Hydrogen bonding
... • Sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride) has the formula SOCl2. • The two other products of the reaction (sulphur dioxide and HCl) are both gases. That means that they separate themselves from the reaction mixture. ...
... • Sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride) has the formula SOCl2. • The two other products of the reaction (sulphur dioxide and HCl) are both gases. That means that they separate themselves from the reaction mixture. ...
Grant MacEwan College - Faculty Web Pages
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
... Description: This is the second course in organic chemistry. The topics covered include structural and chemical properties of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic compounds. Aldehyde, ketones, amines, carboxylic acids, and carboxylic acid derivatives. Illustration of these functiona ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... Chapter 1: Structure and Bonding -you should know; 1. Atomic Structure- Orbitals, Electron Configurations 2. Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory 3. Hybridization: sp3 Orbitals and the Structure of Methane, sp2 Orbitals and the Structure of Ethylene, sp Orbitals and the Structure of Acet ...
... Chapter 1: Structure and Bonding -you should know; 1. Atomic Structure- Orbitals, Electron Configurations 2. Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory 3. Hybridization: sp3 Orbitals and the Structure of Methane, sp2 Orbitals and the Structure of Ethylene, sp Orbitals and the Structure of Acet ...
Aldonic acids
... Uronic acids (syn., glycuronic acids) – derivatives of aldoses containing in their chain terminal positions an aldehyde group and a carboxyl group. They can be derived from any aldose by changing its terminal hydroxymethyl group to carboxyl group. Similarly as aldoses, they normally exist in cyclic ...
... Uronic acids (syn., glycuronic acids) – derivatives of aldoses containing in their chain terminal positions an aldehyde group and a carboxyl group. They can be derived from any aldose by changing its terminal hydroxymethyl group to carboxyl group. Similarly as aldoses, they normally exist in cyclic ...
Synthesis of Imidine Hydrochloride and Some
... propioimidate hydrochloride (5): A mixture of (0.1 mole) of (comp. 1) dissolved in (40 ml) of dry chloroform and (0.1 mole) of absolute ethanol is cooled to 0 C and saturated with dry hydrogen chloride gas. The flask is stoppered and place in refrigerator for 7 days and then equal volume of dry et ...
... propioimidate hydrochloride (5): A mixture of (0.1 mole) of (comp. 1) dissolved in (40 ml) of dry chloroform and (0.1 mole) of absolute ethanol is cooled to 0 C and saturated with dry hydrogen chloride gas. The flask is stoppered and place in refrigerator for 7 days and then equal volume of dry et ...
Bimolecular reactions of the chromium
... insertion into C-H and C-C bonds. Besides the investigation of the reactivity of bare metal ions, a study of the modification of the reactivity of the central metal ions of mrdinatively unsaturated metal complexes by the ligands is a major field of research in metal-organic chemistry.2 Usually the c ...
... insertion into C-H and C-C bonds. Besides the investigation of the reactivity of bare metal ions, a study of the modification of the reactivity of the central metal ions of mrdinatively unsaturated metal complexes by the ligands is a major field of research in metal-organic chemistry.2 Usually the c ...
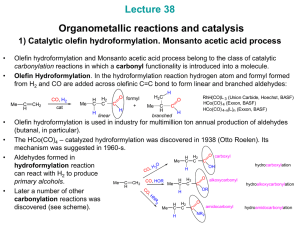
Slide 1
... become much stronger and it becomes possible to decrease CO pressure without causing catalyst decomposition. becomes stronger Bulkier PR3 favor greater linear / branched becomes more hydride-like H aldehyde ratios ( up to 8 : 1). CO Finally, more hydride-like Co-H promotes aldehyde OC Co hydrogenati ...
... become much stronger and it becomes possible to decrease CO pressure without causing catalyst decomposition. becomes stronger Bulkier PR3 favor greater linear / branched becomes more hydride-like H aldehyde ratios ( up to 8 : 1). CO Finally, more hydride-like Co-H promotes aldehyde OC Co hydrogenati ...
A Few More Notes on Acidity
... Ka is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of an acid into H+ and its conjugate base. Where possible, Ka values are measured using water as the solvent. ...
... Ka is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of an acid into H+ and its conjugate base. Where possible, Ka values are measured using water as the solvent. ...
Iodoform Test - organicchem.org
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
Chapter 8 - profpaz.com
... 1. In the reaction below, if 0.552 moles of aluminum react with 0.887 moles of chlorine, what is the limiting reactant and theoretical yield of AlCl3 in moles? ...
... 1. In the reaction below, if 0.552 moles of aluminum react with 0.887 moles of chlorine, what is the limiting reactant and theoretical yield of AlCl3 in moles? ...
Procedure - organicchem.org
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
Chemistry 262 Quiz 2 Winter 2017 The following
... Ethanol + HBr, then Mg/ether, then HCHO, then H3O+, then NaH, then CH3CH2Br c. Ethanol + CH3CH2CH2OH + H2SO4/140C d. Ethanol + NaH, then HCHO, then H3O+, then HBr, then Mg/ether, then CH3CH2CH2Br e. Ethanol + H2SO4/180°C, then CH3CH2CH2Br ...
... Ethanol + HBr, then Mg/ether, then HCHO, then H3O+, then NaH, then CH3CH2Br c. Ethanol + CH3CH2CH2OH + H2SO4/140C d. Ethanol + NaH, then HCHO, then H3O+, then HBr, then Mg/ether, then CH3CH2CH2Br e. Ethanol + H2SO4/180°C, then CH3CH2CH2Br ...
Reactions of Molecules with Oxygen
... Oxidation Reactions of Alcohols What oxidizing agent is used in the selective oxidation of alcohols? Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is the oxidizing agent [O] used in many alcohol oxidation reactions. The K2Cr2O7 solution must be acidified first by adding sulfuric acid, H2SO4. This provides an appr ...
... Oxidation Reactions of Alcohols What oxidizing agent is used in the selective oxidation of alcohols? Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is the oxidizing agent [O] used in many alcohol oxidation reactions. The K2Cr2O7 solution must be acidified first by adding sulfuric acid, H2SO4. This provides an appr ...
conversion of the OH group into a better leaving group, and
... • The mechanism of ether cleavage is SN1 or SN2, depending on the identity of R. • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the ...
... • The mechanism of ether cleavage is SN1 or SN2, depending on the identity of R. • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the ...
Review on N acylation reaction
... chlorides with advantages while some disadvantages which can be avoided by using recently developed reagents when required. Thionyl chloride is volatile and excess can be distilled off at the end, leaving acid chloride. Only gaseous by-products are given out, no tedious workup is required for purifi ...
... chlorides with advantages while some disadvantages which can be avoided by using recently developed reagents when required. Thionyl chloride is volatile and excess can be distilled off at the end, leaving acid chloride. Only gaseous by-products are given out, no tedious workup is required for purifi ...
Document
... • Methanol (CH3OH) • Often Called Wood Alcohol (Distilled From Wood) • Prepared Now via Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions • Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) • Made Through Fermentation of Sugars, in Alcoholic Drinks • Common Solvent in Organic Labs (Absolute Ethanol) • Ethylene Glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) ...
... • Methanol (CH3OH) • Often Called Wood Alcohol (Distilled From Wood) • Prepared Now via Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions • Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) • Made Through Fermentation of Sugars, in Alcoholic Drinks • Common Solvent in Organic Labs (Absolute Ethanol) • Ethylene Glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) ...
model paper-1 - WordPress.com
... b) Which out of NH3 and NF3 has higher dipole moment and why? 3M 15. a) Under what conditions, real gases show ideal gas behavior? On a ship sailing in Pacific Ocean where temperature is 26.40C, a balloon is filled with 1.4L air. What will be the volume of the balloon when the ship reaches Indian Oc ...
... b) Which out of NH3 and NF3 has higher dipole moment and why? 3M 15. a) Under what conditions, real gases show ideal gas behavior? On a ship sailing in Pacific Ocean where temperature is 26.40C, a balloon is filled with 1.4L air. What will be the volume of the balloon when the ship reaches Indian Oc ...
Chapter Fifteen
... The following compounds are named as propylamines because the propyl group in each is the largest alkyl group: ...
... The following compounds are named as propylamines because the propyl group in each is the largest alkyl group: ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.