General properties of urea : It is water
... amide (twice over) Its properties are essentially those of amides . ...
... amide (twice over) Its properties are essentially those of amides . ...
Iodoform Test - organicchem.org
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
Spring 2015 CH 421 Name ________________________________________ 1. Consider the structures of vanillin and vanillyl alcohol.
... 6. If the reduction reaction went to about 90% completion (i.e. about 10% of vanillin is still left), both vanillin and vanillyl alcohol would be isolated by precipitation from water, since they are both insoluble in water. Considering their physical properties and the methods ...
... 6. If the reduction reaction went to about 90% completion (i.e. about 10% of vanillin is still left), both vanillin and vanillyl alcohol would be isolated by precipitation from water, since they are both insoluble in water. Considering their physical properties and the methods ...
Procedure - organicchem.org
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
... formation of an enolate which reacts with the electrophilic I2 to generate an -iodomethylketone. Addition of two more equivalents of base and I2 lead to formation of the -triiodoketone. Hydroxide ion then reacts with the carbonyl carbon of the ketone in a nucleophilic acyl substitution, liberating ...
Pre Ch15 HW
... unsaturated hydrocarbon (628) geometric (cis-trans) isomers (628) alkyne (CnH2n–2) (630) aromatic hydrocarbon (631) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (633) Section 15.3 alkyl group (635) addition reaction (635) elimination reaction (635) substitution reaction (636) Section 15.4 alcohol ( ...
... unsaturated hydrocarbon (628) geometric (cis-trans) isomers (628) alkyne (CnH2n–2) (630) aromatic hydrocarbon (631) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (633) Section 15.3 alkyl group (635) addition reaction (635) elimination reaction (635) substitution reaction (636) Section 15.4 alcohol ( ...
Review sheet - Paws.wcu.edu.
... Chapter 10: all except 10.9 Chapter 11: all except 1, 12 and 13 Chapter 13: sections 13.8 – 13.11 only Chapter 14: section 14.1 only Chapter 15: sections 2, 3, 5, 6, and 10 only Chapter 16: all except 16.8, 16.9 Chapter 17: all except 17.10, 17.11 Chapter 18: sections 1, 2, 3 Chapter 19: all except ...
... Chapter 10: all except 10.9 Chapter 11: all except 1, 12 and 13 Chapter 13: sections 13.8 – 13.11 only Chapter 14: section 14.1 only Chapter 15: sections 2, 3, 5, 6, and 10 only Chapter 16: all except 16.8, 16.9 Chapter 17: all except 17.10, 17.11 Chapter 18: sections 1, 2, 3 Chapter 19: all except ...
Grignard Reaction - This is Synthesis
... Heating beyond the boiling point of the employed solvent allows reduction of the reaction time. Typically the formation of the Grignard reagent as well as the Grignard reaction itself require 30-60 minutes at reflux. Under sealed vessel conditions both steps, especially the Grignard reaction, can be ...
... Heating beyond the boiling point of the employed solvent allows reduction of the reaction time. Typically the formation of the Grignard reagent as well as the Grignard reaction itself require 30-60 minutes at reflux. Under sealed vessel conditions both steps, especially the Grignard reaction, can be ...
Organic Reactions Worksheet
... iv) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reaction, use [O] convention c. Using any secondary alcohol: i) Give the displayed (structural formula) which it could be oxidized to ii) State which homologous series the products are part of iii) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reac ...
... iv) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reaction, use [O] convention c. Using any secondary alcohol: i) Give the displayed (structural formula) which it could be oxidized to ii) State which homologous series the products are part of iii) Write the balanced equation for each oxidizing reac ...
ppt
... Copyright © J. M. McBride 2010. Some rights reserved. Except for cited third-party materials, and those used by visiting speakers, all content is licensed under a Creative Commons License (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0). Use of this content constitutes your acceptance of the noted license ...
... Copyright © J. M. McBride 2010. Some rights reserved. Except for cited third-party materials, and those used by visiting speakers, all content is licensed under a Creative Commons License (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0). Use of this content constitutes your acceptance of the noted license ...
- EdShare - University of Southampton
... They can be formed in elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes. An example of this is the reaction between 2-bromopentane and hot ethanolic KOH. Using your knowledge of reaction mechanisms, draw appropriate curly arrows to complete the elimination mechanism for this reaction, forming the ...
... They can be formed in elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes. An example of this is the reaction between 2-bromopentane and hot ethanolic KOH. Using your knowledge of reaction mechanisms, draw appropriate curly arrows to complete the elimination mechanism for this reaction, forming the ...
- EdShare - University of Southampton
... Draw the mechanism of the reaction between CH3CH2CH2Br and hot KOH(aq) using the curly arrow model. State the name of the mechanism, and include any relevant dipoles. ...
... Draw the mechanism of the reaction between CH3CH2CH2Br and hot KOH(aq) using the curly arrow model. State the name of the mechanism, and include any relevant dipoles. ...
paper 14 organic synthesis: disconnection approach - e
... Syllabus for Post-Graduate Course in Chemistry ...
... Syllabus for Post-Graduate Course in Chemistry ...
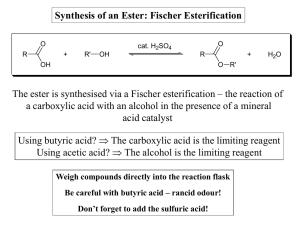
Synthesis of an Ester: Fischer Esterification The ester is synthesised
... As a result, they are partially extracted into the aqueous layer during work-up, reducing the amount recovered. ...
... As a result, they are partially extracted into the aqueous layer during work-up, reducing the amount recovered. ...
- professional publication
... Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions Effect of Substituent Groups, Determination of Orientation, Determination of Relative Reactivity, Classification of Substituent Groups, Mechanism of Nitration, Sulphonation, Halogenation, Friedel Craft’s Alkylation and Friedel Craft’s Acylation, Reactivity and Or ...
... Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions Effect of Substituent Groups, Determination of Orientation, Determination of Relative Reactivity, Classification of Substituent Groups, Mechanism of Nitration, Sulphonation, Halogenation, Friedel Craft’s Alkylation and Friedel Craft’s Acylation, Reactivity and Or ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... starting material) are both positively charged. Electronegative groups would destabilize both. However, the effect may be greater on the reactant because the positive charge is transferred to the carbonyl carbon by both an inductive and resonance effect, while in the intermediate there is only an in ...
... starting material) are both positively charged. Electronegative groups would destabilize both. However, the effect may be greater on the reactant because the positive charge is transferred to the carbonyl carbon by both an inductive and resonance effect, while in the intermediate there is only an in ...
Document
... The pKb values of some amines are shown in Table 16 of the Data Booklet. Write an equation for the reaction of ethylamine with water. State and explain how the basicity of ethylamine compares to that of ammonia. ...
... The pKb values of some amines are shown in Table 16 of the Data Booklet. Write an equation for the reaction of ethylamine with water. State and explain how the basicity of ethylamine compares to that of ammonia. ...
organic quiz 2
... 17) In a reaction between hex-2-ene and hydrochloric acid (aqueous hydrogen chloride), which of the following will be the product(s)? a) 1-chlorohexane only b) 2-chlorohexane only c) 3-chlorohexane only d) both (b) and (c) 18) DNA is a natural polymer composed of a) glucose monomers b) nucleotide mo ...
... 17) In a reaction between hex-2-ene and hydrochloric acid (aqueous hydrogen chloride), which of the following will be the product(s)? a) 1-chlorohexane only b) 2-chlorohexane only c) 3-chlorohexane only d) both (b) and (c) 18) DNA is a natural polymer composed of a) glucose monomers b) nucleotide mo ...
Organic Synthesis Part 2
... Reaction with carbonyl compounds is by donation of hydride, to give a transient alkoxide/alane pair which combines to give an alkoxytrihydroaluminate. This can go on to donate the remaining three hydrides in the same way, although at a reduced rate. We can exploit this by deliberately making trialko ...
... Reaction with carbonyl compounds is by donation of hydride, to give a transient alkoxide/alane pair which combines to give an alkoxytrihydroaluminate. This can go on to donate the remaining three hydrides in the same way, although at a reduced rate. We can exploit this by deliberately making trialko ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... Consider the atomic number of the atoms bonded directly to a specific sp2 carbon 1,1 on same side = Z ...
... Consider the atomic number of the atoms bonded directly to a specific sp2 carbon 1,1 on same side = Z ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... Acetals are used to “protect” the carbonyl groups of aldehydes and ketones when one wants to have some other part of the molecule react without affecting the aldehyde or ketone functional group. They can be used this way because they are fairly unreactive and the carbonyl functional group can be reg ...
... Acetals are used to “protect” the carbonyl groups of aldehydes and ketones when one wants to have some other part of the molecule react without affecting the aldehyde or ketone functional group. They can be used this way because they are fairly unreactive and the carbonyl functional group can be reg ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... yields an alcohol • Nucleophilic addition of the equivalent of a carbon anion, or carbanion. A carbon–magnesium bond is strongly polarized, so a Grignard reagent reacts for all practical purposes as R : MgX +. ...
... yields an alcohol • Nucleophilic addition of the equivalent of a carbon anion, or carbanion. A carbon–magnesium bond is strongly polarized, so a Grignard reagent reacts for all practical purposes as R : MgX +. ...
Reductive etherification of substituted cyclohexanones with
... donors. With MeOH only acetal formation occurred. Acid sites appear to be essential, since with Na-MCM-22 as catalyst in the etherification of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone only a 5% yield was obtained after 24 h. The reductive etherification is irreversible. Starting from the ether, water and acetone i ...
... donors. With MeOH only acetal formation occurred. Acid sites appear to be essential, since with Na-MCM-22 as catalyst in the etherification of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone only a 5% yield was obtained after 24 h. The reductive etherification is irreversible. Starting from the ether, water and acetone i ...
No Slide Title
... Consider the atomic number of the atoms bonded directly to a specific sp2 carbon 1,1 on same side = Z ...
... Consider the atomic number of the atoms bonded directly to a specific sp2 carbon 1,1 on same side = Z ...
9. E1: Alkenes from alcohols - Web Pages
... carbocation. In the following step (step 3), a molecule of water deprotonates the carbocation at either of the adjacent carbons. The remaining electrons flow towards the positive charge producing a π–bond between the carbons and forming a double bond. ...
... carbocation. In the following step (step 3), a molecule of water deprotonates the carbocation at either of the adjacent carbons. The remaining electrons flow towards the positive charge producing a π–bond between the carbons and forming a double bond. ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.