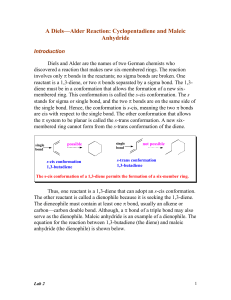
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
... reactants governs how easily the reactants produce a Diels-Alder product. When you give someone directions, you tell them where to go. In that case, you are the “director.” A group that “tells another group where to go” is called a directing group. A directing group can either donate or withdraw ele ...
... reactants governs how easily the reactants produce a Diels-Alder product. When you give someone directions, you tell them where to go. In that case, you are the “director.” A group that “tells another group where to go” is called a directing group. A directing group can either donate or withdraw ele ...
Metal-catalysed approaches to amide bond formation
... As the preparation of amides from carboxylic acids is difficult to achieve in a catalytic manner, their derivatives, particularly esters, have been explored as an alternative in catalytic amide forming reactions. In 2003, a simple procedure was published by Ranu and Dutta, using a catalytic amount of ...
... As the preparation of amides from carboxylic acids is difficult to achieve in a catalytic manner, their derivatives, particularly esters, have been explored as an alternative in catalytic amide forming reactions. In 2003, a simple procedure was published by Ranu and Dutta, using a catalytic amount of ...
CHEM 263 (AS 40) Organic Chemistry II Winter 2017 Instructor: Dr
... functional groups in organic chemistry are discussed. Functional groups covered include alkenes, alkynes, aromatic compounds, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives. The presence of these functional groups in natural products is emphas ...
... functional groups in organic chemistry are discussed. Functional groups covered include alkenes, alkynes, aromatic compounds, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids and carboxylic acid derivatives. The presence of these functional groups in natural products is emphas ...
CHEM 494 Lecture 10b - UIC Department of Chemistry
... Quaternary Ammonium Salts (R4N+ X-) Nitrogen atoms are positively charged when bonded to four substituents: when all of these substituents are carbon, the molecule is referred to as a quaternary ammonium ion. ...
... Quaternary Ammonium Salts (R4N+ X-) Nitrogen atoms are positively charged when bonded to four substituents: when all of these substituents are carbon, the molecule is referred to as a quaternary ammonium ion. ...
IA Practical Report Properties of Alkanes and Alkenes
... a) What kind of reaction occurred when water, H2SO4, and cyclohexene were mixed? b) What function did H2SO4 serve in the reaction? c) Define catalyst. d) Draw the reaction of 2-butene with sulphuric acid and water. Draw the reaction that would occur for cyclohexene. e) Where would this new chemical ...
... a) What kind of reaction occurred when water, H2SO4, and cyclohexene were mixed? b) What function did H2SO4 serve in the reaction? c) Define catalyst. d) Draw the reaction of 2-butene with sulphuric acid and water. Draw the reaction that would occur for cyclohexene. e) Where would this new chemical ...
Results
... for each critical point (reactants, transition states, intermediates, products) Geometry optimization at MP2/6-31G(d) and B3LYP/6-31G(d) level of theory was performed for all reactions but those including water clusters (see below) Zero-point energy correction was performed. reaction rates were calc ...
... for each critical point (reactants, transition states, intermediates, products) Geometry optimization at MP2/6-31G(d) and B3LYP/6-31G(d) level of theory was performed for all reactions but those including water clusters (see below) Zero-point energy correction was performed. reaction rates were calc ...
Review for Ch. 20 21
... Both of these reactions finish up by hydrolyzing the amide, via the mechanism shown above (either in acid or base) ...
... Both of these reactions finish up by hydrolyzing the amide, via the mechanism shown above (either in acid or base) ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... mechanism must equal the overall reaction equation. The reaction is a substitution reaction in which the nucleophile chloride takes the place of the OH. Thus, it is known as an SN reaction. ...
... mechanism must equal the overall reaction equation. The reaction is a substitution reaction in which the nucleophile chloride takes the place of the OH. Thus, it is known as an SN reaction. ...
organic chemistry reaction scheme
... *Note: Lithium aluminium hydride (or Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III)), LiAlH4, is one of the few reagents that can reduce an acid to an alcohol; the initial product is an alkoxide which the alcohol is liberated by hydrolysis. The –H ion acts as a nucleophile, and can attack the carbon atom of the ...
... *Note: Lithium aluminium hydride (or Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III)), LiAlH4, is one of the few reagents that can reduce an acid to an alcohol; the initial product is an alkoxide which the alcohol is liberated by hydrolysis. The –H ion acts as a nucleophile, and can attack the carbon atom of the ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon ...
... Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon ...
Amines
... resistant to fading, and so are important in the dye industry. The colour results from the joining of the two delocalized electron systems via the N=N group. Colour can be altered by changing the number and type of functional groups attached. ...
... resistant to fading, and so are important in the dye industry. The colour results from the joining of the two delocalized electron systems via the N=N group. Colour can be altered by changing the number and type of functional groups attached. ...
INTRODUCTION TO LEWIS ACID
... Lewis acids and bases are defined in terms of electron pair transfers. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor, and a Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. An organic transformation (the creation of products from reactants) essentially results from a process of breaking bonds and forming new ones. ...
... Lewis acids and bases are defined in terms of electron pair transfers. A Lewis base is an electron pair donor, and a Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor. An organic transformation (the creation of products from reactants) essentially results from a process of breaking bonds and forming new ones. ...
121. Acceptorless Dehydrogenation with Metal
... can be as high as 0.1%. Scope of the substrates are quite large. Aryl, alkyl, alkeyl(some examples) are both appropriate substituent groups of the substrates. Detailed studied about the operation pattern of catalysts will be a new orientation in modern chemistry. ...
... can be as high as 0.1%. Scope of the substrates are quite large. Aryl, alkyl, alkeyl(some examples) are both appropriate substituent groups of the substrates. Detailed studied about the operation pattern of catalysts will be a new orientation in modern chemistry. ...
Phenol - wellswaysciences
... This is written as an equilibrium: C2H5OH + H2O D C2H5O- + H3O+ C2H5OH D C2H5O- + H+ is the simpler alternative. This equilibrium lies LEFT because there is a high electron density on the O- which attracts the proton back to recombine. • The ethoxide ion is a good base due to the +I effect of the ch ...
... This is written as an equilibrium: C2H5OH + H2O D C2H5O- + H3O+ C2H5OH D C2H5O- + H+ is the simpler alternative. This equilibrium lies LEFT because there is a high electron density on the O- which attracts the proton back to recombine. • The ethoxide ion is a good base due to the +I effect of the ch ...
Translation
... 6. The ribosome moves towards the 3’ end of the mRNA strand 7. Because of the move of the ribosome, what there is a shift in the tRNA bindings site (A P E) 8. tRNA leaves the ribosome from the E site ...
... 6. The ribosome moves towards the 3’ end of the mRNA strand 7. Because of the move of the ribosome, what there is a shift in the tRNA bindings site (A P E) 8. tRNA leaves the ribosome from the E site ...
Process for the manufacture of maleic acid anhydride copolymers
... ganic compounds, such as ole?n hydrocarbons and ole ?nically unsaturated aromatic hydrocarbons, in the co ...
... ganic compounds, such as ole?n hydrocarbons and ole ?nically unsaturated aromatic hydrocarbons, in the co ...
GRADE 12A: Chemistry 6
... Ask students to use the library or the Internet to research the work of Otto Witt and describe his contribution to the azo dye industry. Also ask them to research azo dye production worldwide and present the data in a suitable format. Describe to the whole class the stages of synthesising an azo dye ...
... Ask students to use the library or the Internet to research the work of Otto Witt and describe his contribution to the azo dye industry. Also ask them to research azo dye production worldwide and present the data in a suitable format. Describe to the whole class the stages of synthesising an azo dye ...
AROMATIC CHEMISTRY
... The term ‘aromatic’ was first used in the nineteenth century to describe a group of compounds which have pleasant aromas. These compounds, which include benzene, are very different to aliphatic compounds. The term is still used, since it is useful to classify aromatic and aliphatic compounds separat ...
... The term ‘aromatic’ was first used in the nineteenth century to describe a group of compounds which have pleasant aromas. These compounds, which include benzene, are very different to aliphatic compounds. The term is still used, since it is useful to classify aromatic and aliphatic compounds separat ...
19 Amines and Amides Study Goals
... derivatives. Amines are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary and named according to IUPAC and common naming systems. Heterocyclic amines are introduced and their role in alkaloids and other physiological amines is described. Demonstration: Amines and Amides Amines and amides are introduced ...
... derivatives. Amines are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary and named according to IUPAC and common naming systems. Heterocyclic amines are introduced and their role in alkaloids and other physiological amines is described. Demonstration: Amines and Amides Amines and amides are introduced ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylations of N,O- and
... Mechanism. To our surprise, the use of one equiv enol silane 4a with N,O-acetal l a did not lead to product 5a with 5 mol% 2; however, when two equiv were used, product 5a was formed in good yield. Although silyl ketene acetals can be quenched through silyl transfer reactions with alcohols, enol sil ...
... Mechanism. To our surprise, the use of one equiv enol silane 4a with N,O-acetal l a did not lead to product 5a with 5 mol% 2; however, when two equiv were used, product 5a was formed in good yield. Although silyl ketene acetals can be quenched through silyl transfer reactions with alcohols, enol sil ...
- Thieme Connect
... The amide functionality is ubiquitous, and amides are also versatile educts in organic synthesis; thus there is continuing interest in their synthesis.1 Of particular interest are possibilities of direct conversion of simple substrates into amides which bypass conventional routes, such as reaction o ...
... The amide functionality is ubiquitous, and amides are also versatile educts in organic synthesis; thus there is continuing interest in their synthesis.1 Of particular interest are possibilities of direct conversion of simple substrates into amides which bypass conventional routes, such as reaction o ...
Handbook for the Lab Course Organic Chemistry I
... Participation in the preliminary talks and seminars is compulsory to pass the course and obtain the certificate. Repeated unexcused absence can result in failing of the course. If you cannot attend a mandatory seminar for a profound reason, please get in touch with Steffen Friedrich (steffen.friedri ...
... Participation in the preliminary talks and seminars is compulsory to pass the course and obtain the certificate. Repeated unexcused absence can result in failing of the course. If you cannot attend a mandatory seminar for a profound reason, please get in touch with Steffen Friedrich (steffen.friedri ...
2010 Chemistry Written examination 2
... • give simplified answers with an appropriate number of significant figures to all numerical questions; unsimplified answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No marks will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of ...
... • give simplified answers with an appropriate number of significant figures to all numerical questions; unsimplified answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No marks will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.