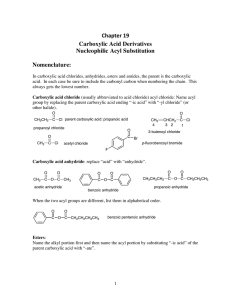
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl
... As we will see, there are two opposing trends: the X-group in each of our carboxylic acid derivatives has a lone pair that can donate electrons to the carbonyl carbon and make the carbonyl carbon LESS electron rich and all of the X-groups have an atom that is MORE electronegative than the carbonyl c ...
... As we will see, there are two opposing trends: the X-group in each of our carboxylic acid derivatives has a lone pair that can donate electrons to the carbonyl carbon and make the carbonyl carbon LESS electron rich and all of the X-groups have an atom that is MORE electronegative than the carbonyl c ...
lec-3- 211( Elim+ Re..
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
dr.ebtehal Lec3
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
Amino Acids and Proteins
... 28.1A General Features of α-Amino Acids The 20 amino acids that occur naturally in proteins differ in the identity of the R group bonded to the α carbon. The R group is called the side chain of the amino acid. The simplest amino acid, called glycine, has R = H. All other amino acids (R ñ H) have a s ...
... 28.1A General Features of α-Amino Acids The 20 amino acids that occur naturally in proteins differ in the identity of the R group bonded to the α carbon. The R group is called the side chain of the amino acid. The simplest amino acid, called glycine, has R = H. All other amino acids (R ñ H) have a s ...
OC 2/e 9 Alcohols
... chromic acid oxidation of a CHO group, it is the hydrated form that is oxidized O R- C-H ...
... chromic acid oxidation of a CHO group, it is the hydrated form that is oxidized O R- C-H ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... Part two of this thesis will discuss research into the syntheses of a novel series of ruthenium complexes and their utilization as ester hydrogenation catalysts. Reduction of esters to the corresponding alcohols is normally carried out using LiAlH4, a stoichiometric type of reaction which produces l ...
... Part two of this thesis will discuss research into the syntheses of a novel series of ruthenium complexes and their utilization as ester hydrogenation catalysts. Reduction of esters to the corresponding alcohols is normally carried out using LiAlH4, a stoichiometric type of reaction which produces l ...
13C NMR - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... tells you the number of chemically nonequivalent CH 3 , CH2 , and CH carbons C do not appear–they must be identifed by comparison with the normal 13C NMR spectrum ways to present a DEPT 13C NMR spectrum: ...
... tells you the number of chemically nonequivalent CH 3 , CH2 , and CH carbons C do not appear–they must be identifed by comparison with the normal 13C NMR spectrum ways to present a DEPT 13C NMR spectrum: ...
chemistry - Textbooks Online
... Chemistry, a branch of science concerned with the properties, structures and composition of substances and their reactions with one another. Inorganic Chemistry studies the preparation, properties and reactions of all chemical elements and their compounds, except those of carbon. Organic Chemistry s ...
... Chemistry, a branch of science concerned with the properties, structures and composition of substances and their reactions with one another. Inorganic Chemistry studies the preparation, properties and reactions of all chemical elements and their compounds, except those of carbon. Organic Chemistry s ...
Organic Chemistry for Highschool Biology students
... 5. Very often, a molecule can be considered to be part of many families because they have more than one functional group. Odor 11 is a good example of this situation. ...
... 5. Very often, a molecule can be considered to be part of many families because they have more than one functional group. Odor 11 is a good example of this situation. ...
amines - Gneet`s
... Pure amines are almost colourless but develop colour on keeping in air for long time because amines are readily oxidized in air to form coloured oxidation product. Solubility Lower members are soluble in water, but solubility decreases with increase in molecular weight. Aromatic amines are insoluble ...
... Pure amines are almost colourless but develop colour on keeping in air for long time because amines are readily oxidized in air to form coloured oxidation product. Solubility Lower members are soluble in water, but solubility decreases with increase in molecular weight. Aromatic amines are insoluble ...
Lithium Bromide Original Commentary
... Alkyl and Alkenyl Bromides. LiBr has been extensively used as a source of bromide in nucleophilic substitution and addition reactions. Interconversion of halides2 and transformation of alcohols to alkyl bromides via the corresponding sulfonate3 or trifluoroacetate4 have been widely used in organic s ...
... Alkyl and Alkenyl Bromides. LiBr has been extensively used as a source of bromide in nucleophilic substitution and addition reactions. Interconversion of halides2 and transformation of alcohols to alkyl bromides via the corresponding sulfonate3 or trifluoroacetate4 have been widely used in organic s ...
Organic Chemistry
... in the electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes, so the product formed is the one with the halogen substituent upon the more highly substituted carbon. Also, rearrangement (hydride or methyl shift to form a more stable carbocation) might occur, typical of reactions that have a carbocation intermediat ...
... in the electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes, so the product formed is the one with the halogen substituent upon the more highly substituted carbon. Also, rearrangement (hydride or methyl shift to form a more stable carbocation) might occur, typical of reactions that have a carbocation intermediat ...
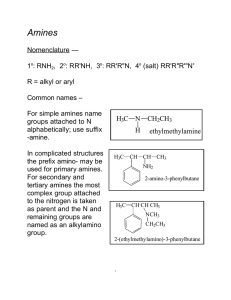
226 amines lec
... 1o: RNH2, 2o: RR'NH, 3o: RR'R"N, 4o (salt) RR'R"R'"N+ R = alkyl or aryl Common names – For simple amines name groups attached to N alphabetically; use suffix -amine. In complicated structures the prefix amino- may be used for primary amines. For secondary and tertiary amines the most complex group a ...
... 1o: RNH2, 2o: RR'NH, 3o: RR'R"N, 4o (salt) RR'R"R'"N+ R = alkyl or aryl Common names – For simple amines name groups attached to N alphabetically; use suffix -amine. In complicated structures the prefix amino- may be used for primary amines. For secondary and tertiary amines the most complex group a ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.