Module - EPS School Projects - Heriot
... Substitution Reactions – Formation of alkyl halides, including Ph3P/CX4; formation of sulfonates; Use of alkyl halides and sulfonates to prepare amines, nitriles, ethers, etc; the Mitsunobu reaction. Addition Reactions – Revision of Markownikoff addition to alkenes, with further examples; mercuric-c ...
... Substitution Reactions – Formation of alkyl halides, including Ph3P/CX4; formation of sulfonates; Use of alkyl halides and sulfonates to prepare amines, nitriles, ethers, etc; the Mitsunobu reaction. Addition Reactions – Revision of Markownikoff addition to alkenes, with further examples; mercuric-c ...
Sample 3 - University of Puget Sound
... The proposed research involves the multistep synthesis of organic and organometallic complexes by using techniques and strategies that are well known. However, the target compounds have not been previously synthesized using these strategies. As such, each individual step of the proposed syntheses wi ...
... The proposed research involves the multistep synthesis of organic and organometallic complexes by using techniques and strategies that are well known. However, the target compounds have not been previously synthesized using these strategies. As such, each individual step of the proposed syntheses wi ...
Lecture Resource ()
... Secondary and tertiary alcohols undergo SN1 reactions with hydrogen halides ...
... Secondary and tertiary alcohols undergo SN1 reactions with hydrogen halides ...
EX. Draw the structure of
... in the absence of air. This breaks carbon-carbon bonds. Steam at more than 800oC is often used as the heat source. ___________________cracking is a low pressure process that passes a powdered catalyst through heavy hydrocarbon fractions at 600oC. ___________________ involves the addition of hydr ...
... in the absence of air. This breaks carbon-carbon bonds. Steam at more than 800oC is often used as the heat source. ___________________cracking is a low pressure process that passes a powdered catalyst through heavy hydrocarbon fractions at 600oC. ___________________ involves the addition of hydr ...
3. Alkanes
... along the longest bridge to the other bridgehead, then along the next longest bridge back to the fist bridgehead. The shortest bridge is numbered last. Interposed in the name in brackets is an expression that denotes the number of carbon atoms in each bridge, in order of decreasing length and separa ...
... along the longest bridge to the other bridgehead, then along the next longest bridge back to the fist bridgehead. The shortest bridge is numbered last. Interposed in the name in brackets is an expression that denotes the number of carbon atoms in each bridge, in order of decreasing length and separa ...
Microsoft Word
... 30 was subsequently reduced to the allylic alcohol 31 by LAH and then oxidized to the corresponding ketone 32. Deprotection of the ketone 32 yielded the keto alcohol 33, which was then converted to the ketone-1,3-dithio acetal 34 (Scheme8). However, further oxidation of the dithio acetal 34 yielded ...
... 30 was subsequently reduced to the allylic alcohol 31 by LAH and then oxidized to the corresponding ketone 32. Deprotection of the ketone 32 yielded the keto alcohol 33, which was then converted to the ketone-1,3-dithio acetal 34 (Scheme8). However, further oxidation of the dithio acetal 34 yielded ...
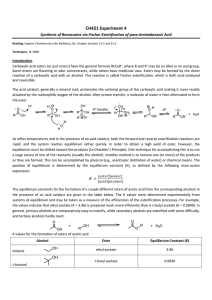
Experimen tt: Dehydration of an Alcohol
... Your explanation should deal with both types of ways that reduce your yield. The first are losses of product through physical means, for example transfer losses or spillage. The second are ways in which the limiting reagent reacts in a way that you don’t want it to react, producing unwanted products ...
... Your explanation should deal with both types of ways that reduce your yield. The first are losses of product through physical means, for example transfer losses or spillage. The second are ways in which the limiting reagent reacts in a way that you don’t want it to react, producing unwanted products ...
Benzocaine Synthesis via Esterification
... Carboxylic acid esters (or just esters) have the general formula RCO2R', where R and R' may be an alkyl or an aryl group. Some esters are flavoring or odor concentrates, while others have medicinal uses. Esters may be formed by the direct reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol. This reaction ...
... Carboxylic acid esters (or just esters) have the general formula RCO2R', where R and R' may be an alkyl or an aryl group. Some esters are flavoring or odor concentrates, while others have medicinal uses. Esters may be formed by the direct reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol. This reaction ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... Looking at a structural formula, identify the “parent chain.” Remember that the parent chain can be bent. Know that trichloromethane is “chloroform.” Give examples of substituted hydrocarbons. Know the names of side groups: methyl –CH3 ethyl –C2H5 bromo –Br iodo –I chloro –Cl Start numbe ...
... Looking at a structural formula, identify the “parent chain.” Remember that the parent chain can be bent. Know that trichloromethane is “chloroform.” Give examples of substituted hydrocarbons. Know the names of side groups: methyl –CH3 ethyl –C2H5 bromo –Br iodo –I chloro –Cl Start numbe ...
Ring-closing metathesis

Ring-closing metathesis, or RCM, is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.The most commonly synthesized ring sizes are between 5-7 atoms; however, reported syntheses include 45- up to 90- membered macroheterocycles. These reactions are metal-catalyzed and proceed through a metallacyclobutane intermediate. It was first published by Dider Villemin in 1980 describing the synthesis of an Exaltolide precursor, and later become popularized by Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock, who shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Yves Chauvin, in 2005 for their combined work in olefin metathesis. RCM is a favorite among organic chemists due to its synthetic utility in the formation of rings, which were previously difficult to access efficiently, and broad substrate scope. Since the only major by-product is ethylene, these reactions may also be considered atom economic, an increasingly important concern in the development of green chemistry.There are several reviews published on ring-closing metathesis.