WRL0437.tmp
... *Secondary alkyl groups can be involved in either SN1 or SN2, depending on the conditions of the reaction. SN2 Mechanism: If the R group cannot support a stable carbocation, such as primary alkyl chains, SN2 reactions occur. The oxonium ion leaves as the halide attacks the same primary carbon, in on ...
... *Secondary alkyl groups can be involved in either SN1 or SN2, depending on the conditions of the reaction. SN2 Mechanism: If the R group cannot support a stable carbocation, such as primary alkyl chains, SN2 reactions occur. The oxonium ion leaves as the halide attacks the same primary carbon, in on ...
Chapter 13
... Clayton State University CHEM 1152 Chapter Objectives Dr. Susan F. Hornbuckle Chapter 13 1. Be able to name (using IUPAC nomenclature rules or common names if given in class) an alcohol and an ether given a structural formula. 2. Be able to draw an alcohol and an ether given the name of a compound ( ...
... Clayton State University CHEM 1152 Chapter Objectives Dr. Susan F. Hornbuckle Chapter 13 1. Be able to name (using IUPAC nomenclature rules or common names if given in class) an alcohol and an ether given a structural formula. 2. Be able to draw an alcohol and an ether given the name of a compound ( ...
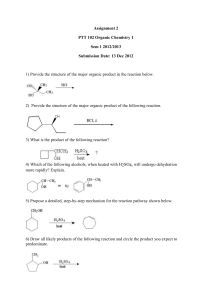
Assignment 2 Group A and B
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: ESTERIFICATION
... isn’t very soluble in water, but you are talking about quite small quantities of reaction mixture poured into quite a lot of water.) ...
... isn’t very soluble in water, but you are talking about quite small quantities of reaction mixture poured into quite a lot of water.) ...
Reactions to know from Chapters 17, 18, 19
... Alcohols can react with hemi-acetals to form acetals H+ ...
... Alcohols can react with hemi-acetals to form acetals H+ ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... Alcohols and phenolshave much higher boiling points than similar alkanes and alkyl halides ...
... Alcohols and phenolshave much higher boiling points than similar alkanes and alkyl halides ...
The Fermentation of Fruit
... The actual formula has 12 reactions but for this presentation we have used the simplified version In the 1930’s 2 German biochemists, G.Embdem & O.Meyerhof worked out the sequence of reactions of how glucose ferments. ...
... The actual formula has 12 reactions but for this presentation we have used the simplified version In the 1930’s 2 German biochemists, G.Embdem & O.Meyerhof worked out the sequence of reactions of how glucose ferments. ...
Part B: Short Written Response - bourre-chem-11
... number of carbons. Use the data in the table below to state the pattern between the molecular formula and the boiling point of alcohols. (2 marks) ...
... number of carbons. Use the data in the table below to state the pattern between the molecular formula and the boiling point of alcohols. (2 marks) ...
Alcohols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... –OH and an –OR bound to the same carbon. NOTE: An oxygen in a ring structure is considered part of an –OR group. ...
... –OH and an –OR bound to the same carbon. NOTE: An oxygen in a ring structure is considered part of an –OR group. ...
20130409085519
... The R group bonded to the oxygen will have a yl ending and the R group bonded to the C=O will have an oate ending. ...
... The R group bonded to the oxygen will have a yl ending and the R group bonded to the C=O will have an oate ending. ...
assignment 4-2
... Hydrogen bonding in organic compounds influences their characteristic properties, such as boiling point, solubility, etc. Alcohols show hydrogen bonding due to the presence of an oxygen atom. Which of the compounds shown below shows the greatest hydrogen-bonding effect? a. CH3 – CH2 – OH c. CH3 – OH ...
... Hydrogen bonding in organic compounds influences their characteristic properties, such as boiling point, solubility, etc. Alcohols show hydrogen bonding due to the presence of an oxygen atom. Which of the compounds shown below shows the greatest hydrogen-bonding effect? a. CH3 – CH2 – OH c. CH3 – OH ...
Problem Set Chapter 13 Solutions February 28, 2013 13.27 Draw
... 4.15 ppm = A CH2 group that is attached to an alkene with one neighboring proton 5.70 ppm = An alkene proton attached to a CH2 group (c) Propose a structure for A. ...
... 4.15 ppm = A CH2 group that is attached to an alkene with one neighboring proton 5.70 ppm = An alkene proton attached to a CH2 group (c) Propose a structure for A. ...
othschem.pbworks.com
... Esters are easily characterised by their distinct odour, often used in artificial flavouring. The reaction may occur as : Acid and heat Butanoic acid + methanol --> methyl butanoate + water (an apple odour) NOTE: when naming esters, the first part of the name is derived from the part that came from ...
... Esters are easily characterised by their distinct odour, often used in artificial flavouring. The reaction may occur as : Acid and heat Butanoic acid + methanol --> methyl butanoate + water (an apple odour) NOTE: when naming esters, the first part of the name is derived from the part that came from ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: THE REACTION WITH SODIUM
... b) There would be fizzing and a colourless gas would be given off which pops if tested with a lighted splint. (Note: You are probably too old and sophisticated to be told this, but an observation is what you see or detect by some other sense! You do not observe hydrogen being given off – that is a d ...
... b) There would be fizzing and a colourless gas would be given off which pops if tested with a lighted splint. (Note: You are probably too old and sophisticated to be told this, but an observation is what you see or detect by some other sense! You do not observe hydrogen being given off – that is a d ...
Chemistry Revision - Trinity School Nottingham
... polymers strengthAdding a side group to the monomer- eg CH3 Increasing the chain length of the polymer Substituting a Cl atom for an H atom in the ...
... polymers strengthAdding a side group to the monomer- eg CH3 Increasing the chain length of the polymer Substituting a Cl atom for an H atom in the ...
File
... obtain more useful alkanes and alkenes; describe addition reactions of alkenes, ie by ethene and propene, with: (i) hydrogen in the presence of a suitable catalyst, ie Ni, to form alkanes, (ii) halogens to form dihalogenoalkanes, including the use of bromine to detect the presence of a double C=C bo ...
... obtain more useful alkanes and alkenes; describe addition reactions of alkenes, ie by ethene and propene, with: (i) hydrogen in the presence of a suitable catalyst, ie Ni, to form alkanes, (ii) halogens to form dihalogenoalkanes, including the use of bromine to detect the presence of a double C=C bo ...
TEST - Alcohols and ethers A brief guide to alcohol, ether and epoxy
... ethanol, CH3CH2OH (note that a locator number is not needed on a two-carbon chain). On longer chains the location of the hydroxyl group determines chain numbering. For example: (CH3)2C=CHCH(OH)CH3 is 4-methyl-3-penten-2-ol. Other examples of IUPAC nomenclature are shown below, together with the comm ...
... ethanol, CH3CH2OH (note that a locator number is not needed on a two-carbon chain). On longer chains the location of the hydroxyl group determines chain numbering. For example: (CH3)2C=CHCH(OH)CH3 is 4-methyl-3-penten-2-ol. Other examples of IUPAC nomenclature are shown below, together with the comm ...
ALKENES and SULPHURIC ACID
... Use the BACK button (or HISTORY file or GO menu, if you have to explore several pages) on your browser if you want to return to this page. ...
... Use the BACK button (or HISTORY file or GO menu, if you have to explore several pages) on your browser if you want to return to this page. ...
Organic Chemistry –Syllabus- one Semester Sackler faculty of
... Organic Compounds + Alkanes double bond equivalent, alkyl group, Nomenclature (IUPAC rules), intermolecular forces( van der Waals force, Dipole–dipole interaction, Hydrogen bonds), Solubility, Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cy ...
... Organic Compounds + Alkanes double bond equivalent, alkyl group, Nomenclature (IUPAC rules), intermolecular forces( van der Waals force, Dipole–dipole interaction, Hydrogen bonds), Solubility, Conformations of alkanes(staggered-eclipsd) , Cycloalkanes, geometric isomers, The chair conformation of cy ...
Document
... • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the reaction of (CH3)3COCH3 with HI, the 3° alkyl group undergoes nucleophilic substi ...
... • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the reaction of (CH3)3COCH3 with HI, the 3° alkyl group undergoes nucleophilic substi ...
$doc.title
... Phenol Acidity • Phenols (pKa ~10) are much more acidic than alcohols (pKa ~ 16) because of resonance stabiliza1on of the phenoxide ion • Phenols react with NaOH solu1ons (but alcohols do not), forming ...
... Phenol Acidity • Phenols (pKa ~10) are much more acidic than alcohols (pKa ~ 16) because of resonance stabiliza1on of the phenoxide ion • Phenols react with NaOH solu1ons (but alcohols do not), forming ...
Lecture 4 - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... onto an organic compound, we form an alcohol – As long as that organic compound isn’t benzene or the carbon isn’t a carbonyl carbon ...
... onto an organic compound, we form an alcohol – As long as that organic compound isn’t benzene or the carbon isn’t a carbonyl carbon ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.