5.2. Related mechanisms of halogen chemistry A large variety of
... methyl group of guaiacol that has a minor benzylic character because of the lone-pair electrons of the ether oxygen). Abstraction of hydrogen from the two CH2 groups and even more so the tertiary C-H bonds of -pinene (if all of them persist in the SOA) is expected as well. Hydrogen abstraction from ...
... methyl group of guaiacol that has a minor benzylic character because of the lone-pair electrons of the ether oxygen). Abstraction of hydrogen from the two CH2 groups and even more so the tertiary C-H bonds of -pinene (if all of them persist in the SOA) is expected as well. Hydrogen abstraction from ...
Esterification
... 1/ Weigh 1.0g of Phenol into a small conical flask. HAZARD 2/Add 18cm3 of 1M NaOH(aq) and bung the flask. 3/ HAZARD In a fume cupboard add 2cm3 of Benzoyl chloride in small quantities at a time. 4/ Fit a bung and shake vigorously with occasional cooling under the tap or in ice water. Releasing the g ...
... 1/ Weigh 1.0g of Phenol into a small conical flask. HAZARD 2/Add 18cm3 of 1M NaOH(aq) and bung the flask. 3/ HAZARD In a fume cupboard add 2cm3 of Benzoyl chloride in small quantities at a time. 4/ Fit a bung and shake vigorously with occasional cooling under the tap or in ice water. Releasing the g ...
Chapter 6A Chemical Reactions CHAPTER OUTLINE
... the transfer of hydrogen atoms produces energy in the cells. q For example, cellular respiration is an oxidationreduction process that transfers energy from the bonds in glucose to form ATP. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 ...
... the transfer of hydrogen atoms produces energy in the cells. q For example, cellular respiration is an oxidationreduction process that transfers energy from the bonds in glucose to form ATP. C6H12O6 + 6 O2 ...
jeep 2014 - apres midi jeunes chercheurs
... Baylis-Hillman reaction of HMF and analogues in bio-based solvent-water mixtures Jia-Neng TAN, Mohammed AHMAR, Yves QUENEAU ...
... Baylis-Hillman reaction of HMF and analogues in bio-based solvent-water mixtures Jia-Neng TAN, Mohammed AHMAR, Yves QUENEAU ...
Lecture Resource ()
... The goal is to convert the OH group into a better leaving group such that the acyl chloride can be prepared ...
... The goal is to convert the OH group into a better leaving group such that the acyl chloride can be prepared ...
Phosphoric Trichloride
... with alcohols to produce alkyl phosphate esters and is therefore a versatile phosphating agent.1 As a selective and inexpensive reagent giving high yields in simple operations under mild conditions, it is tremendously used in ...
... with alcohols to produce alkyl phosphate esters and is therefore a versatile phosphating agent.1 As a selective and inexpensive reagent giving high yields in simple operations under mild conditions, it is tremendously used in ...
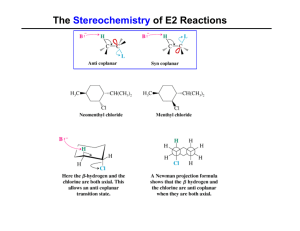
Elimination Reactions
... In this, two-step process, the rate of the reaction is dependent on the rate of ionization of the substrate (as was the case in the SN1 reaction) ...
... In this, two-step process, the rate of the reaction is dependent on the rate of ionization of the substrate (as was the case in the SN1 reaction) ...
O V O O RO OH t-BuOOH, CH2Cl2, Ti(OPr-i)4(cat), 20 oC (L)
... These are not actually enantiomers of each other, but rather diastereomers, because the chirality of the C bearing the ethyl is the same in each case ((R)-). For the dihydroxylations, however, they function as the complementary systems to get enantiomeric products; the unofficial term pseudoenantiom ...
... These are not actually enantiomers of each other, but rather diastereomers, because the chirality of the C bearing the ethyl is the same in each case ((R)-). For the dihydroxylations, however, they function as the complementary systems to get enantiomeric products; the unofficial term pseudoenantiom ...
Practice Final Exam, Chemistry 2220, Organic Chem II 1. Rank the
... 22. Which of these compounds best fits these data? It is soluble in water, and turns red litmus blue; has only one major IR band, at 2950 cm-1, and has the following 1H NMR spectrum: 2.7 ppm, 2H; 2.2 ppm, 6H; 1.0 ppm, 3H. A. N,N-dimethylethanamine B. propanoic acid C. 2-propanol D. 2-methylpropane ...
... 22. Which of these compounds best fits these data? It is soluble in water, and turns red litmus blue; has only one major IR band, at 2950 cm-1, and has the following 1H NMR spectrum: 2.7 ppm, 2H; 2.2 ppm, 6H; 1.0 ppm, 3H. A. N,N-dimethylethanamine B. propanoic acid C. 2-propanol D. 2-methylpropane ...
Review for Exam #1
... CH3—CH2—Cl CH3—Br IUPAC Name chloroethane bromomethane Common Name ethyl chloride methyl bromide ...
... CH3—CH2—Cl CH3—Br IUPAC Name chloroethane bromomethane Common Name ethyl chloride methyl bromide ...
Chapter 15
... • The substitution reaction of aromatic rings and the reactions of side chains of alkyl and alkenyl benzenes, when taken together, offer us a powerful set of reactions for organic synthesis with great regio-control • Part of the skill is using these reactions is deciding the order in which reactions ...
... • The substitution reaction of aromatic rings and the reactions of side chains of alkyl and alkenyl benzenes, when taken together, offer us a powerful set of reactions for organic synthesis with great regio-control • Part of the skill is using these reactions is deciding the order in which reactions ...
Demonstrate skill in organic chemistry techniques.
... Analyze chemical reactions or processes to determine greenness. Learning Objectives Compare methods using parameters such as relative chemical hazards of reagents, environmental impact of materials and waste, transportation hazards, difficulty of synthetic method, and reaction efficiency. Perform an ...
... Analyze chemical reactions or processes to determine greenness. Learning Objectives Compare methods using parameters such as relative chemical hazards of reagents, environmental impact of materials and waste, transportation hazards, difficulty of synthetic method, and reaction efficiency. Perform an ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.