H2N-CH2-CH(NH2)—CH2—CH3,
... azolines by condensation of acylated ethylene diamine of platinum nitrate or with solutions of other halide in ‘the presence of dehydrating agents is described in vU.S. free platinum salts or complexes, as for example com Patents Nos. 2,399,601 and 2,404,299. The obtained 2 mercial “P-salt” [(NO2)2- ...
... azolines by condensation of acylated ethylene diamine of platinum nitrate or with solutions of other halide in ‘the presence of dehydrating agents is described in vU.S. free platinum salts or complexes, as for example com Patents Nos. 2,399,601 and 2,404,299. The obtained 2 mercial “P-salt” [(NO2)2- ...
Chapter 5—Chemical Reactions
... 5.6—Replacement Reactions • Single-replacement reactions—one element replaces another in a compound. They are always redox reactions because an element turns into an ion and an ion turns into an element • The general form of the equation for a single replacement reaction (also known as substitution ...
... 5.6—Replacement Reactions • Single-replacement reactions—one element replaces another in a compound. They are always redox reactions because an element turns into an ion and an ion turns into an element • The general form of the equation for a single replacement reaction (also known as substitution ...
CHM 222 - Jefferson State Community College
... Demonstrate an understanding of reactions involving aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives including nomenclature, synthesis and mechanisms. 1. Name and draw aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 2. Propose a synthesis for each type of compound listed above. ...
... Demonstrate an understanding of reactions involving aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives including nomenclature, synthesis and mechanisms. 1. Name and draw aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 2. Propose a synthesis for each type of compound listed above. ...
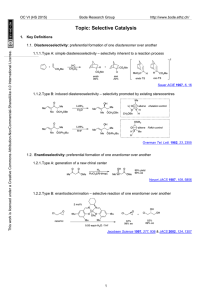
Changing counterion can switch the preference for selective 1,2
... Regioisomer: The positional isomers formed from different locations of bond formation/cleavage. Note: The term “regiospecific” to refer to a reaction that is 100% regioselective is discouraged, and has no correlation to the difference between “stereoselective” and “stereospecific” ...
... Regioisomer: The positional isomers formed from different locations of bond formation/cleavage. Note: The term “regiospecific” to refer to a reaction that is 100% regioselective is discouraged, and has no correlation to the difference between “stereoselective” and “stereospecific” ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
... carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and the carbon that was formerly the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule ...
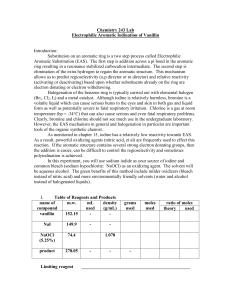
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Vanillin
... form as well as potentially severe to fatal respiratory irritation. Chlorine is a gas at room temperature (bp = -34C) that can also cause serious and even fatal respiratory problems. Clearly, bromine and chlorine should not see much use in the undergraduate laboratory. However, the EAS mechanism in ...
... form as well as potentially severe to fatal respiratory irritation. Chlorine is a gas at room temperature (bp = -34C) that can also cause serious and even fatal respiratory problems. Clearly, bromine and chlorine should not see much use in the undergraduate laboratory. However, the EAS mechanism in ...
n - TU Chemnitz
... excess of HN3.[4] We thought, that the diazides 11 may have been formed but overseen in literature. Actually we found that only acrolein 9a lead to a diazide 11 (Figure 3). O ...
... excess of HN3.[4] We thought, that the diazides 11 may have been formed but overseen in literature. Actually we found that only acrolein 9a lead to a diazide 11 (Figure 3). O ...
o-chem - WordPress.com
... soda lime (NaOH & CaO) give alkanes containing one carbon atom less than the carboxylic acid. • This process of elimination of CO2from a carboxylic acid is known as decarboxylation. ...
... soda lime (NaOH & CaO) give alkanes containing one carbon atom less than the carboxylic acid. • This process of elimination of CO2from a carboxylic acid is known as decarboxylation. ...
Going Bananas Over Isoamyl Acetate
... acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester is only about 8° C higher than the boiling points of the polar acetic acid and 1-butanol, ...
... acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester is only about 8° C higher than the boiling points of the polar acetic acid and 1-butanol, ...
Document
... • Conversion of p Bond to 2 s Bonds Typically Energy Favored • Two s Bonds Higher Energy than One p + One s • Overall Process is thus Typically Exothermic ...
... • Conversion of p Bond to 2 s Bonds Typically Energy Favored • Two s Bonds Higher Energy than One p + One s • Overall Process is thus Typically Exothermic ...
Physical Organic Chemistry
... Elimination reaction: to eliminate two atoms, two groups, or one atom and one group without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and n ...
... Elimination reaction: to eliminate two atoms, two groups, or one atom and one group without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and n ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... If it is A AC2 (with Nu), the intermediate and reactant (the protonated starting material) are both positively charged. Electronegative groups would destabilize both. However, the effect may be greater on the reactant because the positive charge is transferred to the carbonyl carbon by both an induc ...
... If it is A AC2 (with Nu), the intermediate and reactant (the protonated starting material) are both positively charged. Electronegative groups would destabilize both. However, the effect may be greater on the reactant because the positive charge is transferred to the carbonyl carbon by both an induc ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.