Supplementary Methods (doc 30K)
... Supplemental methods DNA Constructs and reagents The NF-кB p65 and p50 expression plasmids were used to produce full-length p65 and p50 protein. It was made by cloning PCR products into the HindIII and EcoRV sites of pFlag-CMV-2 expression vector as described before. (Hertlein E et al. 2005). The NF ...
... Supplemental methods DNA Constructs and reagents The NF-кB p65 and p50 expression plasmids were used to produce full-length p65 and p50 protein. It was made by cloning PCR products into the HindIII and EcoRV sites of pFlag-CMV-2 expression vector as described before. (Hertlein E et al. 2005). The NF ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... Question: How many electrons does carbon need to fill its outer energy level? Answer: Therefore, each carbon atom can make ____ covalent bonds with other types of atoms or additional carbons. ...
... Question: How many electrons does carbon need to fill its outer energy level? Answer: Therefore, each carbon atom can make ____ covalent bonds with other types of atoms or additional carbons. ...
Chapter 4 • Lesson 21
... The ribosome's job is to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains, which are in turn combined into proteins. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is RNA that makes up part of the structure of a ribosome and assists in translation. During translation, up to two tRNA molecules are connected to the mRNA at a time ...
... The ribosome's job is to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains, which are in turn combined into proteins. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is RNA that makes up part of the structure of a ribosome and assists in translation. During translation, up to two tRNA molecules are connected to the mRNA at a time ...
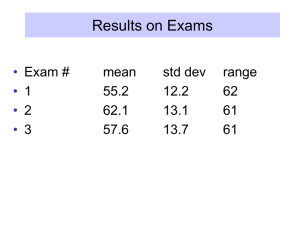
No Slide Title
... Problem 15.5 Consider a hypothetical regulatory scheme in which citrulline induces the production of urea cycle enzymes. Four genes (citA, citB, citC, citD) affecting the activity or regulation of the enzymes were analyzed by assaying the wild-type and mutant strains for argininosuccinate lyase act ...
... Problem 15.5 Consider a hypothetical regulatory scheme in which citrulline induces the production of urea cycle enzymes. Four genes (citA, citB, citC, citD) affecting the activity or regulation of the enzymes were analyzed by assaying the wild-type and mutant strains for argininosuccinate lyase act ...
Post-transcriptional gene control
... • hnRNPs prevent formation of secondary structures within pre-mRNAs • hnRNP proteins are multidomain with one or more RNA binding domains and at least one domain for interaction with other proteins • some hnRNPs contribute to pre-mRNA recognition by RNA processing enzymes • The two most common RNA b ...
... • hnRNPs prevent formation of secondary structures within pre-mRNAs • hnRNP proteins are multidomain with one or more RNA binding domains and at least one domain for interaction with other proteins • some hnRNPs contribute to pre-mRNA recognition by RNA processing enzymes • The two most common RNA b ...
nucleus
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
... suggested that genes coded for enzymes each disease (phenotype) is caused by non-functional gene product ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... Insert the most appropriate words in each of the following spaces: A section of DNA that causes the production of a protein is called a ___________________. Sections of DNA that do not code for a particular protein are called _____________________________. The protein _______________________________ ...
... Insert the most appropriate words in each of the following spaces: A section of DNA that causes the production of a protein is called a ___________________. Sections of DNA that do not code for a particular protein are called _____________________________. The protein _______________________________ ...
Biology, Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Study Guide 1. What two
... 6. Describe Watson and Crick's model of DNA structure. 7. Predict the sequence of a complementary strand of DNA. ...
... 6. Describe Watson and Crick's model of DNA structure. 7. Predict the sequence of a complementary strand of DNA. ...
The nitrogenous bases
... These genes are blueprints and need to remain safe – kept inside the nucleus Copies can be made though – a messenger ...
... These genes are blueprints and need to remain safe – kept inside the nucleus Copies can be made though – a messenger ...
Y13 Biology Y2 PLCs Student Teacher 1
... phosphorylation of glucose to glucose phosphate, using ATP production of triose phosphate oxidation of triose phosphate to pyruvate with a net gain of ATP and reduced NAD. If respiration is only anaerobic, pyruvate can be converted to ethanol or lactate using reduced NAD. The oxidised NAD prod ...
... phosphorylation of glucose to glucose phosphate, using ATP production of triose phosphate oxidation of triose phosphate to pyruvate with a net gain of ATP and reduced NAD. If respiration is only anaerobic, pyruvate can be converted to ethanol or lactate using reduced NAD. The oxidised NAD prod ...
video slide - Wild about Bio
... transcription is immediately translated without more processing In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription ...
... transcription is immediately translated without more processing In a eukaryotic cell, the nuclear envelope separates transcription ...
DNA Notesheet
... _ _ 2. L: LOCATE evidence from the text (notes) to support your answer. _ _ _ 3. A: ADD additional evidence OR your own ANALYSIS (how does your evidence support your answer?) _ _ _ _ _ 4. M: MAKE a meaningful conclusion or connection: _ _ _ _ ...
... _ _ 2. L: LOCATE evidence from the text (notes) to support your answer. _ _ _ 3. A: ADD additional evidence OR your own ANALYSIS (how does your evidence support your answer?) _ _ _ _ _ 4. M: MAKE a meaningful conclusion or connection: _ _ _ _ ...
AQA Biology - Centre of the Cell
... • the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide • a functional RNA (including ribosomal RNA and tRNAs). A gene occupies a fixed position, called a locus, on a particular DNA molecule. A sequence of three DNA bases, called a triplet, codes for a specific amino acid. The genetic code is universal, non-over ...
... • the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide • a functional RNA (including ribosomal RNA and tRNAs). A gene occupies a fixed position, called a locus, on a particular DNA molecule. A sequence of three DNA bases, called a triplet, codes for a specific amino acid. The genetic code is universal, non-over ...
Histone Modifications Associated with Heterochromatin and
... gypsy contains a su(Hw) binding site ...
... gypsy contains a su(Hw) binding site ...
DNA REVIEW SHEET (answer in COMPLETE sentences on another
... Why did S cells maintain ability to synthesize capsules while R cells could not? What does the term transformation mean in terms of DNA? Describe/diagram Avery et. al (1944) experiment. Describe and diagram the experiment performed by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase in 1952? What did this experiment ...
... Why did S cells maintain ability to synthesize capsules while R cells could not? What does the term transformation mean in terms of DNA? Describe/diagram Avery et. al (1944) experiment. Describe and diagram the experiment performed by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase in 1952? What did this experiment ...
Chapter 20 Notes: DNA Technology
... D. Medical uses; to help parents have children with specific traits E. Medical uses; to help diagnose some diseases ...
... D. Medical uses; to help parents have children with specific traits E. Medical uses; to help diagnose some diseases ...
Test your nucleic acid knowledge!
... DNA is often resuspended in molecular-grade water or _______. ...
... DNA is often resuspended in molecular-grade water or _______. ...
pGLO™ Transformation and Purification of Green Fluorescent
... Central Framework of Molecular Biology ...
... Central Framework of Molecular Biology ...
Document
... • process of converting an mRNA message into a strand of amino acids that will be processed into a mature functional protein • performed by the ribosome in combination with tRNA molecules • prokaryotes - translation of mRNA can begin before transcription has finished – no separation between the mRNA ...
... • process of converting an mRNA message into a strand of amino acids that will be processed into a mature functional protein • performed by the ribosome in combination with tRNA molecules • prokaryotes - translation of mRNA can begin before transcription has finished – no separation between the mRNA ...
DNA - hdueck
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...
... Ribonucleic Acid Types (p 288-295) There are several types. We will focus on the main 3 types: rRNA: large, makes up structure of ribosomes. - Large globular structure, forms structure with proteins to form ribosome tRNA: smaller, contains amino acid to match code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRN ...