Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle
... siRNAs dependent pathways can act either in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus ie, PTGS (post transcriptional gene silencing) mediated by RISC (RNAi induced silencing complex) and TGS (transcriptional gene silencing) mediated by RITS (RNAi induced transcriptional silencing complex) siRNAs induce tran ...
... siRNAs dependent pathways can act either in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus ie, PTGS (post transcriptional gene silencing) mediated by RISC (RNAi induced silencing complex) and TGS (transcriptional gene silencing) mediated by RITS (RNAi induced transcriptional silencing complex) siRNAs induce tran ...
vertebrate genome evolution and function illuminated by chicken
... • Most do not code for protein – Only 111 out of 481overlap with protein-coding exons – Some are developmental enhancers. – Nonexonic UCEs tend to cluster in introns or in vicinity of genes encoding transcription factors regulating development – 88 are more than 100 kb away from an annotated gene; m ...
... • Most do not code for protein – Only 111 out of 481overlap with protein-coding exons – Some are developmental enhancers. – Nonexonic UCEs tend to cluster in introns or in vicinity of genes encoding transcription factors regulating development – 88 are more than 100 kb away from an annotated gene; m ...
Chapt 11
... Prokaryotes and eukaryotes employ regulatory proteins (activators and repressors) that – bind to specific segments of DNA and – either promote or block the binding of RNA polymerase, turning the transcription of genes on and off. ...
... Prokaryotes and eukaryotes employ regulatory proteins (activators and repressors) that – bind to specific segments of DNA and – either promote or block the binding of RNA polymerase, turning the transcription of genes on and off. ...
Genes - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... •Genes that encode proteins are transcribed and the transcript is processed to make mRNA. •Next the base sequence in the mRNA must be translated into amino acid sequences in a polypeptide. •Once polypeptides are formed, they fold up and combine with other molecules, but this is the realm of biochemi ...
... •Genes that encode proteins are transcribed and the transcript is processed to make mRNA. •Next the base sequence in the mRNA must be translated into amino acid sequences in a polypeptide. •Once polypeptides are formed, they fold up and combine with other molecules, but this is the realm of biochemi ...
Slajd 1
... - usually tri-nucleotide (AWG in E. coli) recognized by the Cascade complex (CasA in E. coli) - probably allows tolerance to self (prevents autoimmunity against spacer DNA sequences complementary to crRNAs they encode) Jiang and Marraffini, AnnuRevMicro, 2016 ...
... - usually tri-nucleotide (AWG in E. coli) recognized by the Cascade complex (CasA in E. coli) - probably allows tolerance to self (prevents autoimmunity against spacer DNA sequences complementary to crRNAs they encode) Jiang and Marraffini, AnnuRevMicro, 2016 ...
En/Spm-Mu
... cis Determinants for Excision: Approx. 180 bp at the 5’ end and 300 bp of 3’ end represent cis determinants. Contained in these regions are reiterations of a 12-bp sequence motif that is recognized by TNPA protein with 6 motifs present at 5’ end and 8 at 3’ end. Trans-factors: TNPA and TNPD (transpo ...
... cis Determinants for Excision: Approx. 180 bp at the 5’ end and 300 bp of 3’ end represent cis determinants. Contained in these regions are reiterations of a 12-bp sequence motif that is recognized by TNPA protein with 6 motifs present at 5’ end and 8 at 3’ end. Trans-factors: TNPA and TNPD (transpo ...
medical genetics what is medical genetics?
... DNA polymerase is one of the key replication enzymes. It travels along the single DNA strand, adding free nucleotides to the 3' end of the new strand.( 3' and 5' referred to no. of the carbon atom in the pentose sugar to which the base is attached). Nucleotides can be added only to this end of the s ...
... DNA polymerase is one of the key replication enzymes. It travels along the single DNA strand, adding free nucleotides to the 3' end of the new strand.( 3' and 5' referred to no. of the carbon atom in the pentose sugar to which the base is attached). Nucleotides can be added only to this end of the s ...
Gen660_Lecture12B_NetworkEvo_2014
... Mcm1 is a co-factor that works with many different site-specific TFs Tuch. et al. performed ChIP-chip on Mcm1 orthologs in multiple fungi. * Found dramatic differences in inferred Mcm1-TF interactions and modules ...
... Mcm1 is a co-factor that works with many different site-specific TFs Tuch. et al. performed ChIP-chip on Mcm1 orthologs in multiple fungi. * Found dramatic differences in inferred Mcm1-TF interactions and modules ...
File
... 1. Redundant: several codons may code for the same amino acid Ex. 3 codons are stop signals ...
... 1. Redundant: several codons may code for the same amino acid Ex. 3 codons are stop signals ...
DNA vs. RNA - Houston ISD
... The “language” of mRNA instructions is called the genetic code (from DNA) RNA contains four different bases: A, U, C, and G Letters read “3” at a time = codon Codon = a group of three nucleotides on messenger RNA that specify a particular amino acid. ...
... The “language” of mRNA instructions is called the genetic code (from DNA) RNA contains four different bases: A, U, C, and G Letters read “3” at a time = codon Codon = a group of three nucleotides on messenger RNA that specify a particular amino acid. ...
Protein Synthesis DNA vs. RNA
... The “language” of mRNA instructions is called the genetic code (from DNA) RNA contains four different bases: A, U, C, and G Letters read “3” at a time = codon Codon = a group of three nucleotides on messenger RNA that specify a particular amino acid. ...
... The “language” of mRNA instructions is called the genetic code (from DNA) RNA contains four different bases: A, U, C, and G Letters read “3” at a time = codon Codon = a group of three nucleotides on messenger RNA that specify a particular amino acid. ...
Chapter 20
... What would you look for if you wanted to find an unknown protein coding gene? Scientists use computers to search for short coding sequences similar to those present in known genes. these are called “express service tags” ...
... What would you look for if you wanted to find an unknown protein coding gene? Scientists use computers to search for short coding sequences similar to those present in known genes. these are called “express service tags” ...
The QIAexpressionist™
... • Synthetic bacterial ribosomal binding site for high translation rates. • Strong, constitutive CAG promoter that mediates transient mammalian expression. It consists of the chicken β-actin promoter with the CMV immediate-early enhancer upstream, and a splicing acceptor site of the β-globin gene dow ...
... • Synthetic bacterial ribosomal binding site for high translation rates. • Strong, constitutive CAG promoter that mediates transient mammalian expression. It consists of the chicken β-actin promoter with the CMV immediate-early enhancer upstream, and a splicing acceptor site of the β-globin gene dow ...
Study suggests common mechanism activating
... Identification of focally amplified lineage-specific super-enhancers in human epithelial cancers, Nature Genetics (2015). DOI: 10.1038/ng.3470 ...
... Identification of focally amplified lineage-specific super-enhancers in human epithelial cancers, Nature Genetics (2015). DOI: 10.1038/ng.3470 ...
ucla1 - WEHI Bioinformatics
... The information content of various species in terms of the number of nucleotides in the genome. The complete genome sequences were determined in the years as designated. The increase of the GenBank nucleotide sequence database is also shown together with the release dates. (Bit s) ...
... The information content of various species in terms of the number of nucleotides in the genome. The complete genome sequences were determined in the years as designated. The increase of the GenBank nucleotide sequence database is also shown together with the release dates. (Bit s) ...
Ch. 5A: Transforming Bacteria with Recombinant Plasmids
... If transformed with the pARA-R plasmid bacteria can be identified Ampicillin will prevent the growth of cells that do not carry an ampicillin resistance gene Arabinose will activate the bacteria promoter that controls expression of the rfp gene. ...
... If transformed with the pARA-R plasmid bacteria can be identified Ampicillin will prevent the growth of cells that do not carry an ampicillin resistance gene Arabinose will activate the bacteria promoter that controls expression of the rfp gene. ...
Slide 1
... If transformed with the pARA-R plasmid bacteria can be identified Ampicillin will prevent the growth of cells that do not carry an ampicillin resistance gene Arabinose will activate the bacteria promoter that controls expression of the rfp gene. ...
... If transformed with the pARA-R plasmid bacteria can be identified Ampicillin will prevent the growth of cells that do not carry an ampicillin resistance gene Arabinose will activate the bacteria promoter that controls expression of the rfp gene. ...
5echap12guidedreading
... 3. How does the rapid reproduction of bacteria make them a good choice for cloning a foreign gene? ...
... 3. How does the rapid reproduction of bacteria make them a good choice for cloning a foreign gene? ...
Techniques
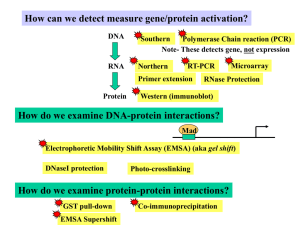
... If use anti-phosphoERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe only ____________________ If use anti-ERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe ___________________ ...
... If use anti-phosphoERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe only ____________________ If use anti-ERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe ___________________ ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription
... 3. Where in the cell does the process of transcription occur? 4. What enzyme completes the process of transcription? 5. What molecule is produced from transcription? 6. Where does this molecule go after it is made? ...
... 3. Where in the cell does the process of transcription occur? 4. What enzyme completes the process of transcription? 5. What molecule is produced from transcription? 6. Where does this molecule go after it is made? ...
Chapter 7 Review
... to change (wobble) while allowing the codon to still code for a particular amino acid. 71. (a) The three stop codons tRNA sequences do not code for any amino acid. (b) Answers may vary. Sample answer: To determine their function you could perform an experiment that places the stop codon immediately ...
... to change (wobble) while allowing the codon to still code for a particular amino acid. 71. (a) The three stop codons tRNA sequences do not code for any amino acid. (b) Answers may vary. Sample answer: To determine their function you could perform an experiment that places the stop codon immediately ...
universitetet i oslo
... can be assigned by homology searching can be probed by directed mutagenesis can be deduced from their location in genomes can be found by exon trapping are known for most genes in sequenced genomes 9. Telomers are located at the ends of ribosomal RNA in centromers in the middle of chromosomes at the ...
... can be assigned by homology searching can be probed by directed mutagenesis can be deduced from their location in genomes can be found by exon trapping are known for most genes in sequenced genomes 9. Telomers are located at the ends of ribosomal RNA in centromers in the middle of chromosomes at the ...