Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry
... also contain other elements. In fact, many common groups of atoms can occur within organic molecules, these groups of atoms are called functional groups. One good example is the hydroxyl functional group. The hydroxyl group consists of a single oxygen atom bound to a single hydrogen atom (-OH). The ...
... also contain other elements. In fact, many common groups of atoms can occur within organic molecules, these groups of atoms are called functional groups. One good example is the hydroxyl functional group. The hydroxyl group consists of a single oxygen atom bound to a single hydrogen atom (-OH). The ...
Naming Organic Compounds I
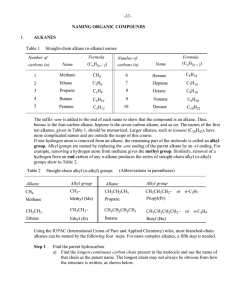
... ten alkanes, given in Table 1, should be memorized. Larger alkanes, such as icosane (C20H42), have more complicated names and are outside the scope of this course. If one hydrogen atom is removed from an alkane, the remaining part of the molecule is called an alkyl group. Alkyl groups are named by r ...
... ten alkanes, given in Table 1, should be memorized. Larger alkanes, such as icosane (C20H42), have more complicated names and are outside the scope of this course. If one hydrogen atom is removed from an alkane, the remaining part of the molecule is called an alkyl group. Alkyl groups are named by r ...
IUPAC System of Nomenclature
... CH3 CH3 CH2 CHCH2 CH2 CH3 is regarded as being "made" from the following parent: ...
... CH3 CH3 CH2 CHCH2 CH2 CH3 is regarded as being "made" from the following parent: ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... 30-C1.2k identify and describe significant organic compounds in daily life, demonstrating generalized knowledge of their origins and applications 30-C1.3k name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsatur ...
... 30-C1.2k identify and describe significant organic compounds in daily life, demonstrating generalized knowledge of their origins and applications 30-C1.3k name and draw structural, condensed structural and line diagrams and formulas, using IUPAC nomenclature guidelines, for saturated and unsatur ...
中国科学技术大学有机合成讲义-2
... permanganate in the presence of t-butyl alcohol and aqueous NaH2PO4 was shown to effectively oxidize the aldehyde in the following polyoxygenated substrate to the corresponding carboxylic acid whereas Jones reagent, RuCl3(H2O)n-NaIO4, and silver oxide failed. ...
... permanganate in the presence of t-butyl alcohol and aqueous NaH2PO4 was shown to effectively oxidize the aldehyde in the following polyoxygenated substrate to the corresponding carboxylic acid whereas Jones reagent, RuCl3(H2O)n-NaIO4, and silver oxide failed. ...
108B Carbohydrate Activity KEY
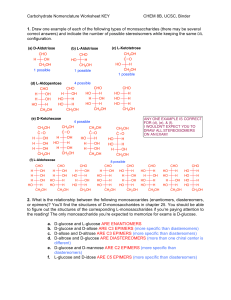
... 6. Draw Haworth projections and the chair conformation for the following aldohexoses using the backbone structures from #5. Consult Fig 25.3 of McMurry; memorize the structure of DGlucose for the final exam. Left or right side on Fischer projection ...
... 6. Draw Haworth projections and the chair conformation for the following aldohexoses using the backbone structures from #5. Consult Fig 25.3 of McMurry; memorize the structure of DGlucose for the final exam. Left or right side on Fischer projection ...
7: Reactions of Haloalkanes, Alcohols, and Amines. Nucleophilic
... In fact, when R3 C-Br has fewer than two CH3 groups, it does not react at all by the S N1 mechanism (see Figure7.13). These changes in SN1 rates result from the effect of alkyl groups such as CH3 on the stability of R3 C+ that forms in the first step of the SN1 mechanism. Carbocation Stability. The ...
... In fact, when R3 C-Br has fewer than two CH3 groups, it does not react at all by the S N1 mechanism (see Figure7.13). These changes in SN1 rates result from the effect of alkyl groups such as CH3 on the stability of R3 C+ that forms in the first step of the SN1 mechanism. Carbocation Stability. The ...
CHEM 203 Material
... Linear geometry of the carbon atoms in acetylene and related structures as predicted by VSEPR and as confirmed by experiment Association of linear geometry about a carbon atom with sp hybridization Principle: atoms can produce bonded states in which significant electrostatic unbalances exist Formal ...
... Linear geometry of the carbon atoms in acetylene and related structures as predicted by VSEPR and as confirmed by experiment Association of linear geometry about a carbon atom with sp hybridization Principle: atoms can produce bonded states in which significant electrostatic unbalances exist Formal ...
Biomass Program
... for syngas production, however, are based on natural gas, the cheapest option being remote or stranded reserves. Economic considerations dictate that the production of liquid fuels from syngas today translates into the use of natural gas as the hydrocarbon source. Nevertheless, the syngas production ...
... for syngas production, however, are based on natural gas, the cheapest option being remote or stranded reserves. Economic considerations dictate that the production of liquid fuels from syngas today translates into the use of natural gas as the hydrocarbon source. Nevertheless, the syngas production ...
Reactions
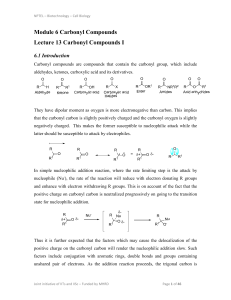
... Alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or ketones using a modified form of CrO3 called PCC for pyridinium chlorochromate, (C5H6NCrO3Cl). It is a milder reagent and if you use it carefully you can stop the reaction at the intermediate ...
... Alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or ketones using a modified form of CrO3 called PCC for pyridinium chlorochromate, (C5H6NCrO3Cl). It is a milder reagent and if you use it carefully you can stop the reaction at the intermediate ...
Preliminary Screening — Technical and Economic Assessment of Synthesis Gas
... production operation in a gas-to-liquids plant amounts to greater than half of the capital cost of the plant. The choice of technology for syngas production also depends on the scale of the synthesis operation. Syngas production from solid fuels can require an even greater capital investment with th ...
... production operation in a gas-to-liquids plant amounts to greater than half of the capital cost of the plant. The choice of technology for syngas production also depends on the scale of the synthesis operation. Syngas production from solid fuels can require an even greater capital investment with th ...
Perfumery_Synthetics_and_Isolates_pg_283
... found that on chromic oxidation linalool yielded an aldehyde similar to or identical with citral. This was rather puzzling since it was already known that the primary alcohol, geraniol, gave citral on similar treatment and that linalool possessed an asymmetric carbon atom since it exhibited optical ...
... found that on chromic oxidation linalool yielded an aldehyde similar to or identical with citral. This was rather puzzling since it was already known that the primary alcohol, geraniol, gave citral on similar treatment and that linalool possessed an asymmetric carbon atom since it exhibited optical ...
File
... 6. How can you tell the difference between a “cis” and “trans” isomer? In what types of hydrocarbons can they be found? 7. What is an aromatic compound, and what is the simplest aromatic structure? 8. Do aromatic hydrocarbons react more than saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbons? Explain why. 9. Wha ...
... 6. How can you tell the difference between a “cis” and “trans” isomer? In what types of hydrocarbons can they be found? 7. What is an aromatic compound, and what is the simplest aromatic structure? 8. Do aromatic hydrocarbons react more than saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbons? Explain why. 9. Wha ...
2 - Humble ISD
... groups are on the lowest numbers Methyl is on carbon #2 of the parent chain Methyl is on carbon #4 of the parent chain ...
... groups are on the lowest numbers Methyl is on carbon #2 of the parent chain Methyl is on carbon #4 of the parent chain ...
CH 3
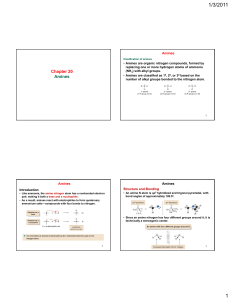
... H In aromatic compounds the C atoms are sp2 hybrids, so that each C atom has one remaining p-electron involved in p-bonding Three sp2 hybrid orbitals arrange themselves as far apart as possible which is at 120° to each other in a plane. The remaining p orbital is at right angles to them. Each carbon ...
... H In aromatic compounds the C atoms are sp2 hybrids, so that each C atom has one remaining p-electron involved in p-bonding Three sp2 hybrid orbitals arrange themselves as far apart as possible which is at 120° to each other in a plane. The remaining p orbital is at right angles to them. Each carbon ...
CH 3
... H In aromatic compounds the C atoms are sp2 hybrids, so that each C atom has one remaining p-electron involved in p-bonding Three sp2 hybrid orbitals arrange themselves as far apart as possible which is at 120° to each other in a plane. The remaining p orbital is at right angles to them. Each carbon ...
... H In aromatic compounds the C atoms are sp2 hybrids, so that each C atom has one remaining p-electron involved in p-bonding Three sp2 hybrid orbitals arrange themselves as far apart as possible which is at 120° to each other in a plane. The remaining p orbital is at right angles to them. Each carbon ...
Ans:- (i) Gluconic acid - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2, Kribhco, Surat
... with increasing dilution the molar conductance increases rapidly because of greater extent of ionization at greater dilution. These are dissociated more or less completely at low dilutions. Their molar conductances therefore show slight increase with increasing dilution. At low conc, the interionic ...
... with increasing dilution the molar conductance increases rapidly because of greater extent of ionization at greater dilution. These are dissociated more or less completely at low dilutions. Their molar conductances therefore show slight increase with increasing dilution. At low conc, the interionic ...
Hydrogenation, Transfer Hydrogenat- ion and Hydrogen Transfer Reactions
... The word “chirality” is derived from the Greek, χειρ (kheir) which means “hand”. Our hands cannot be superimposed onto each other but are mirror images of each other. Chirality can be traced back to the beginning of the 1900s, when the phrase was first introduced by Lord Kelvin,3 whose original stat ...
... The word “chirality” is derived from the Greek, χειρ (kheir) which means “hand”. Our hands cannot be superimposed onto each other but are mirror images of each other. Chirality can be traced back to the beginning of the 1900s, when the phrase was first introduced by Lord Kelvin,3 whose original stat ...
Example 4
... Break the O-H bond of one alcohol. Break one of the C=O Break the H-H bond. bonds. Form a bond between the carbonyl carbon and the O of Break one of the C=O the alcohol. Form a bond between the H and the O of the bonds. Form a bond carbonyl to form a HEMIACETAL. between the alpha-carbon and one H. F ...
... Break the O-H bond of one alcohol. Break one of the C=O Break the H-H bond. bonds. Form a bond between the carbonyl carbon and the O of Break one of the C=O the alcohol. Form a bond between the H and the O of the bonds. Form a bond carbonyl to form a HEMIACETAL. between the alpha-carbon and one H. F ...
A Crash Course In Organic Chemistry
... portion of a molecule that undergoes predictable reactions. All other organic compounds can be considered to be derivatives of hydrocarbons ...
... portion of a molecule that undergoes predictable reactions. All other organic compounds can be considered to be derivatives of hydrocarbons ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.