Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and
... [Fehling solution is a mixture of Fehling solution A and Fehling solution B in 1: 1 ratio. Fehling solution A is aqueous copper sulphate and Fehling solution B is alkaline sodium potassium tartrate which is also called, Rochelle salt.] (c) Benedict solution With it, aldehydes (except benzaldehyde) a ...
... [Fehling solution is a mixture of Fehling solution A and Fehling solution B in 1: 1 ratio. Fehling solution A is aqueous copper sulphate and Fehling solution B is alkaline sodium potassium tartrate which is also called, Rochelle salt.] (c) Benedict solution With it, aldehydes (except benzaldehyde) a ...
Iron(II) Chloride–1,1′-Binaphthyl-2,2′-diamine
... In our preliminary studies, the synthesis was carried out starting from ethanol via a domino alcohol oxidation in the presence of the FeCl2–BINAM complex as the catalyst and dicumyl peroxide (DCP), followed by condensation of the resulting aldehyde with indole (1) in ethanol, at 120 °C. To our surpr ...
... In our preliminary studies, the synthesis was carried out starting from ethanol via a domino alcohol oxidation in the presence of the FeCl2–BINAM complex as the catalyst and dicumyl peroxide (DCP), followed by condensation of the resulting aldehyde with indole (1) in ethanol, at 120 °C. To our surpr ...
Ch 12- 13 - Phillips Scientific Methods
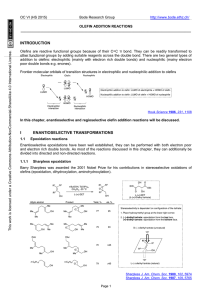
... Addition of water to alkenes: Hydration Alcohol is produced on treatment of the alkene with water in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, such as H2SO4. Markovnikov’s rule can be used to predict the product when water adds to an unsymmetrically substituted alkene. Hydrated alkenes produce alcohol ...
... Addition of water to alkenes: Hydration Alcohol is produced on treatment of the alkene with water in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, such as H2SO4. Markovnikov’s rule can be used to predict the product when water adds to an unsymmetrically substituted alkene. Hydrated alkenes produce alcohol ...
POLYMER END-GROUP ANALYSIS: THE DETERMINATION OF
... sources. Synthetic polymers are known to us as various fibers (e.g., Dacron), plastics (e.g., polyvinyl chloride), abbreviated PVC, and polystyrene), and elastomers. See Fig. 1. Like PVC and polystyrene, the compound involved in this experiment is synthesized from only one kind of monomer molecule, ...
... sources. Synthetic polymers are known to us as various fibers (e.g., Dacron), plastics (e.g., polyvinyl chloride), abbreviated PVC, and polystyrene), and elastomers. See Fig. 1. Like PVC and polystyrene, the compound involved in this experiment is synthesized from only one kind of monomer molecule, ...
[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School
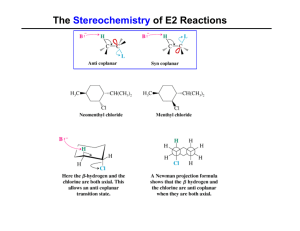
... Racemic mixture: d+ l forms Inversion of configuration (Walden inversion) d to l form(vice-versa) Order: CH3X <10<20<30 < Allyl < benzyl Order : CH3X > 10 > 20 > 30 Nu can attack from back side as well as well The nucleophile(Nu-) can attack from from front side,however former predominates back side ...
... Racemic mixture: d+ l forms Inversion of configuration (Walden inversion) d to l form(vice-versa) Order: CH3X <10<20<30 < Allyl < benzyl Order : CH3X > 10 > 20 > 30 Nu can attack from back side as well as well The nucleophile(Nu-) can attack from from front side,however former predominates back side ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... Examine relationship between aromatic structure and reactivity Relationship critical to understanding of how biological molecules/pharmaceutical agents are synthesized ...
... Examine relationship between aromatic structure and reactivity Relationship critical to understanding of how biological molecules/pharmaceutical agents are synthesized ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... Examine relationship between aromatic structure and reactivity Relationship critical to understanding of how biological molecules/pharmaceutical agents are synthesized ...
... Examine relationship between aromatic structure and reactivity Relationship critical to understanding of how biological molecules/pharmaceutical agents are synthesized ...
CHE-05 Organic Chemistry
... 2 Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid is more acidic than benzenecarboxylic acid. A tertiary carbocation is more stable than a primary carbocation. Aniline is less basic than ammonia. The pKa of monochloroethanoic acid is less than that of ethanoic acid. ...
... 2 Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid is more acidic than benzenecarboxylic acid. A tertiary carbocation is more stable than a primary carbocation. Aniline is less basic than ammonia. The pKa of monochloroethanoic acid is less than that of ethanoic acid. ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Elements of Chemical Change
... substance is its molecular weight expressed in grams. Thus, a GMW of NaOH would be 40 grams, where the atomic weights are as follows: Na = 23, O = 16, and H = 1. Thus, .5 GMW of NaOH would be 20 grams, and so forth. A mole is one-gram molecular weight of a substance. Thus, a mole of NaOH is 40 grams ...
... substance is its molecular weight expressed in grams. Thus, a GMW of NaOH would be 40 grams, where the atomic weights are as follows: Na = 23, O = 16, and H = 1. Thus, .5 GMW of NaOH would be 20 grams, and so forth. A mole is one-gram molecular weight of a substance. Thus, a mole of NaOH is 40 grams ...
File
... • As with phosphines, this allows bonding from carbene to metal (lone pair in sp2 orbital) and back-bonding (to empty p orbital) • Back bonding is significant in fisher and schrock carbenes but not with nucleophilic ...
... • As with phosphines, this allows bonding from carbene to metal (lone pair in sp2 orbital) and back-bonding (to empty p orbital) • Back bonding is significant in fisher and schrock carbenes but not with nucleophilic ...
CHEM 242 Organic Chemistry II-Bender
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 13 – 20, 22, and 23. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step synthesis. Laboratory is included and chapter ...
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 13 – 20, 22, and 23. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step synthesis. Laboratory is included and chapter ...
Chpt 23Final7e
... The synthesis begins with an aldol reaction using nitromethane, followed by reduction to give a βaminoalcohol that then undergoes the ring expansion reaction. Problem 23.12 Show how to convert toluene to 3-hydroxybenzoic acid using the same set of reactions as in Example 23.12, but changing the orde ...
... The synthesis begins with an aldol reaction using nitromethane, followed by reduction to give a βaminoalcohol that then undergoes the ring expansion reaction. Problem 23.12 Show how to convert toluene to 3-hydroxybenzoic acid using the same set of reactions as in Example 23.12, but changing the orde ...
Lecture 1: Key Concepts in Stereoselective Synthesis
... Overall, the reactions are exothermic but nearly ergoneutral. The electronic effect on this reaction is almost purely a result of kinetics, not thermodynamics. Factors, as the equilibrium constants, for these additions are similar (entries 2 vs. 1, 3 vs. 1). In contrast, steric properties of the ami ...
... Overall, the reactions are exothermic but nearly ergoneutral. The electronic effect on this reaction is almost purely a result of kinetics, not thermodynamics. Factors, as the equilibrium constants, for these additions are similar (entries 2 vs. 1, 3 vs. 1). In contrast, steric properties of the ami ...
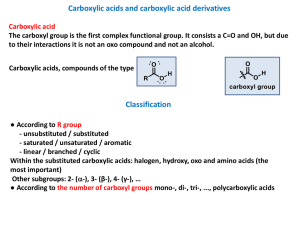
carboxylic acid
... Easier from salts (eg. On the presence of solid NaOH). Aromatic carboxylic acids can loose CO2 easier. ...
... Easier from salts (eg. On the presence of solid NaOH). Aromatic carboxylic acids can loose CO2 easier. ...
Chapter 10 Outline: Alcohols
... Alcohols have pKas in the range of 16-18. Only methanol has an acidity less than water (pKa 15.5 and will protonate water preferentially). In general, all alcohols will be less polar and less acidic than water. What happens when water is in solution with ethanol (pKa = 15.9)? ...
... Alcohols have pKas in the range of 16-18. Only methanol has an acidity less than water (pKa 15.5 and will protonate water preferentially). In general, all alcohols will be less polar and less acidic than water. What happens when water is in solution with ethanol (pKa = 15.9)? ...
11_Phenolics - WordPress.com
... Chemical burns from skin exposures can be decontaminated by washing with polyethylene glycol, isopropyl alcohol, or perhaps even copious amounts of water.[21] Removal of contaminated clothing is required, as well as immediate hospital treatment for large splashes. This is particularly important if t ...
... Chemical burns from skin exposures can be decontaminated by washing with polyethylene glycol, isopropyl alcohol, or perhaps even copious amounts of water.[21] Removal of contaminated clothing is required, as well as immediate hospital treatment for large splashes. This is particularly important if t ...
HIGHLIGHTS OF NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS
... b) occurs with formation of carbocation intermediates in the rate determining step c) involves one transition state per step. The rate-determining step involves a high polarity transition state d) follows first order (unimolecular) kinetics. That is, rate=k[substrate] In nucleophilic substitutions a ...
... b) occurs with formation of carbocation intermediates in the rate determining step c) involves one transition state per step. The rate-determining step involves a high polarity transition state d) follows first order (unimolecular) kinetics. That is, rate=k[substrate] In nucleophilic substitutions a ...
Reactions of Oxacyclopropanes
... Thiols are less hydrogen-bonded and more acidic than alcohols. Compared to oxygen, sulfur has a large size, diffuse orbitals and a relatively ...
... Thiols are less hydrogen-bonded and more acidic than alcohols. Compared to oxygen, sulfur has a large size, diffuse orbitals and a relatively ...
part 1
... • The reaction is completely enantioselective. Reduction of pyruvic acid with NADH catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase affords solely the S enantiomer . • NADH reduces a variety of different carbonyl compounds in biological systems. The configuration of the product (R or S) depends on the enzyme used ...
... • The reaction is completely enantioselective. Reduction of pyruvic acid with NADH catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase affords solely the S enantiomer . • NADH reduces a variety of different carbonyl compounds in biological systems. The configuration of the product (R or S) depends on the enzyme used ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.




![[1] Ans1.Dows-proc - Sacred Heart School Moga,Best ICSE School](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015878975_1-55791b331e05591620375059b6f74bac-300x300.png)