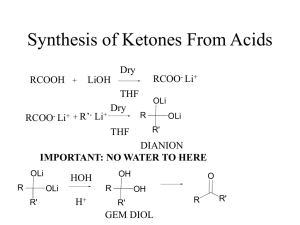
Biehl PPT Part2
... From ethyl benzene? Side-chain oxidation!!!! Appears as if we could start with benzoic acid and introduce ethyl group by EtLi. ...
... From ethyl benzene? Side-chain oxidation!!!! Appears as if we could start with benzoic acid and introduce ethyl group by EtLi. ...
Chemistry Final Test
... (A) Hydrogen bonding stabilizes the α-helix proteins. (B) Heat can disrupt tertiary structure. (C) Nonpolar groups tend to face the outside of a protein in an aqueous solution. (D) Ionized amino acid side chains can form salt bridges within a protein. (E) Disulfide bonds provide strong intrachain in ...
... (A) Hydrogen bonding stabilizes the α-helix proteins. (B) Heat can disrupt tertiary structure. (C) Nonpolar groups tend to face the outside of a protein in an aqueous solution. (D) Ionized amino acid side chains can form salt bridges within a protein. (E) Disulfide bonds provide strong intrachain in ...
1. Four of the structural isomers of C4H10O are alcohols. One of
... Hydrogen and ethanol are used as motor car fuel. Suggest the advantages and disadvantages of each of these fuels in this application. Use the table, and your answers to part (a) above to help you. ...
... Hydrogen and ethanol are used as motor car fuel. Suggest the advantages and disadvantages of each of these fuels in this application. Use the table, and your answers to part (a) above to help you. ...
DEHYDRATION - ALKENE TEST EXERCISES
... 1. Give a detailed mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol to cyclohexene. ...
... 1. Give a detailed mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol to cyclohexene. ...
Addition Reactions
... acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is regioselective; hydrogen adds preferentially to the sp2 carbon with less # of hydrogens. ...
... acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene is regioselective; hydrogen adds preferentially to the sp2 carbon with less # of hydrogens. ...
carbonyl chemistry 1
... Thus, the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or a ketone can be protected in the form of an acetal or ketal. Deprotection following reaction on other regions of the molecule then yields the carbonyl group again – this then is the first protection/deprotection protocol we have encountered. In general, sim ...
... Thus, the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or a ketone can be protected in the form of an acetal or ketal. Deprotection following reaction on other regions of the molecule then yields the carbonyl group again – this then is the first protection/deprotection protocol we have encountered. In general, sim ...
Quarter 3: Post Test Review
... 44. ________ mmHg = __________torr = _________Pascals = __________kilopascals Convert 2983.4 mmHg into torr. ___________________ convert in Pascals ________________ E. Bonding and Electron Configurations 45. Besides metallic, what are the other two types of bonding. _____________ and __________ b. d ...
... 44. ________ mmHg = __________torr = _________Pascals = __________kilopascals Convert 2983.4 mmHg into torr. ___________________ convert in Pascals ________________ E. Bonding and Electron Configurations 45. Besides metallic, what are the other two types of bonding. _____________ and __________ b. d ...
壹 - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... 12. Explain how the laser generates light. What is meant by population inversion in laser action? (10 %) 13. What would be the effect of the following on the “plate height” of a column in gas chromatography? Explain! (6 %) (a) Increasing the weight of the stationary phase relative to the packing wei ...
... 12. Explain how the laser generates light. What is meant by population inversion in laser action? (10 %) 13. What would be the effect of the following on the “plate height” of a column in gas chromatography? Explain! (6 %) (a) Increasing the weight of the stationary phase relative to the packing wei ...
Chapter 20 reactions of carbonyls
... • Carbonyl compounds that also contain N–H or O–H bonds undergo an acid–base reaction with organometallic reagents, not nucleophilic addition. ...
... • Carbonyl compounds that also contain N–H or O–H bonds undergo an acid–base reaction with organometallic reagents, not nucleophilic addition. ...
Named Reactions Of Haloalkanes and haloarenes
... 3)Friedel craft’s reaction In this reaction, benzene is treated with alkyl halide or acyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride acting as a catalyst. As a result,a hydrogen atom in the ring gets replaced either by alkyl group or acyl group. ...
... 3)Friedel craft’s reaction In this reaction, benzene is treated with alkyl halide or acyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride acting as a catalyst. As a result,a hydrogen atom in the ring gets replaced either by alkyl group or acyl group. ...
Topic 16 Assessed Homework - A
... By considering the optical activity of these products formed from Q and R, explain why this method would not distinguish between Q and R. ...
... By considering the optical activity of these products formed from Q and R, explain why this method would not distinguish between Q and R. ...
2.10 Organic synthesis – Oxidation of alcohols
... heating under reflux and distillation. 2. Explain why each process is used, and describe what happens in each process. ...
... heating under reflux and distillation. 2. Explain why each process is used, and describe what happens in each process. ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... • Acyl azides provide access to primary amines via an isocyanate • Concerted reaction ...
... • Acyl azides provide access to primary amines via an isocyanate • Concerted reaction ...
Organic Chemistry 1 1st Hour Exam Student ID # Name
... 1. Draw as many skeletal structures of the isomers (constitutional isomers or stereoisomers) for a compound with the molecular formula C5H10 as possible and name each isomer according to the IUPAC nomenclature. You may use the condensed formula to draw the structure if you want. ...
... 1. Draw as many skeletal structures of the isomers (constitutional isomers or stereoisomers) for a compound with the molecular formula C5H10 as possible and name each isomer according to the IUPAC nomenclature. You may use the condensed formula to draw the structure if you want. ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... When any carboxylic acid is treated with LiAlH4, it is reduced all the way to the 1o alcohol because LAH is a very powerful reducing agent and aldehydes are very easily reduced. Any aldehyde that might be formed in the reaction mixture is immediately reduced by the LAH to the 1° alcohol. ...
... When any carboxylic acid is treated with LiAlH4, it is reduced all the way to the 1o alcohol because LAH is a very powerful reducing agent and aldehydes are very easily reduced. Any aldehyde that might be formed in the reaction mixture is immediately reduced by the LAH to the 1° alcohol. ...
SNC2DExamChemistryreview
... Chemistry Exam Review 1. What is a chemical change? List how can you tell that a reaction or a material has had a chemical change? 2. In the earlier chemistry courses we learned about physical properties of materials. Give at least 5 different examples of physical properties? 3. Given the following ...
... Chemistry Exam Review 1. What is a chemical change? List how can you tell that a reaction or a material has had a chemical change? 2. In the earlier chemistry courses we learned about physical properties of materials. Give at least 5 different examples of physical properties? 3. Given the following ...
ch16 by dr. Dina
... Dissolving aldehydes (or ketones) in water causes formation of an equilibrium between the carbonyl compound and its hydrate The hydrate is also called a gem-diol (gem i.e. geminal, indicates the presence of two identical substituents on the same carbon) The equilibrum favors a ketone over its hyd ...
... Dissolving aldehydes (or ketones) in water causes formation of an equilibrium between the carbonyl compound and its hydrate The hydrate is also called a gem-diol (gem i.e. geminal, indicates the presence of two identical substituents on the same carbon) The equilibrum favors a ketone over its hyd ...
Organic Chemistry Unit Test
... ____ 7.Ethanoic acid can be prepared from ethene by a. reduction with H2, followed by reaction with a strong oxidizer b. addition of HCl, followed by reaction with H2O c. addition of H2O followed by reaction with a strong oxidizer d. addition of Br2, followed by reduction with H2 ...
... ____ 7.Ethanoic acid can be prepared from ethene by a. reduction with H2, followed by reaction with a strong oxidizer b. addition of HCl, followed by reaction with H2O c. addition of H2O followed by reaction with a strong oxidizer d. addition of Br2, followed by reduction with H2 ...
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the
... Reduction to an aldehyde can be accomplished by using a more reactive carboxylic acid derivatives such as an acyl chloride, ester or nitrile and a less reactive hydride source ...
... Reduction to an aldehyde can be accomplished by using a more reactive carboxylic acid derivatives such as an acyl chloride, ester or nitrile and a less reactive hydride source ...
NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin
... While either of these reagents can be employed for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones, there are vast differences between the reactivites of the LAH and NaBH4. Sodium borohydride is a rather mild reducing agent, reducing aldehydes and ketones selectively in the presence of more highly ...
... While either of these reagents can be employed for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones, there are vast differences between the reactivites of the LAH and NaBH4. Sodium borohydride is a rather mild reducing agent, reducing aldehydes and ketones selectively in the presence of more highly ...
Development of a Greener Selective Acylation Method for Steroids
... found. However a greener alternative to dichloromethane was looked into to develop a more environmentally friendly method for the selective acylation of the steroid of interest. Ethyl acetate was chosen as a possible alternative solvent to dichloromethane. The reaction was first conducted using dich ...
... found. However a greener alternative to dichloromethane was looked into to develop a more environmentally friendly method for the selective acylation of the steroid of interest. Ethyl acetate was chosen as a possible alternative solvent to dichloromethane. The reaction was first conducted using dich ...
types of organic reactions
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
Reduction Reactions
... Chemoselectivity. Many different functional groups can be reduced in a variety of ways. We often need to selectively reduce one functional group whilst leaving others intact. In the case of carboxylic acid derivatives there are two possible reduction products: aldehdye and alcohol. Ideally we need m ...
... Chemoselectivity. Many different functional groups can be reduced in a variety of ways. We often need to selectively reduce one functional group whilst leaving others intact. In the case of carboxylic acid derivatives there are two possible reduction products: aldehdye and alcohol. Ideally we need m ...
Precipitate Lab Report Power Point with Answers
... Temperature change, odor change, precipitate formation, irreversibility, color change, and new bubble formation are the evidence for a chemical reaction occuring. Not every time one of these changes is proof of a chemical reaction, but often they are. Sometimes chemical reactions can occur with no o ...
... Temperature change, odor change, precipitate formation, irreversibility, color change, and new bubble formation are the evidence for a chemical reaction occuring. Not every time one of these changes is proof of a chemical reaction, but often they are. Sometimes chemical reactions can occur with no o ...
Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
... Constraints on Enolate Alkylation • SN2 reaction: the leaving group X can be chloride, bromide, iodide, or tosylate • R should be primary or methyl and preferably should be allylic or benzylic • Secondary halides react poorly, and tertiary halides don't react at all because of competing elimination ...
... Constraints on Enolate Alkylation • SN2 reaction: the leaving group X can be chloride, bromide, iodide, or tosylate • R should be primary or methyl and preferably should be allylic or benzylic • Secondary halides react poorly, and tertiary halides don't react at all because of competing elimination ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.























