* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
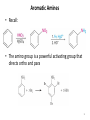
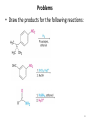
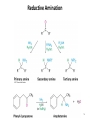
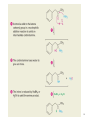
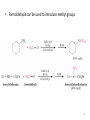
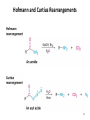
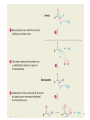
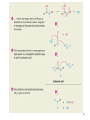
Aromatic Amines • Recall: • The amino group is a powerful activating group that directs ortho and para 1 Reduction of Nitro Compounds • Catalytic hydrogenation: • Reduction with finely divided metal powders: 23.11 Synthesis of Amines 2 Reduction of Nitro Compounds • LiAlH4 and NaBH4 fail to provide the amine 23.11 Synthesis of Amines 3 Problems • Draw the products for the following reactions: 4 Reductive Amination 5 6 7 • Sodium cyanoborohydride, NaBH3CN and sodium triacetoxyborohydride, NaBH(OAc)3, are common choices in the lab for the reduction step • Formaldehyde can be used to introduce methyl groups 9 23.7 Alkylation and Acylation Reactions of Amines 10 Problem • Draw the complete mechanism for the following problem: 11 Hofmann and Curtius Rearrangements 12 The Hofmann Rearrangement • Sometimes called the Hofmann hypobromite reaction • Cl2 is sometimes used in place of Br2 • A primary amide is the required starting compound 23.11 Synthesis of Amines 13 14 15 The Curtius Rearrangement • Acyl azides provide access to primary amines via an isocyanate • Concerted reaction 16 The Curtius Rearrangement • The resulting isocyanate can be hydrated in acid or base • Carbamic acids spontaneously decarboxylate 23.11 Synthesis of Amines 17 Hofmann vs. Curtius • In the Hofmann rearrangement, the isocyanate cannot be isolated as the reaction is carried out in aqueous base 23.11 Synthesis of Amines 18 Curtius and Hofmann Rearrangements • In both of these reactions, the alkyl group migrates with complete retention of configuration 23.11 Synthesis of Amines 19 Problems • Draw the mechanisms for the following rxns 20 21 Acylation of Amines • Amines can be converted into amides by reaction with acid chlorides, anhydrides, or esters. 22 23 • See section 21.8 for review of these rxns 24