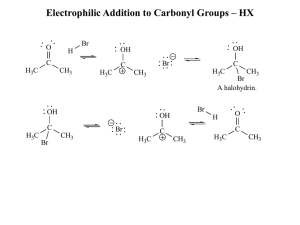
Electrophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups – HX
... Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups: Enolate and Aldol Reactions • This reaction is known as the aldol reaction. It takes an aldehyde and converts it into an alcohol (while extending the carbon chain). • If an aldol reaction is worked up under acidic conditions, an E2 reaction will follow, giv ...
... Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups: Enolate and Aldol Reactions • This reaction is known as the aldol reaction. It takes an aldehyde and converts it into an alcohol (while extending the carbon chain). • If an aldol reaction is worked up under acidic conditions, an E2 reaction will follow, giv ...
N-oxidation - WordPress.com
... The dichloroacetamide portion of the molecule undergoes oxidative dechlorination to yield a chemically reactive oxamyl chloride intermediate that can react with water to form the corresponding oxamic acid metabolite or can acylate microsomal proteins. Thus, it appears that in several instances, oxi ...
... The dichloroacetamide portion of the molecule undergoes oxidative dechlorination to yield a chemically reactive oxamyl chloride intermediate that can react with water to form the corresponding oxamic acid metabolite or can acylate microsomal proteins. Thus, it appears that in several instances, oxi ...
chapter-15
... The Carbonyl Group In this and several following chapters, we study the physical and chemical properties of classes of compounds containing the carbonyl group, C=O • aldehydes and ketones (Chapter 13) ...
... The Carbonyl Group In this and several following chapters, we study the physical and chemical properties of classes of compounds containing the carbonyl group, C=O • aldehydes and ketones (Chapter 13) ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... dissociation, but the dissociation is followed by loss of a proton from the b-carbon (attached to the C+) rather than by substitution. E1 & SN1 normally occur in competition, whenever an alkyl halide is treated in a protic solvent with a nonbasic, poor nucleophile. Note: The best E1 substrates a ...
... dissociation, but the dissociation is followed by loss of a proton from the b-carbon (attached to the C+) rather than by substitution. E1 & SN1 normally occur in competition, whenever an alkyl halide is treated in a protic solvent with a nonbasic, poor nucleophile. Note: The best E1 substrates a ...
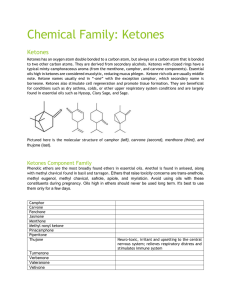
Chemical Family Ketones
... Chemical Family: Ketones Ketones Ketones has an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon atom, but always on a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms. They are derived from secondary alcohols. Ketones with closed rings have a typical minty-camphoraceous aroma (from the menthone, camphor, ...
... Chemical Family: Ketones Ketones Ketones has an oxygen atom double bonded to a carbon atom, but always on a carbon atom that is bonded to two other carbon atoms. They are derived from secondary alcohols. Ketones with closed rings have a typical minty-camphoraceous aroma (from the menthone, camphor, ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... dissociation, but the dissociation is followed by loss of a proton from the b-carbon (attached to the C+) rather than by substitution. E1 & SN1 normally occur in competition, whenever an alkyl halide is treated in a protic solvent with a nonbasic, poor nucleophile. Note: The best E1 substrates a ...
... dissociation, but the dissociation is followed by loss of a proton from the b-carbon (attached to the C+) rather than by substitution. E1 & SN1 normally occur in competition, whenever an alkyl halide is treated in a protic solvent with a nonbasic, poor nucleophile. Note: The best E1 substrates a ...
Alkyl Halides SN and E reactions
... dissociation, but the dissociation is followed by loss of a proton from the b-carbon (attached to the C+) rather than by substitution. E1 and SN1 normally occur in competition, whenever an alkyl halide is treated in a protic solvent with a nonbasic, poor nucleophile. Note: The best E1 substrates ...
... dissociation, but the dissociation is followed by loss of a proton from the b-carbon (attached to the C+) rather than by substitution. E1 and SN1 normally occur in competition, whenever an alkyl halide is treated in a protic solvent with a nonbasic, poor nucleophile. Note: The best E1 substrates ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... eliminations, often with his long-time collaborator E. D. Hughes, led to I ncorporation into the standard language of chemistry of such words as nucleophile, electrophile, inductive and mesomeric (resonance) effects, and such symbols as SN1, SN2, E1, E2, BAC2 and others. His monumental book "Structu ...
... eliminations, often with his long-time collaborator E. D. Hughes, led to I ncorporation into the standard language of chemistry of such words as nucleophile, electrophile, inductive and mesomeric (resonance) effects, and such symbols as SN1, SN2, E1, E2, BAC2 and others. His monumental book "Structu ...
Development of New Synthetic Routes to Organoboronates by Catalytic Allylic Substitution and
... activation of organic substrates such as alkanes and aromatics.138-166 Extensive mechanistic studies have revealed metal boryl complexes167-169 as key intermediates. For example, Hartwig and co-workers138 have demonstrated that alkanes (16) may undergo regioselective terminal functionalization by c ...
... activation of organic substrates such as alkanes and aromatics.138-166 Extensive mechanistic studies have revealed metal boryl complexes167-169 as key intermediates. For example, Hartwig and co-workers138 have demonstrated that alkanes (16) may undergo regioselective terminal functionalization by c ...
Manganese-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Alkyl Iodides
... All reactions were carried out in flame-dried or oven dried (150 'C) glassware under argon using Schlenk techniques. THF was either distilled or vacuum transferred from sodium benzophenone ketyl, the solvents were stored in Schlenk flasks with Teflon screw caps. Alternatively solvents were stored in ...
... All reactions were carried out in flame-dried or oven dried (150 'C) glassware under argon using Schlenk techniques. THF was either distilled or vacuum transferred from sodium benzophenone ketyl, the solvents were stored in Schlenk flasks with Teflon screw caps. Alternatively solvents were stored in ...
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups Constitutional Isomers
... III. Spectroscopy of Amines: MS • Nitrogen rule: if a molecule has an odd number of nitrogen ...
... III. Spectroscopy of Amines: MS • Nitrogen rule: if a molecule has an odd number of nitrogen ...
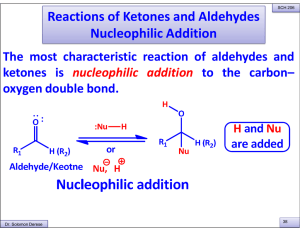
Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes Nucleophilic Addition
... spontaneously from the corresponding hydroxy aldehydes in water. ...
... spontaneously from the corresponding hydroxy aldehydes in water. ...
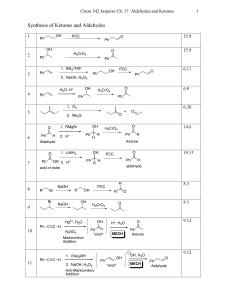
Aldehydes/Ketones Solutions
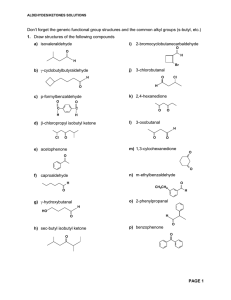
... 6. Write equations showing how the following transformations can be carried out. No mechanisms required but show all reagents and intermediate products formed. More than one step may be necessary a) O O C H ...
... 6. Write equations showing how the following transformations can be carried out. No mechanisms required but show all reagents and intermediate products formed. More than one step may be necessary a) O O C H ...
molecules
... and affords 80% cis- and 10% trans-stilbene oxides, respectively. This catalytic system exhibits a good regioselectivity for epoxidation of R-(+)-limonene. The ratio among 1,2- and 8,9-epoxides was found to be 2.3:1. Selective partial alkane hydroxylation is a particularly challenging problem in org ...
... and affords 80% cis- and 10% trans-stilbene oxides, respectively. This catalytic system exhibits a good regioselectivity for epoxidation of R-(+)-limonene. The ratio among 1,2- and 8,9-epoxides was found to be 2.3:1. Selective partial alkane hydroxylation is a particularly challenging problem in org ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... CH3CH2NH3+ is a weaker acid than NH4+; therefore, CH3CH2NH2 is a stronger base than NH3. ...
... CH3CH2NH3+ is a weaker acid than NH4+; therefore, CH3CH2NH2 is a stronger base than NH3. ...
Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... (1) Thionyl Chloride: We can treat alcohols with boiling thionyl chloride (SOCl2) to convert the alcohol to an alkyl chloride. This method is considerably milder than using concentrated hydrochloric acid and is useful when the molecule contains sensitive functional groups that would react with the s ...
... (1) Thionyl Chloride: We can treat alcohols with boiling thionyl chloride (SOCl2) to convert the alcohol to an alkyl chloride. This method is considerably milder than using concentrated hydrochloric acid and is useful when the molecule contains sensitive functional groups that would react with the s ...
13-Elimination Reactions
... SN1 mechanism, usually loses all the stereochemical information of the substrate as the reaction proceeds. The E2 mechanism, similar to the SN2 mechanism, is a concerted mechanism. A concerted reaction usually requires that the substrate have a specific conformation. The conformation must allow the ...
... SN1 mechanism, usually loses all the stereochemical information of the substrate as the reaction proceeds. The E2 mechanism, similar to the SN2 mechanism, is a concerted mechanism. A concerted reaction usually requires that the substrate have a specific conformation. The conformation must allow the ...
amine
... NAMING AMINES Amines may be named using either common or IUPAC rules For common names, list the alkyl groups attached to the N in ABC order and use the suffix –amine, which is written as one word Prefixes di- and tri- are used if identical groups are present ...
... NAMING AMINES Amines may be named using either common or IUPAC rules For common names, list the alkyl groups attached to the N in ABC order and use the suffix –amine, which is written as one word Prefixes di- and tri- are used if identical groups are present ...
Mannich Reaction - SUST Repository
... that the solubility of the Mannich derivatives increases in water due to protonation of basic amine nitrogen atom.48 Mulundocandin, a class of lipopeptides, showed excellent in vitro activity against Candida species. However, poor solubility restricts its widespread application. Lal et al.carried ou ...
... that the solubility of the Mannich derivatives increases in water due to protonation of basic amine nitrogen atom.48 Mulundocandin, a class of lipopeptides, showed excellent in vitro activity against Candida species. However, poor solubility restricts its widespread application. Lal et al.carried ou ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.