Protein Synthesis
... The sequence of bases in an mRNA molecule serves as instructions for the order in which amino acids are joined to produce a polypeptide Ribosomes decode the instructions by using codons, sets of 3 bases that each code for 1 amino acid Each codon is matched to an anticodon, or complementary sequence ...
... The sequence of bases in an mRNA molecule serves as instructions for the order in which amino acids are joined to produce a polypeptide Ribosomes decode the instructions by using codons, sets of 3 bases that each code for 1 amino acid Each codon is matched to an anticodon, or complementary sequence ...
dna ppt ques – ANSWERS2
... 2. The mRNA then leaves the ___NUCLEUS_________ and attaches itself to a __RIBOSOME_______________ and passes on the ___MESSAGE__________. 3. The tRNA then attaches to ___MRNA_______ and hooks up the ____AMINO ACIDS___ in the right order. Then it goes back to pick up some __MORE________(like a _TAX ...
... 2. The mRNA then leaves the ___NUCLEUS_________ and attaches itself to a __RIBOSOME_______________ and passes on the ___MESSAGE__________. 3. The tRNA then attaches to ___MRNA_______ and hooks up the ____AMINO ACIDS___ in the right order. Then it goes back to pick up some __MORE________(like a _TAX ...
Science Notebook DNA, RNA, and Protein
... one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed from the final mRNA process by which mRNA directs the synthesis of a protein long strands of RNA that are com ...
... one amino acid nucleic acid made of ribose, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil intervening DNA sequences that are transcribed and then removed from the final mRNA process by which mRNA directs the synthesis of a protein long strands of RNA that are com ...
Ch_17 From Gene to Protein
... RNA polymerase unwinds DNA ~20 base pairs at a time reads DNA 3’5’ builds RNA 5’3’ (the energy governs the synthesis!) ...
... RNA polymerase unwinds DNA ~20 base pairs at a time reads DNA 3’5’ builds RNA 5’3’ (the energy governs the synthesis!) ...
PDF
... common developmental stages. Subtle differences in these stages generate numerous leaf shapes, from simple leaves with undivided blades (e.g. Arabidopsis) to compound leaves, which consist of several subunits called leaflets (e.g. tomato). Now, Naomi Ori and co-workers report that the transcription ...
... common developmental stages. Subtle differences in these stages generate numerous leaf shapes, from simple leaves with undivided blades (e.g. Arabidopsis) to compound leaves, which consist of several subunits called leaflets (e.g. tomato). Now, Naomi Ori and co-workers report that the transcription ...
Study Guide for Understanding the Concept of Protein Synthesis
... DNA contains the genetic material and serves as the blueprint for protein synthesis. The doublestranded DNA "unzips" -- leaving the second strand as a pattern (template) of instruction for RNA. [Think of a "zipper". Zipped, the zipper has the appearance of one (1) strand. When unzipped, it is obviou ...
... DNA contains the genetic material and serves as the blueprint for protein synthesis. The doublestranded DNA "unzips" -- leaving the second strand as a pattern (template) of instruction for RNA. [Think of a "zipper". Zipped, the zipper has the appearance of one (1) strand. When unzipped, it is obviou ...
Method of localizing, either mRNA within the cytoplasm or DNA
... triethanolamine (neutralization of positive charges) • HCl (protein extraction and denaturation of target sequence) ...
... triethanolamine (neutralization of positive charges) • HCl (protein extraction and denaturation of target sequence) ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Transcription initiation was assumed to end as RNA polymerase formed 1st phosphodiester bond • Carpousis and Gralla found that very small oligonucleotides (2-6 nt long) are made without RNA polymerase leaving the DNA • Abortive transcripts such as these have been found up to 10 nt ...
... • Transcription initiation was assumed to end as RNA polymerase formed 1st phosphodiester bond • Carpousis and Gralla found that very small oligonucleotides (2-6 nt long) are made without RNA polymerase leaving the DNA • Abortive transcripts such as these have been found up to 10 nt ...
DNA & RNA - East Pennsboro High School
... Assembly of amino acids at the ribosome to produce a protein Initiation – joining of mRNA, tRNA & ribosome ...
... Assembly of amino acids at the ribosome to produce a protein Initiation – joining of mRNA, tRNA & ribosome ...
Slide 1
... Evolution connection: Transcription and translation Chi, Y., Martick, M., Lares, M., Kim, R., Scott, W. G., and Kim, S. (2008). Capturing hammerhead ribozyme structures in action by modulating general base catalysis. PLoS biology. 6: e234. Lincoln, T. A., and Joyce, G. F. (2009). Self-sustained rep ...
... Evolution connection: Transcription and translation Chi, Y., Martick, M., Lares, M., Kim, R., Scott, W. G., and Kim, S. (2008). Capturing hammerhead ribozyme structures in action by modulating general base catalysis. PLoS biology. 6: e234. Lincoln, T. A., and Joyce, G. F. (2009). Self-sustained rep ...
TNA: Transcription and Triplet Code
... written as -75 - -110) is called the GC box. • This is observed only every now and again, i.e., this is rare. • Between -40 and -75 is a region of four nucleotides, CAAT, called the cat box. This is observed a bit more frequently than the GC box. ...
... written as -75 - -110) is called the GC box. • This is observed only every now and again, i.e., this is rare. • Between -40 and -75 is a region of four nucleotides, CAAT, called the cat box. This is observed a bit more frequently than the GC box. ...
Reliable transfer of transcriptional gene regulatory networks
... the prediction quality is limited by the low level of evolutionary conservation of the transcription factor binding sites, even within organisms of the same genus. Results: Here we present an integrated bioinformatics workflow that assures the reliability of transferred gene regulatory networks. Our ...
... the prediction quality is limited by the low level of evolutionary conservation of the transcription factor binding sites, even within organisms of the same genus. Results: Here we present an integrated bioinformatics workflow that assures the reliability of transferred gene regulatory networks. Our ...
Vocabulary List
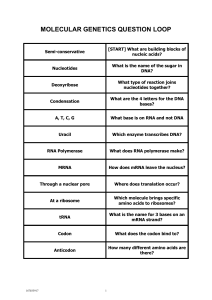
... 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the process of making another copy of the genetic code by a semi-conservative process. Occurs within the nucleus 7. DNA Polymerase – enzyme that links DNA nucleotides together during ...
... 5. Nitrogenous Bases – the parts of DNA and RNA that pair (A,T,C,G for DNA and A,U,C,G for RNA). 6. DNA Replication – the process of making another copy of the genetic code by a semi-conservative process. Occurs within the nucleus 7. DNA Polymerase – enzyme that links DNA nucleotides together during ...
DNA cr.eu updated plg latest
... • The structure of euchromatin is reminiscent of an unfolded set of beads along a string, where in those beads represent nucleosomes. • Nucleosomes consist of eight proteins known as histone with approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wound around them; in euchromatin, this wrapping is loose so that th ...
... • The structure of euchromatin is reminiscent of an unfolded set of beads along a string, where in those beads represent nucleosomes. • Nucleosomes consist of eight proteins known as histone with approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wound around them; in euchromatin, this wrapping is loose so that th ...
doc14873 - Mrothery.co.uk
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
3rd Quarter Assessment Review - Belle Vernon Area School District
... • Why? To make the template for a Protein • How? • 1. RNA Polymerase breaks HYDROGEN bonds between nitrogen bases of the DNA molecule • 2. An RNA nucleotides NOW fills in next to ONE of the exposed DNA nucleotides creating a strand of Messenger/mRNA and continues this process until it reaches a STOP ...
... • Why? To make the template for a Protein • How? • 1. RNA Polymerase breaks HYDROGEN bonds between nitrogen bases of the DNA molecule • 2. An RNA nucleotides NOW fills in next to ONE of the exposed DNA nucleotides creating a strand of Messenger/mRNA and continues this process until it reaches a STOP ...
Chapter08_Outline
... upon themselves to acquire well-defined structures – domains • Domains interact with each other and often have specialized functions • Individual domains in a protein usually have independent evolutionary origins; they come together in various combinations to create genes with novel functions via du ...
... upon themselves to acquire well-defined structures – domains • Domains interact with each other and often have specialized functions • Individual domains in a protein usually have independent evolutionary origins; they come together in various combinations to create genes with novel functions via du ...
Questions with Answers
... Name three distinct locations that a cell might deliver its proteins to and describe the mechanisms that it would use to get them there. Nucleus: NLS on finished polypeptide and importin function Cytosol: mRNA simply gets transcribed by free ribosome. All proteins that do not have a sorting signal r ...
... Name three distinct locations that a cell might deliver its proteins to and describe the mechanisms that it would use to get them there. Nucleus: NLS on finished polypeptide and importin function Cytosol: mRNA simply gets transcribed by free ribosome. All proteins that do not have a sorting signal r ...
BI0I 121 cell and tissues
... Eukaryotic transcription factors bind to A. base pairs exposed in the major groove of DNA. B. base pairs exposed in the minor groove of DNA. C. repeating ribosy]. residues in the backbone of DNA. D. DNA polymerase. E. ...
... Eukaryotic transcription factors bind to A. base pairs exposed in the major groove of DNA. B. base pairs exposed in the minor groove of DNA. C. repeating ribosy]. residues in the backbone of DNA. D. DNA polymerase. E. ...
Biology
... Has two “phases” of “Mitosis-like stages” For humans, it takes a cell with 46 chromosomes and makes cells with 23. ...
... Has two “phases” of “Mitosis-like stages” For humans, it takes a cell with 46 chromosomes and makes cells with 23. ...
Details about TIC involvement
... single molecule technologies, this time inside cells and animals. These include a mouse line in which individual mRNA molecules of an endogenous gene can be detected by fluorescence, as well as a biosensor reporting on the translational state of single mRNAs in live cells and animals. Using these te ...
... single molecule technologies, this time inside cells and animals. These include a mouse line in which individual mRNA molecules of an endogenous gene can be detected by fluorescence, as well as a biosensor reporting on the translational state of single mRNAs in live cells and animals. Using these te ...
Genome Biology and
... – co-localization with red fluorescent protein (RFP) markers to refine the subcellular localization ...
... – co-localization with red fluorescent protein (RFP) markers to refine the subcellular localization ...