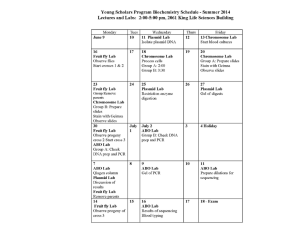
Chapter 4 Notes
... letters of the Latin alphabet put together make up different Roman numerals. VII= 7, XXX=30, III=3. • A long string of amino acids form a protein. Such as multiple letters equal a larger number. • Proteins are the messengers for many processes in the cell. ...
... letters of the Latin alphabet put together make up different Roman numerals. VII= 7, XXX=30, III=3. • A long string of amino acids form a protein. Such as multiple letters equal a larger number. • Proteins are the messengers for many processes in the cell. ...
lecture 1
... Chain of nucleotides has alternating sugar and phosphate components, called the “sugarphosphate backbone.” Nitrogenous bases stick off backbone at regular intervals. ...
... Chain of nucleotides has alternating sugar and phosphate components, called the “sugarphosphate backbone.” Nitrogenous bases stick off backbone at regular intervals. ...
Bio1A Unit 1-2 Biological Molecules Notes File
... Single stranded, uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) mRNA - messenger RNA – “work order” determines what proteins are made rRNA – component of ribosomes (haloenzyme that makes protein) tRNA – transfer RNA – brings amino acids to ribosome to make proteins ...
... Single stranded, uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) mRNA - messenger RNA – “work order” determines what proteins are made rRNA – component of ribosomes (haloenzyme that makes protein) tRNA – transfer RNA – brings amino acids to ribosome to make proteins ...
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
... 4. List the three types of RNA and explain the function of each. mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm rRNA: combines with proteins to form the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & C ...
... 4. List the three types of RNA and explain the function of each. mRNA: carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the cytoplasm rRNA: combines with proteins to form the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & C ...
Microbial Genomics
... complete microbial genomes and how this nucleotide sequence data is transformed into biological data. This is called the top down approach. ...
... complete microbial genomes and how this nucleotide sequence data is transformed into biological data. This is called the top down approach. ...
Filters Applied to ENCODE Data
... noise. Both the MCS intervals (from the binMCS95 table) and the phastConsElements have already been limited to the top 5% of the genome. The threshold for the RP scores was determined by calibration studies on a reference set of regulatory elements in the HBB complex (King et al. 2005). All DNAse I ...
... noise. Both the MCS intervals (from the binMCS95 table) and the phastConsElements have already been limited to the top 5% of the genome. The threshold for the RP scores was determined by calibration studies on a reference set of regulatory elements in the HBB complex (King et al. 2005). All DNAse I ...
How does DNA copy itself?
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
... • Only known molecule to be able to duplicate itself • Basic: unzips itself, find complementary base pairs ...
Protein synthesis: An expressive couple
... novel link between transcription and translation in eukaryotes. mRNAs shuttle between polysomes (sites of active translation) and processing bodies (PBs), the latter being complexes in which non-translating mRNAs accumulate and may be degraded. It is increasingly evident that translation and mRNA de ...
... novel link between transcription and translation in eukaryotes. mRNAs shuttle between polysomes (sites of active translation) and processing bodies (PBs), the latter being complexes in which non-translating mRNAs accumulate and may be degraded. It is increasingly evident that translation and mRNA de ...
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
... rRNA: forms the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, what is the corresponding sequence in a strand of mRNA? What tRNA sequence would pair up t ...
... rRNA: forms the ribosome tRNA: carries amino acids to the ribosome so that proteins can be made 5. Who discovered the structure of DNA? Watson & Crick 6. IF a sequence of codons on a DNA strand is AAC TAG GGT, what is the corresponding sequence in a strand of mRNA? What tRNA sequence would pair up t ...
lecture 03b
... closely related. • Bacteria attach by means of a sex pilus, hold each other close, and DNA is transferred. • Plasmids other than F plasmids, such as resistance plasmids, can also be exchanged, leading to antibioticresistant bacteria. ...
... closely related. • Bacteria attach by means of a sex pilus, hold each other close, and DNA is transferred. • Plasmids other than F plasmids, such as resistance plasmids, can also be exchanged, leading to antibioticresistant bacteria. ...
NUCLEOTIDES AND NUCLEIC ACIDS 2
... • c. they bear genes and act as a functional unit of heredity. • d. they are capable of reproducing its physical and chemical structure through successive cell division. ...
... • c. they bear genes and act as a functional unit of heredity. • d. they are capable of reproducing its physical and chemical structure through successive cell division. ...
Biology II – Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
... Occurs at many points on the molecule – all happening at the same time Reduces the copying time dramatically o The cell where replication occurs has a built-in “proofreader” – allows for very little error in copying – approximately one error per billion nucleotides occurs o DNA also has the abil ...
... Occurs at many points on the molecule – all happening at the same time Reduces the copying time dramatically o The cell where replication occurs has a built-in “proofreader” – allows for very little error in copying – approximately one error per billion nucleotides occurs o DNA also has the abil ...
An Overview of Protein Synthesis
... Types of RNA: 1) mRNA = messenger RNA – carries the code for the protein to the ribosome. Made from the DNA template. 2) tRNA = transfer RNA – transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome for polypeptide synthesis. 3) rRNA = ribosomal RNA – structural component of ribosomes. Provides the ...
... Types of RNA: 1) mRNA = messenger RNA – carries the code for the protein to the ribosome. Made from the DNA template. 2) tRNA = transfer RNA – transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome for polypeptide synthesis. 3) rRNA = ribosomal RNA – structural component of ribosomes. Provides the ...
Ch 5
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
Section L Regulation of Transcription in Prokaryotes
... More then 17 heat-shock proteins are expressed in E.coli through transcription by RNApol using an alternative s32 , which have own specific promoter consensus sequence ...
... More then 17 heat-shock proteins are expressed in E.coli through transcription by RNApol using an alternative s32 , which have own specific promoter consensus sequence ...
BiochemReview
... • The 5’ end of the intron to be removed is called the splice donor. 3’ end is the splice acceptor. • 1) 5’ end of the intron is cleaved. • 2) This is stuck onto an A residue about 20 bp in front of acceptor site. This makes a strange 5’-2’ bond. This is called the lariat. • 3) 3’ end of intron clea ...
... • The 5’ end of the intron to be removed is called the splice donor. 3’ end is the splice acceptor. • 1) 5’ end of the intron is cleaved. • 2) This is stuck onto an A residue about 20 bp in front of acceptor site. This makes a strange 5’-2’ bond. This is called the lariat. • 3) 3’ end of intron clea ...
Molecules to Eye Color - Springfield School District
... 2 identical strands of DNA An enzyme called DNA polymerase “unzips” the two strands by breaking the H-bonds. Nucleotides with complimentary bases are attached to the exposed strands ...
... 2 identical strands of DNA An enzyme called DNA polymerase “unzips” the two strands by breaking the H-bonds. Nucleotides with complimentary bases are attached to the exposed strands ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Webquest
... Step 3: What molecules are involved in protein synthesis? Use an internet search engine to help you answer these: 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the poly ...
... Step 3: What molecules are involved in protein synthesis? Use an internet search engine to help you answer these: 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the poly ...
DNA Structure, Replication and Protein Synthesis
... Insert the most appropriate words in each of the following spaces: A section of DNA that causes the production of a protein is called a ___________________. Sections of DNA that do not code for a particular protein are called _____________________________. The protein ____________________________ ...
... Insert the most appropriate words in each of the following spaces: A section of DNA that causes the production of a protein is called a ___________________. Sections of DNA that do not code for a particular protein are called _____________________________. The protein ____________________________ ...
Biology - Raleigh Charter High School
... nucleosome. The nucleosome bead is DNA wound around a protein core made of two of these histones: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H1, another histone attaches to the DNA near the bead when the chromatin undergoes the next level of packing. ...
... nucleosome. The nucleosome bead is DNA wound around a protein core made of two of these histones: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H1, another histone attaches to the DNA near the bead when the chromatin undergoes the next level of packing. ...
Slide 1
... - Three ways to reveal DNA “chromatin remodeling” 2. Methylation - highly repetitive sequences - imprinted genes - Barr bodies Some proteins bind to the methylated cytosines, and may either recruit repressors or interrupt transcription factor binding. ...
... - Three ways to reveal DNA “chromatin remodeling” 2. Methylation - highly repetitive sequences - imprinted genes - Barr bodies Some proteins bind to the methylated cytosines, and may either recruit repressors or interrupt transcription factor binding. ...
From DNA To Protein
... • DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids • mRNA – the messenger RNA; carries the message from the DNA instructing the ribosome which sequence of amino acids to bond together • tRNA – the transfer RNA; brings amino acids to the ribosome • rRNA – the ribosomal RNA; with proteins physically composes the ri ...
... • DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids • mRNA – the messenger RNA; carries the message from the DNA instructing the ribosome which sequence of amino acids to bond together • tRNA – the transfer RNA; brings amino acids to the ribosome • rRNA – the ribosomal RNA; with proteins physically composes the ri ...