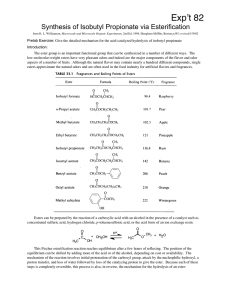
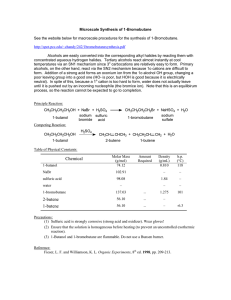
H3PO4 in a Direct Synthesis of Oligo–Poly(ethylene phosphate)
... This is only one example of many similar reactions that could proceed at different sites of macromolecules and at different degrees of polymerization. However, in syntheses at lower temperatures, practically no di- or triethylene glycol units in the backbone were observed. In the presence of catalys ...
... This is only one example of many similar reactions that could proceed at different sites of macromolecules and at different degrees of polymerization. However, in syntheses at lower temperatures, practically no di- or triethylene glycol units in the backbone were observed. In the presence of catalys ...
Ch 7: Reactions
... cations of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: • AB + CD ---> AD + CB • One example of a double displacement reaction is the reaction of lead (II) nitrate with potassium iodide to form lead (II) iodide and potassiu ...
... cations of two different molecules switch places, forming two entirely different compounds. These reactions are in the general form: • AB + CD ---> AD + CB • One example of a double displacement reaction is the reaction of lead (II) nitrate with potassium iodide to form lead (II) iodide and potassiu ...
Preparation and Reaction of Carboxylic Acids - IDC
... nucleophilic group are important for preparing functional derivatives of carboxylic acids. The alcohols provide a usefulreference chemistry against which this class of transformations may be evaluated. In general, the hydroxyl group proved to be a poor leaving group, and virtually all alcohol reacti ...
... nucleophilic group are important for preparing functional derivatives of carboxylic acids. The alcohols provide a usefulreference chemistry against which this class of transformations may be evaluated. In general, the hydroxyl group proved to be a poor leaving group, and virtually all alcohol reacti ...
Gas Chromatography: Analyzing Alkene Isomers David L. Flanigan
... Ease of alcohol dehydration follows the general trend: 3° > 2° > 1°. This trend is based on the fact that most acid catalyzed alcohol dehydrations proceed through the E1 mechanism. In order for the elimination to occur a good leaving group and a base sufficiently strong enough to remove a β-proton m ...
... Ease of alcohol dehydration follows the general trend: 3° > 2° > 1°. This trend is based on the fact that most acid catalyzed alcohol dehydrations proceed through the E1 mechanism. In order for the elimination to occur a good leaving group and a base sufficiently strong enough to remove a β-proton m ...
Grignard Reaction - This is Synthesis
... Fig. 2 One-pot, two-step reaction to form triphenylmethanol ...
... Fig. 2 One-pot, two-step reaction to form triphenylmethanol ...
Oxidation of alcohol to carboxylic acid under mild acidic condition
... Corey’s lactone was fist synthesized by E.J.Corey from cyclopentadiene[1] and it is key starting material for synthesis of prostaglandins [2] and prostaglandin possess a diverse range of biological activities including the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension[3], chronic constipation and ir ...
... Corey’s lactone was fist synthesized by E.J.Corey from cyclopentadiene[1] and it is key starting material for synthesis of prostaglandins [2] and prostaglandin possess a diverse range of biological activities including the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension[3], chronic constipation and ir ...
Chem 30CL-Lecture 15..
... Selectivity: terminal alkyne > terminal alkene ~ internal alkyne > disubstituted alkene It is much more chemoselective and easier to handle than B2H6 ...
... Selectivity: terminal alkyne > terminal alkene ~ internal alkyne > disubstituted alkene It is much more chemoselective and easier to handle than B2H6 ...
Presented by Arianne Hunter
... Catalytically generated metal carbenes are highly versatile for insertion into carbon– hydrogen and heteroatom–hydrogen bonds C–H bond insertions are mechanistically different from X–H bond insertions due to their low bond polarity ...
... Catalytically generated metal carbenes are highly versatile for insertion into carbon– hydrogen and heteroatom–hydrogen bonds C–H bond insertions are mechanistically different from X–H bond insertions due to their low bond polarity ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.