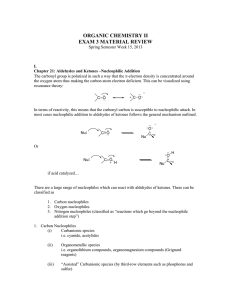
Mechanism of Aldol Condensation
... Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis, providing a good way to form carbon– carbon bonds. For example, the Robinson annulation reaction sequence features an aldol condensation; the Wieland-Miescher ketone product is an important starting material for many organic syntheses. Aldol co ...
... Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis, providing a good way to form carbon– carbon bonds. For example, the Robinson annulation reaction sequence features an aldol condensation; the Wieland-Miescher ketone product is an important starting material for many organic syntheses. Aldol co ...
PowerPoint **
... a. Baylis-Hillman reaction: An acrylate ester reacts with an aldehyde in the presence of an amine or phosphine catalyst. ...
... a. Baylis-Hillman reaction: An acrylate ester reacts with an aldehyde in the presence of an amine or phosphine catalyst. ...
1. 4-methyl-4-octanol oxidizes to form a) 4-methyl-4
... a) are, are not b) are not, are not c) are, are d) are not, are 21.Of the following, which would have the highest boiling point? a) propane b) propanal c) propanoic acid d) methyl ethyl ether. 22. Of the following aldehydes, which is most soluble in water a) methanoic acid b) ethananoic acid c) prop ...
... a) are, are not b) are not, are not c) are, are d) are not, are 21.Of the following, which would have the highest boiling point? a) propane b) propanal c) propanoic acid d) methyl ethyl ether. 22. Of the following aldehydes, which is most soluble in water a) methanoic acid b) ethananoic acid c) prop ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - Aldehydes and Ketones C=O C C C
... • hydrolysis of the CN group to COOH is possible ...
... • hydrolysis of the CN group to COOH is possible ...
Substitution reactions of carbonyl compounds at the α
... acetates, respectively. As you might expect, alkylation of an enolate is a powerful tool for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds under relatively mild conditions. The Haloform Reaction: While enolates are great for forming new carbon-carbon bonds, the first reaction we’ll look at is a method for t ...
... acetates, respectively. As you might expect, alkylation of an enolate is a powerful tool for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds under relatively mild conditions. The Haloform Reaction: While enolates are great for forming new carbon-carbon bonds, the first reaction we’ll look at is a method for t ...
Determining structure of copper complexes with nicotinic
... complexes with aroylhydrazones derived from nicotinic acid hydrazide and salicylaldehide derivatives having different substituents on the benzene ring. Aroylhydrazones can be involved in keto-enol tautomeric interconversion, when the hydrogen atom in keto form moves from amino to carbonyl group, for ...
... complexes with aroylhydrazones derived from nicotinic acid hydrazide and salicylaldehide derivatives having different substituents on the benzene ring. Aroylhydrazones can be involved in keto-enol tautomeric interconversion, when the hydrogen atom in keto form moves from amino to carbonyl group, for ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... What can happen? Reactants are the aldehyde and concentrated hydroxide. Hydroxide ion can act both as Base, but remember we have no acidic hydrogens (no a hydrogens). Nucleophile, attacking carbonyl group. ...
... What can happen? Reactants are the aldehyde and concentrated hydroxide. Hydroxide ion can act both as Base, but remember we have no acidic hydrogens (no a hydrogens). Nucleophile, attacking carbonyl group. ...
aldehyde ketone
... Due to the polarity of the C=O bond, a permanent dipole moment exists in aldehydes and ketones (dipole-dipole forces). Thus, the MP/BP of aldehydes and ketones is mid-range – higher than that of alkanes or alkenes (London forces) but lower than that of alcohols (hydrogen bonds). Nomenclature – IUPAC ...
... Due to the polarity of the C=O bond, a permanent dipole moment exists in aldehydes and ketones (dipole-dipole forces). Thus, the MP/BP of aldehydes and ketones is mid-range – higher than that of alkanes or alkenes (London forces) but lower than that of alcohols (hydrogen bonds). Nomenclature – IUPAC ...
COUPLING REACTIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
... The addition of dihydrogen to Vaska's complex and other transition metals is a reversible reaction. The hydrogen can be released again if the reaction moves to the left in a reductive elimination. That reversibility makes transition metal compounds useful for hydrogen storage. Hydrogen gas is volumi ...
... The addition of dihydrogen to Vaska's complex and other transition metals is a reversible reaction. The hydrogen can be released again if the reaction moves to the left in a reductive elimination. That reversibility makes transition metal compounds useful for hydrogen storage. Hydrogen gas is volumi ...
Common aldehydes and ketones
... Nonetheless, the enol form is important for some reactions. Furthermore, the deprotonated intermediate in the interconversion of the two forms, referred to as an enolate anion, is important in carbonyl chemistry, in large part because it is a strong nucleophile. ...
... Nonetheless, the enol form is important for some reactions. Furthermore, the deprotonated intermediate in the interconversion of the two forms, referred to as an enolate anion, is important in carbonyl chemistry, in large part because it is a strong nucleophile. ...
organic chemistry ii
... When a nucleophile attacks a CA derivative, a tetrahedral intermediate (unstable) forms, which subsequently dissociates into a new CA derivative (or into a carboxylate) Reactions of Nitriles Nitriles are extremely versatile as precursors; they can be converted into (i) carboxylic acids, (ii) imines, ...
... When a nucleophile attacks a CA derivative, a tetrahedral intermediate (unstable) forms, which subsequently dissociates into a new CA derivative (or into a carboxylate) Reactions of Nitriles Nitriles are extremely versatile as precursors; they can be converted into (i) carboxylic acids, (ii) imines, ...
ADDITION REACTIONS
... sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) (sodium borohydride), NaBH4 aqueous or alcoholic solution Nucleophilic addition (also reduction as it is addition of H¯) H¯ (hydride ion) Alcohols Aldehydes are REDUCED to primary (1°) alcohols. Ketones are REDUCED to secondary (2°) alcohols. CH3CHO + 2[H] ...
... sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) (sodium borohydride), NaBH4 aqueous or alcoholic solution Nucleophilic addition (also reduction as it is addition of H¯) H¯ (hydride ion) Alcohols Aldehydes are REDUCED to primary (1°) alcohols. Ketones are REDUCED to secondary (2°) alcohols. CH3CHO + 2[H] ...
Chapter_Sixteen_lecture
... ketones by loss of alcohol and establish an equilibrium with the aldehyde or ketone. – When equilibrium is reached, very little hemiacetal is present. ...
... ketones by loss of alcohol and establish an equilibrium with the aldehyde or ketone. – When equilibrium is reached, very little hemiacetal is present. ...
This is the first exam with targeted syntheses that you
... Most of the reactions of aldehydes and ketones in these chapters are nucleophilic addition reactions. The oxygen in C=O polarizes the bond. Therefore, while electrophilic addition (electrophile first, followed by nucleophile) was favored for the comparatively non-polar, electron-rich alkene, carbony ...
... Most of the reactions of aldehydes and ketones in these chapters are nucleophilic addition reactions. The oxygen in C=O polarizes the bond. Therefore, while electrophilic addition (electrophile first, followed by nucleophile) was favored for the comparatively non-polar, electron-rich alkene, carbony ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
11. Oxidation of alcohols, hydrolysis of halogenoalkanes and
... Structural formula: CH3CH(OH)CH3 ...
... Structural formula: CH3CH(OH)CH3 ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
File
... 1. Name the type of reaction and draw structural diagrams to represent the following reactions: a) Reaction of propene to form an alcohol. b) Reaction of 3-methyl-2-pentanol with HBr. c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and ...
... 1. Name the type of reaction and draw structural diagrams to represent the following reactions: a) Reaction of propene to form an alcohol. b) Reaction of 3-methyl-2-pentanol with HBr. c) Reaction of 1-bromo-3-methylpropane with sodium hydroxide. 2. Write balanced equations and name the reactants and ...
benzylic alcohols
... Electron-withdrawing substituents decrease the yields and orthosubstituensts hinder the reaction e.g. neither 2, 4 dinitro-nor 2, 6 dimethyl benzaldehyde can be prepared in this way. The reaction involves hydride –ion transfer. At the acidity employed, the quaternary benzyl salt is hydrolyzed to the ...
... Electron-withdrawing substituents decrease the yields and orthosubstituensts hinder the reaction e.g. neither 2, 4 dinitro-nor 2, 6 dimethyl benzaldehyde can be prepared in this way. The reaction involves hydride –ion transfer. At the acidity employed, the quaternary benzyl salt is hydrolyzed to the ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much better leaving group) is the leaving group in this reaction (step 2) and the produc ...
... hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much better leaving group) is the leaving group in this reaction (step 2) and the produc ...
handout alkenes from alcohols
... hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much better leaving group) is the leaving group in this reaction (step 2) and the produc ...
... hydroxyl group in R-OH is a poor-leaving group because it would have to leave as a hydroxide ion (HO-). Therefore, an acid is used to protonate the alcohol (step 1) and form R-OH2+ (see Figure 2). Thus, water (a much better leaving group) is the leaving group in this reaction (step 2) and the produc ...
CN>Chapter 22CT>Carbonyl Alpha
... In the haloform reaction, there is an -substitution whereby the methyl ketone is trihalogenated at the position. The trihalomethyl group is displaced by –OH. This reaction is used as a test for methyl ketones. + reactions would come from reactions a, and b; while – reactions would come from c, d, ...
... In the haloform reaction, there is an -substitution whereby the methyl ketone is trihalogenated at the position. The trihalomethyl group is displaced by –OH. This reaction is used as a test for methyl ketones. + reactions would come from reactions a, and b; while – reactions would come from c, d, ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
Organic Synthesis
... CH3 H The methyl group has been written out in full to make it obvious. The same result could be obtained using option 3, the Wittig reaction: ...
... CH3 H The methyl group has been written out in full to make it obvious. The same result could be obtained using option 3, the Wittig reaction: ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.