(1) End labelling
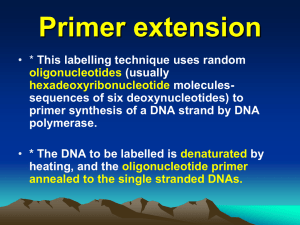
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
DNA (double helix)
... Different genes are activated in different cells, creating the specific proteins that give a particular cell type its character. http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/NIH/gene03.html ...
... Different genes are activated in different cells, creating the specific proteins that give a particular cell type its character. http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/NIH/gene03.html ...
Lect13_HistonesChromatin
... • Select short fragments (two nearby cuts) to sequence • Map to active promoters and enhancers Ling et al, MCB 2010 ...
... • Select short fragments (two nearby cuts) to sequence • Map to active promoters and enhancers Ling et al, MCB 2010 ...
Poster Specifications - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... – Work on gene of own choice or choose from list of suggested genes – Prepare results as • Powerpoint presentation (ca. 6-10 slides) • Poster (A0 or 6-10 slides) • Written 2 page summary of project ...
... – Work on gene of own choice or choose from list of suggested genes – Prepare results as • Powerpoint presentation (ca. 6-10 slides) • Poster (A0 or 6-10 slides) • Written 2 page summary of project ...
Genome Instability and Repair
... they often inactivated (Federoff lab). The cloned DNA was used to isolate the gene from mutant lines. This process is also called "Transposon trapping“. ...
... they often inactivated (Federoff lab). The cloned DNA was used to isolate the gene from mutant lines. This process is also called "Transposon trapping“. ...
Which diagram most correctly represents the process of mitosis
... was generated in the cell membrane of a cell and now carries its transcript of the DNA code - moves to the cytoplasm, where it attaches temporarily to tiny structures called mitochondria. There, molecules of mRNA direct the assembly of small molecules called amino acids (of which 20 kinds exist) int ...
... was generated in the cell membrane of a cell and now carries its transcript of the DNA code - moves to the cytoplasm, where it attaches temporarily to tiny structures called mitochondria. There, molecules of mRNA direct the assembly of small molecules called amino acids (of which 20 kinds exist) int ...
notes 12B
... 3. The amino acid binds to the 3’ end; the opposite end of the molecule contains an _______________ that binds to the mRNA codon in a _______________ fashion. 4. There is at least one _______________ molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer _______________ than c ...
... 3. The amino acid binds to the 3’ end; the opposite end of the molecule contains an _______________ that binds to the mRNA codon in a _______________ fashion. 4. There is at least one _______________ molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer _______________ than c ...
From DNA to Proteins
... – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the blueprint for protein assembly to the ribosome. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) combines with proteins to form ribosomes upon which polypeptides are assembled. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome. ...
... – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the blueprint for protein assembly to the ribosome. – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) combines with proteins to form ribosomes upon which polypeptides are assembled. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome. ...
DNA Structure
... joining individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule. Each strand serves as a template for another one. 3. What enzymes are involved in DNA replication and what reactions do they catalyze? DNA polymerase joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule (a polymer). It also proofreads each ...
... joining individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule. Each strand serves as a template for another one. 3. What enzymes are involved in DNA replication and what reactions do they catalyze? DNA polymerase joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule (a polymer). It also proofreads each ...
MCDB 1030 – Spring 2003
... triglyceride. (In a phospholipid, a phosphate group takes the place of one of the fatty acid tails of a triglyceride.) c) Why do phospholipids form bilayers? Phospholipids have polar and non-polar regions (they are amphipathic). In water they form bilayers so that the tails can associate with each o ...
... triglyceride. (In a phospholipid, a phosphate group takes the place of one of the fatty acid tails of a triglyceride.) c) Why do phospholipids form bilayers? Phospholipids have polar and non-polar regions (they are amphipathic). In water they form bilayers so that the tails can associate with each o ...
Differences between DNA and RNA • Ribonucleic acid is similar to
... The Three Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries DNA-encoded information into the cytosol, where it can be translated into proteins o Remember, the DNA can’t leave the nucleus, so it needs a messenger (mRNA) to deliver the code to the cytosol • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – combine with certain prot ...
... The Three Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries DNA-encoded information into the cytosol, where it can be translated into proteins o Remember, the DNA can’t leave the nucleus, so it needs a messenger (mRNA) to deliver the code to the cytosol • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – combine with certain prot ...
History—One gene, one polypeptide hypothesis The Overall
... RNA polymerase is the kind of enzyme that joins ribonucleotides to make all the kinds of RNA. RNA polymerase finds the promoter region of a gene with help from transcription factor polypeptides which in turn are signaled by the cell to recognize particular genes. RNA polymerase binds to the DNA doub ...
... RNA polymerase is the kind of enzyme that joins ribonucleotides to make all the kinds of RNA. RNA polymerase finds the promoter region of a gene with help from transcription factor polypeptides which in turn are signaled by the cell to recognize particular genes. RNA polymerase binds to the DNA doub ...
Name
... o Know the scientists involved with Evolution and their contribution to the theory of Evolution. P292-298 o What 5 pieces of evidence suggests occurrences of evolution in organisms? 299304 o Early idea of age of Earth & what life was like here p295 o Darwin’s theory of evolution: Descent with Modifi ...
... o Know the scientists involved with Evolution and their contribution to the theory of Evolution. P292-298 o What 5 pieces of evidence suggests occurrences of evolution in organisms? 299304 o Early idea of age of Earth & what life was like here p295 o Darwin’s theory of evolution: Descent with Modifi ...
DNA
... related metabolic functions is organized as a unit - Operon – Promoter (sequence), operator (sequence) and structural genes ( sequence) are called an operon. • The promoter and operator are sites that control structural gene transcription. • Structural genes are expressed as a single messenger RNA. ...
... related metabolic functions is organized as a unit - Operon – Promoter (sequence), operator (sequence) and structural genes ( sequence) are called an operon. • The promoter and operator are sites that control structural gene transcription. • Structural genes are expressed as a single messenger RNA. ...
ara Operon
... • Study of biological processes (example: synthesis of proteins) • Localization and regulation of gene expression • Cell movement • Cell fate during development ...
... • Study of biological processes (example: synthesis of proteins) • Localization and regulation of gene expression • Cell movement • Cell fate during development ...
1 BIOS 1300 SI SI WORKSHEET 8 (Chapter 3 Cont.) SI Leader
... growing mRNA chain 3. Termination - In prokaryotes, transcription ends once a ___________________ sequence is transcribed - In eukaryotes, transcription ends 10-35 nucleotides after a _________________________________ is transcribed II. RNA processing: modifications to an mRNA transcript that occur ...
... growing mRNA chain 3. Termination - In prokaryotes, transcription ends once a ___________________ sequence is transcribed - In eukaryotes, transcription ends 10-35 nucleotides after a _________________________________ is transcribed II. RNA processing: modifications to an mRNA transcript that occur ...
2009 Dental Biochemistry (Questions)
... What is the location of telomeric sequences found in eukaryotic chromosomes? A) At or near the centromere B) In the long arm of chromosome C) In the short arm of Chromosome D) At both ends of chromosome E) At the break point in chromosomal DNA( recombination site) Which of the following eukaryotic D ...
... What is the location of telomeric sequences found in eukaryotic chromosomes? A) At or near the centromere B) In the long arm of chromosome C) In the short arm of Chromosome D) At both ends of chromosome E) At the break point in chromosomal DNA( recombination site) Which of the following eukaryotic D ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation - ISM-Online
... discovered that some proteins are composed of more than one polypeptide subunit and that each subunit is coded for by its own specific gene. Hemoglobin is an example because it’s composed of two pairs of subunits and is coded for by two genes. ...
... discovered that some proteins are composed of more than one polypeptide subunit and that each subunit is coded for by its own specific gene. Hemoglobin is an example because it’s composed of two pairs of subunits and is coded for by two genes. ...
Chapter 10.1
... mRNA “start” codon AUG, signals beginning of protein chain, is oriented in ribosome in the P ...
... mRNA “start” codon AUG, signals beginning of protein chain, is oriented in ribosome in the P ...
Gene Section E2F3 (E2F transcription factor 3) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Genomic amplification of E2F3: FISH image shows HT-1376 bladder cancer cell line (DSMZ acc 397) hybridized with a BAC clone (RPMI-99F1) covering the E2F3 locus at 6p22.3. (See breakpoint diagram below for map.) Note high level genomic amplification comprising multiple tandemly repeated copies of E2F ...
... Genomic amplification of E2F3: FISH image shows HT-1376 bladder cancer cell line (DSMZ acc 397) hybridized with a BAC clone (RPMI-99F1) covering the E2F3 locus at 6p22.3. (See breakpoint diagram below for map.) Note high level genomic amplification comprising multiple tandemly repeated copies of E2F ...
Biology Concepts at a Glance
... o Biomass Pyramid – Mass, Kg, metric tons, etc. Interactions o Competitive Exclusion – one more, one less successful at getting resources ...
... o Biomass Pyramid – Mass, Kg, metric tons, etc. Interactions o Competitive Exclusion – one more, one less successful at getting resources ...
2-14 oncogene and suppressive gene of cancer-xu liyan
... In normal tissues and organisms, such growth-stimulating proteins are regulated, so that growth is appropriately limited. ...
... In normal tissues and organisms, such growth-stimulating proteins are regulated, so that growth is appropriately limited. ...
DNA Structure and Function
... Termination: Occurs @ stop codon Release factor (enzyme) cleaves polypeptide from last tRNA which then leaves P site. Subunits dissociate. ...
... Termination: Occurs @ stop codon Release factor (enzyme) cleaves polypeptide from last tRNA which then leaves P site. Subunits dissociate. ...
RNA
... Translation • Once the DNA code has been Transcribed onto a mRNA molecule, mRNA leaves the nucleus and moves into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm the mRNA combines with the Ribosomes to make Enzymes/Proteins. The Process of reading the mRNA code and building a(n) Enzyme/Protein is called Translatio ...
... Translation • Once the DNA code has been Transcribed onto a mRNA molecule, mRNA leaves the nucleus and moves into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm the mRNA combines with the Ribosomes to make Enzymes/Proteins. The Process of reading the mRNA code and building a(n) Enzyme/Protein is called Translatio ...























