will keep matching it’s anticodon with mRNA’s codon and leaving behind amino acids until it comes to one of the stop codons. (UAG, UGA, UAA) 6. Once tRNA comes to a stop codon, it will stop translating mRNA and the long chain of amino acids will break off and become a protein (polypeptide). ...
Central dogma of molecular biology
... prokaryotic cells, which have no nuclear compartment, the process of transcription and translation may be linked together. In eukaryotic cells, the site of transcription (the cell nucleus) is usually separated from the site of translation (the cytoplasm), so the mRNA must be transported out of the n ...
... prokaryotic cells, which have no nuclear compartment, the process of transcription and translation may be linked together. In eukaryotic cells, the site of transcription (the cell nucleus) is usually separated from the site of translation (the cytoplasm), so the mRNA must be transported out of the n ...
Protein Synthesis (B7)
... – tRNA anticodon (with specific aa) matches up with the mRNA codon – Each tRNA leaves to find another aa as mRNA over one codon & another tRNA brings the next aa ...
... – tRNA anticodon (with specific aa) matches up with the mRNA codon – Each tRNA leaves to find another aa as mRNA over one codon & another tRNA brings the next aa ...
Chapter 2 - Regulation of protein activities
... which down-stream effector molecules they stimulate. For example, Gα5 stimulates adenylyl cyclase and Gα1 inhibits it. The G-protein subunits interact with adenylyl cyclase, phosphodiesterase, phospholipases, ion channels and other proteins. Thus, the same hormone may elicit different responses in d ...
... which down-stream effector molecules they stimulate. For example, Gα5 stimulates adenylyl cyclase and Gα1 inhibits it. The G-protein subunits interact with adenylyl cyclase, phosphodiesterase, phospholipases, ion channels and other proteins. Thus, the same hormone may elicit different responses in d ...
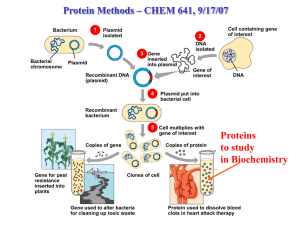
Principles of genetic engineering
... What is genetic engineering • Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: inserting a foreign gene from one sp ...
... What is genetic engineering • Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: inserting a foreign gene from one sp ...
paper - ap pgecet
... recognition sites respectively. The ratios of the number of fragments that will generate on restriction digestion of a genomic DNA of E. coli are approximately (A) 1 : 64 : 16 (B) 16 : 256 : 6 (C) 16 : 256 : 1 (D) 256 : 16 : 1 ...
... recognition sites respectively. The ratios of the number of fragments that will generate on restriction digestion of a genomic DNA of E. coli are approximately (A) 1 : 64 : 16 (B) 16 : 256 : 6 (C) 16 : 256 : 1 (D) 256 : 16 : 1 ...
Answers-to-examination-in-Gene-technology_20121020
... Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of the gene. If the gene product is toxic and harmfu ...
... Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of the gene. If the gene product is toxic and harmfu ...
Protein Synthesis
... Click on the picture to watch a video of the process. Look though all the pictures and write down any questions you have for lecture. ...
... Click on the picture to watch a video of the process. Look though all the pictures and write down any questions you have for lecture. ...