Synthesis of Benzyl Acetate from Acetic Anhydride
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
( i ) in enantioselective nhk reaction
... high enantioselectivity ( 90 %) and good yield ( 72 % ) THF proved to be the best solvent for these catalytic asymmetric reactions and catalyst concentration of 0.025 M gave the best results In contrast to salen ligand 1, ligand 2 was able to effect an enantioselective addition of allyl iodide ...
... high enantioselectivity ( 90 %) and good yield ( 72 % ) THF proved to be the best solvent for these catalytic asymmetric reactions and catalyst concentration of 0.025 M gave the best results In contrast to salen ligand 1, ligand 2 was able to effect an enantioselective addition of allyl iodide ...
thiols and sulfides.
... These rate differences can be explained based on the interplay between strain, entropy, and proximity. Entropy reduction (due to ring closure) increases with increasing ring size. (Reaction rate decrease with increasing ring size.) Ring strain decreases with increasing ring size. (Reaction rate incr ...
... These rate differences can be explained based on the interplay between strain, entropy, and proximity. Entropy reduction (due to ring closure) increases with increasing ring size. (Reaction rate decrease with increasing ring size.) Ring strain decreases with increasing ring size. (Reaction rate incr ...
Kwang-Ting Liu Department of Chemistry National Taiwan
... Introduction • At National Taiwan University there are three different introductory organic chemistry courses, mostly given in sophomore year. In general, an American textbook is chosen for individual section according to the lecturer’s preference. • “Organic Chemistry B” is a two-semester course c ...
... Introduction • At National Taiwan University there are three different introductory organic chemistry courses, mostly given in sophomore year. In general, an American textbook is chosen for individual section according to the lecturer’s preference. • “Organic Chemistry B” is a two-semester course c ...
CH 3 Br + Nu
... 10. Which statement(s) is/are true of an E1 elimination? A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation t ...
... 10. Which statement(s) is/are true of an E1 elimination? A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation t ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylation of r
... Reactions with catalysts 3a,b,d were run with 0.4 mmol of imine 1c, 0.43 mmol of enol silane, and 0.04 mmol of catalyst (10 mol % metal salt, 10.5 mol % (R)-BINAP), and 0.02 mmol of catalyst (5 mol % metal salt, 5.2 mol % (R)-Tol-BINAP) for catalyst 3c at the specified temperature for 24 h. b Reacti ...
... Reactions with catalysts 3a,b,d were run with 0.4 mmol of imine 1c, 0.43 mmol of enol silane, and 0.04 mmol of catalyst (10 mol % metal salt, 10.5 mol % (R)-BINAP), and 0.02 mmol of catalyst (5 mol % metal salt, 5.2 mol % (R)-Tol-BINAP) for catalyst 3c at the specified temperature for 24 h. b Reacti ...
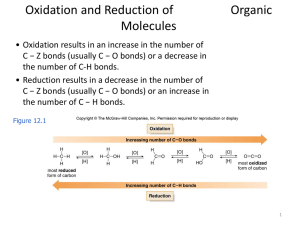
Oxidation and Reduction of Organic Molecules
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
Reactions to functionalize benzene
... Because of its electrons, benzene is a nucleophile and is attracted to electrophiles. Due to the stability of aromatic system, addition reactions aren’t favored. Electrophilic aromatic substitution is the predominant reaction mechanism Hydrogens are easily replaced by electrophilic substituent g ...
... Because of its electrons, benzene is a nucleophile and is attracted to electrophiles. Due to the stability of aromatic system, addition reactions aren’t favored. Electrophilic aromatic substitution is the predominant reaction mechanism Hydrogens are easily replaced by electrophilic substituent g ...
Classification of Halogen Derivatives
... 1. Aryl halides are colourless liquids or colourless solids with characteristic odour. 2. Boiling point generally increases with increase in the size of aryl group or halogen atom. Boiling point order Ar – I > Ar – Br > Ar – Cl > Ar – F 3. The melting point of p -isomer is more than 0- and m-isomer. ...
... 1. Aryl halides are colourless liquids or colourless solids with characteristic odour. 2. Boiling point generally increases with increase in the size of aryl group or halogen atom. Boiling point order Ar – I > Ar – Br > Ar – Cl > Ar – F 3. The melting point of p -isomer is more than 0- and m-isomer. ...
Organic Synthesis Part 2
... (where the active species is a BH3.THF complex) or as its complex with dimethyl sulfide (BH3.Me2S). Since boron is in the same period as aluminium, there are similarities in the mode of action to DIBAL-H (though not in terms of absolute reactivity). Note also the speed of reaction with carboxylic ac ...
... (where the active species is a BH3.THF complex) or as its complex with dimethyl sulfide (BH3.Me2S). Since boron is in the same period as aluminium, there are similarities in the mode of action to DIBAL-H (though not in terms of absolute reactivity). Note also the speed of reaction with carboxylic ac ...
Final Exam Review
... It is particularly important to study and do the problems for the following sections: ...
... It is particularly important to study and do the problems for the following sections: ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.