Introduction to genome biology
... • Genes comprise only about 2% of the human genome; the rest consists of non-coding regions, whose functions may include providing chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (tr ...
... • Genes comprise only about 2% of the human genome; the rest consists of non-coding regions, whose functions may include providing chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (tr ...
Honors Biology Unit 6 Ch. 10 “DNA, RNA & Protein synthesis”
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
U - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... • 3.2 million DNA base pairs • 1.5% encode proteins < = > 98.5% not protein encoding ...
... • 3.2 million DNA base pairs • 1.5% encode proteins < = > 98.5% not protein encoding ...
Crash Course in Biochemistry
... What if shape different? RuBP won’t bind, No reaction. Some mutations change critical active site residues. Genetic Mutations and Disease: sickle cell, PKU ...
... What if shape different? RuBP won’t bind, No reaction. Some mutations change critical active site residues. Genetic Mutations and Disease: sickle cell, PKU ...
Unfolded Protein Response (UPR)
... Looking for transcription factors which bind to BiP promoter Nucleotide sequence of the 2140 to 219 region of the human GRP78 promoter. ...
... Looking for transcription factors which bind to BiP promoter Nucleotide sequence of the 2140 to 219 region of the human GRP78 promoter. ...
DNA
... Before the mRNA can go to the ribosome, it needs to be spliced. – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...
... Before the mRNA can go to the ribosome, it needs to be spliced. – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...
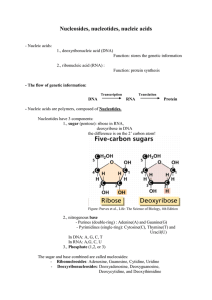
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... The two complementary strands run antiparalel (the 5’-3’ ends are opposite), they form a double helix. Figure: The DNA double helix. ...
... The two complementary strands run antiparalel (the 5’-3’ ends are opposite), they form a double helix. Figure: The DNA double helix. ...
3D Ribbon-like Model
... Francis Crick and Sydney Brenner determined how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for ...
... Francis Crick and Sydney Brenner determined how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for ...
operons operons operons
... • REPRESSABLE OPERONS Usually ON/repressor usually ACTIVE Can be turned off (repressed) Genes for enzymes that make product always needed EX: trp operon makes enzymes used in essential amino acid synthesis ...
... • REPRESSABLE OPERONS Usually ON/repressor usually ACTIVE Can be turned off (repressed) Genes for enzymes that make product always needed EX: trp operon makes enzymes used in essential amino acid synthesis ...
Derived copy of Bis2A 14.1 Bacterial Gene
... the RNA polymerase from binding, and transcribing the downstream genes. It should be noted that the term "operator" is limited to just a few systems and almost always refers to the binding site for a repressor. Conceptually what you need to remember is that there are sites on the DNA that interact w ...
... the RNA polymerase from binding, and transcribing the downstream genes. It should be noted that the term "operator" is limited to just a few systems and almost always refers to the binding site for a repressor. Conceptually what you need to remember is that there are sites on the DNA that interact w ...
1 - contentextra
... 13 Proteins may be fibrous or globular, polar or non-polar. 14 Enzymes are quite specific and work in a way explained by the induced-fit model. This model states the need for a close fit between an enzyme’s active site and the substrate. Once the active site and substrate are together, a conformatio ...
... 13 Proteins may be fibrous or globular, polar or non-polar. 14 Enzymes are quite specific and work in a way explained by the induced-fit model. This model states the need for a close fit between an enzyme’s active site and the substrate. Once the active site and substrate are together, a conformatio ...
Chapter 13.1 and 13.2 RNA, Ribosomes, and Protein Synthesis
... • 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – cell structures where proteins are assembled • 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries amino acids to ribosome and matches them to the mRNA message. ...
... • 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – cell structures where proteins are assembled • 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries amino acids to ribosome and matches them to the mRNA message. ...
File
... 1) Genes in prokaryotes that are arranged in groups of related genes under the control of a single promoter are called ______. a) Opersons. b) Decathlons. c) Klingons. d) Genons (referred to as genoffs when in the inactive configuration). ...
... 1) Genes in prokaryotes that are arranged in groups of related genes under the control of a single promoter are called ______. a) Opersons. b) Decathlons. c) Klingons. d) Genons (referred to as genoffs when in the inactive configuration). ...
PPT# 4 Notes: Mutations and Regulation ... Date______________Per._______
... radiation A, B, and C (better known as Uvr A,B, C) work together with adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In this process, the UVr ABC proteins attach to the ends of DNA molecules and move along the strand like a zipper. As the proteins advance, they unwind the coiled DNA one section at a time. Once a sec ...
... radiation A, B, and C (better known as Uvr A,B, C) work together with adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In this process, the UVr ABC proteins attach to the ends of DNA molecules and move along the strand like a zipper. As the proteins advance, they unwind the coiled DNA one section at a time. Once a sec ...
Stress and Brain Development
... For each hormone, a specific receptor exists within the cell. It is important to note one fundamental difference, however, between the steroid hormones and the other signaling molecules. The receptors for growth factors and neurotransmitters lie on the outer surface of the cell and directly bind the ...
... For each hormone, a specific receptor exists within the cell. It is important to note one fundamental difference, however, between the steroid hormones and the other signaling molecules. The receptors for growth factors and neurotransmitters lie on the outer surface of the cell and directly bind the ...
Unit 2 DNA Outline - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... An operon is a cluster of genes usually coding for proteins related to a particular metabolic pathway, along with the short DNA sequences that control their transcription. The parts of an operon include a repressor and a regulator gene as well as the structural genes. Gene Expression in Eukaryotes S ...
... An operon is a cluster of genes usually coding for proteins related to a particular metabolic pathway, along with the short DNA sequences that control their transcription. The parts of an operon include a repressor and a regulator gene as well as the structural genes. Gene Expression in Eukaryotes S ...
Bioinformatics and Personal Health/Intro computer lab
... transcription factors, inactivating them. When GA is present the DELLA domain binds the protein GID1. This binding causes the DELLA protein to be tagged for degradation (using ubiquitination). With DELLA proteins degraded the transcription factors are able to bind promoters and turn on gene expressi ...
... transcription factors, inactivating them. When GA is present the DELLA domain binds the protein GID1. This binding causes the DELLA protein to be tagged for degradation (using ubiquitination). With DELLA proteins degraded the transcription factors are able to bind promoters and turn on gene expressi ...
File
... Transcription Factors • Interact and form an apparatus that binds DNA at certain sequences • Initiates transcription at specific sites on chromosomes • Respond to signals from outside the cell • Link the genome to the environment • Mutations in transcription factors may cause a wide range of effect ...
... Transcription Factors • Interact and form an apparatus that binds DNA at certain sequences • Initiates transcription at specific sites on chromosomes • Respond to signals from outside the cell • Link the genome to the environment • Mutations in transcription factors may cause a wide range of effect ...
Science and Society: Unit 2 Review Packet Directions: Use your
... 15. What information can be gained from running DNA gel electrophoresis? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 15. What information can be gained from running DNA gel electrophoresis? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Protein Synthesis - MsJacksonsBiologyWiki
... 1. mRNA moves to the cytoplasm and binds with ribosome 2. tRNA brings the anticodon to bind with the Codon 3. Ribosome moves down to mRNA to next codon 4. tRNA anticodon brings & attached next AA with ...
... 1. mRNA moves to the cytoplasm and binds with ribosome 2. tRNA brings the anticodon to bind with the Codon 3. Ribosome moves down to mRNA to next codon 4. tRNA anticodon brings & attached next AA with ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... nucleotides back together. The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed ...
... nucleotides back together. The DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed ...