Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... Alcohol should be primary to avoid carbocations being formed from the alcohol. Expect mechanism to be protonation of alkene to yield more stable carbocation followed by reaction with the weakly nucleophilic alcohol. Not presented. ...
... Alcohol should be primary to avoid carbocations being formed from the alcohol. Expect mechanism to be protonation of alkene to yield more stable carbocation followed by reaction with the weakly nucleophilic alcohol. Not presented. ...
Hmwk_4-09 Key
... but showed approximately the same Vmax. Inhibitor binding is a property of the inhibitor, not the substrate. This argument is definitely an approximation because substrate and inhibitor bind at the same time and could influence one another's binding. It's a very good argument in the case of competit ...
... but showed approximately the same Vmax. Inhibitor binding is a property of the inhibitor, not the substrate. This argument is definitely an approximation because substrate and inhibitor bind at the same time and could influence one another's binding. It's a very good argument in the case of competit ...
08 Arylaliphatic, aminobenzoic, aminosalicylic acids derivat
... C15H15NO2. SPU. Test substance (shows subacid properties) dissolve in dimethyl formamide (alkaline solvent) and titrate with solution of sodium hydroxide NaOH in the mix of methanol СН3ОН and benzene С6Н6 in the presence of the indicator thymol dark blue before dark blue colouring. O ...
... C15H15NO2. SPU. Test substance (shows subacid properties) dissolve in dimethyl formamide (alkaline solvent) and titrate with solution of sodium hydroxide NaOH in the mix of methanol СН3ОН and benzene С6Н6 in the presence of the indicator thymol dark blue before dark blue colouring. O ...
cork institute of technology
... constant (keqm) for a given chemical reaction and predict in each case whether reactants of products are favoured : i) Q = Keqm ii) Q < Keqm iii) Q > Keqm Provide a reason for your predictions in each case. ...
... constant (keqm) for a given chemical reaction and predict in each case whether reactants of products are favoured : i) Q = Keqm ii) Q < Keqm iii) Q > Keqm Provide a reason for your predictions in each case. ...
study material class X (science)
... through water, the solution obtained turn blue litmus red . On bubbling the gas through lime water, it initially became milky and the milkiness disappeared when the gas was passed in excess. Identify the substance =X‘ and write the chemical equations of the reaction involved . Ans: The water insolub ...
... through water, the solution obtained turn blue litmus red . On bubbling the gas through lime water, it initially became milky and the milkiness disappeared when the gas was passed in excess. Identify the substance =X‘ and write the chemical equations of the reaction involved . Ans: The water insolub ...
12_chemistry_impq_CH13_amines_02
... The azo products obtained have an extended conjugate system having both the aromatic rings joined through the –N=N– bond. These compounds are often coloured and are used as dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazo ...
... The azo products obtained have an extended conjugate system having both the aromatic rings joined through the –N=N– bond. These compounds are often coloured and are used as dyes. Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazo ...
Lab 9 - Academic Computer Center
... Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, is the mildest of the three hydride reagents and is easy to use in the lab, because it is soluble in water, methanol and ethanol and does not react with these solvents. Therefore, NaBH4 is the reagent of choice for reducing aldehydes and ketones. Lithium aluminum hydride, ...
... Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, is the mildest of the three hydride reagents and is easy to use in the lab, because it is soluble in water, methanol and ethanol and does not react with these solvents. Therefore, NaBH4 is the reagent of choice for reducing aldehydes and ketones. Lithium aluminum hydride, ...
organic synthesis
... Which of the following produce a mixture of alcohols when treated with OH¯(aq)? • C2H5CHBrCH3 ...
... Which of the following produce a mixture of alcohols when treated with OH¯(aq)? • C2H5CHBrCH3 ...
Page 1 - WordPress.com
... PLA is the condensation polymer formed from lactic acid, and used to make ‘disposable plastic cups’. The polymer is described as 100% biodegradable and 100% compostable.Compostable material breaks down slowly in contact with the moist air in a garden bin. This produces compost that can be used to im ...
... PLA is the condensation polymer formed from lactic acid, and used to make ‘disposable plastic cups’. The polymer is described as 100% biodegradable and 100% compostable.Compostable material breaks down slowly in contact with the moist air in a garden bin. This produces compost that can be used to im ...
Ch 16 Amines - Tennessee Wesleyan College
... • 1o and 2o amines have a Hydrogen bonded to a Nitrogen so they are capable of Hydrogen bonding to each other • 3o Amines do not have a Hydrogen bonded to Nitrogen so they can not Hydrogen bond to one another. • All classes of amines can H-Bond with water and are therefore soluble in water!! ...
... • 1o and 2o amines have a Hydrogen bonded to a Nitrogen so they are capable of Hydrogen bonding to each other • 3o Amines do not have a Hydrogen bonded to Nitrogen so they can not Hydrogen bond to one another. • All classes of amines can H-Bond with water and are therefore soluble in water!! ...
ch11 by dr. Dina
... Hydroxyl groups are poor leaving groups, and as such, are often converted to alkyl halides when a good leaving group is needed Three general methods exist for conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides, depending on the classification of the alcohol and the halogen desired Reaction can occur with phos ...
... Hydroxyl groups are poor leaving groups, and as such, are often converted to alkyl halides when a good leaving group is needed Three general methods exist for conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides, depending on the classification of the alcohol and the halogen desired Reaction can occur with phos ...
Amines - WordPress.com
... basic strength of the compound. But both these factors are to be considered simultaneously. Based on the above concept regarding the strength of the bases the observations noted in the table may be properly rationalized It has been observed that aliphatic secondary amine is most basic among ammonia, ...
... basic strength of the compound. But both these factors are to be considered simultaneously. Based on the above concept regarding the strength of the bases the observations noted in the table may be properly rationalized It has been observed that aliphatic secondary amine is most basic among ammonia, ...
Lesson Plan: Synthesis of Isopentyl Acetate
... ‘work up’ of the reaction mixture prior to product distillation and isolation. Moreover, it is easy to visualize the changes in 1H NMR spectra as reactants are converted to products. Figure 6 compares reactants and products, while Figure 7 includes the initial reaction mixture prior to addition of ...
... ‘work up’ of the reaction mixture prior to product distillation and isolation. Moreover, it is easy to visualize the changes in 1H NMR spectra as reactants are converted to products. Figure 6 compares reactants and products, while Figure 7 includes the initial reaction mixture prior to addition of ...
Required Resources and Materials
... Are they polar? Do they have as intermolecular forces as strong as alcohols? (NO) – more polar than alkanes but less than alcohol – good solvents Naming: adding oxy to smaller alkyl group, and larger alkyl taken as parent chain. e.g. methoxypropane (on board) Ethers can be formed by reaction o ...
... Are they polar? Do they have as intermolecular forces as strong as alcohols? (NO) – more polar than alkanes but less than alcohol – good solvents Naming: adding oxy to smaller alkyl group, and larger alkyl taken as parent chain. e.g. methoxypropane (on board) Ethers can be formed by reaction o ...
Document
... • Final Product Typically Geminal Dihaloalkene • Both Additions Follow Markovnikov’s Rule (explains gem.) • Alumina Accelerates Reaction Rate (as seen w/ Alkenes) ...
... • Final Product Typically Geminal Dihaloalkene • Both Additions Follow Markovnikov’s Rule (explains gem.) • Alumina Accelerates Reaction Rate (as seen w/ Alkenes) ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 14 – Ethers
... When designing a synthesis using an epoxide, it is a good idea to first figure out what nucleophile(s) could be used, then determine where the epoxide was, and write a reaction. Finally, check to see if the nucleophile will attack on the side to give the desired product. ...
... When designing a synthesis using an epoxide, it is a good idea to first figure out what nucleophile(s) could be used, then determine where the epoxide was, and write a reaction. Finally, check to see if the nucleophile will attack on the side to give the desired product. ...
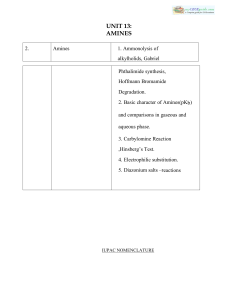
amines
... alkylamines, the ending –amine is added to the name of the alkyl group that bears the nitrogen. When named as alkanamines, the alkyl group is named as an alkane and the -e ...
... alkylamines, the ending –amine is added to the name of the alkyl group that bears the nitrogen. When named as alkanamines, the alkyl group is named as an alkane and the -e ...
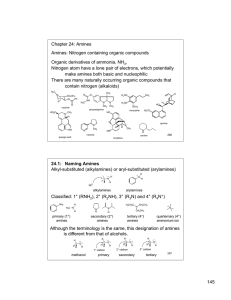
145 Chapter 24: Amines Amines: Nitrogen containing organic
... Table 24.1 (p. 899): pKa values of ammonium ions Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitr ...
... Table 24.1 (p. 899): pKa values of ammonium ions Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitr ...
21. Characterization of the Organic Matter in a Site 147 Core from
... deuteride. The steps are outlined using a carboxylic acid as an example. RCOOH + LiAlD4 - RCD2OH RCD2OH + HI ^ ...
... deuteride. The steps are outlined using a carboxylic acid as an example. RCOOH + LiAlD4 - RCD2OH RCD2OH + HI ^ ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.