Chapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... • Since 1° carbocations are highly unstable, their dehydration cannot occur by an E1 mechanism involving a carbocation intermediate. Therefore, 1° alcohols undergo dehydration following an E2 mechanism. ...
... • Since 1° carbocations are highly unstable, their dehydration cannot occur by an E1 mechanism involving a carbocation intermediate. Therefore, 1° alcohols undergo dehydration following an E2 mechanism. ...
Carbon Chemistry
... • “Functional groups” can introduce elements other than carbon and hydrogen. • We will study only one important functional group which is formed by incorporating the element oxygen in the molecule as –O-H (“hydroxyl group”). • Functional groups are so-named because they result in an organic compound ...
... • “Functional groups” can introduce elements other than carbon and hydrogen. • We will study only one important functional group which is formed by incorporating the element oxygen in the molecule as –O-H (“hydroxyl group”). • Functional groups are so-named because they result in an organic compound ...
Functional Groups - La Salle University
... oxycontin (slow release) percocet (w/ acetominophen) ...
... oxycontin (slow release) percocet (w/ acetominophen) ...
Practice: Chapter 21
... halogen, the atoms are listed alphabetically. Numbers are used to identify the positions of the halogens. The lowest possible position number is given to the substituent that comes first alphabetically. 18. Both alcohols and ethers contain oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The oxygen atom in an alcohol ...
... halogen, the atoms are listed alphabetically. Numbers are used to identify the positions of the halogens. The lowest possible position number is given to the substituent that comes first alphabetically. 18. Both alcohols and ethers contain oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The oxygen atom in an alcohol ...
Synthesizing Organic Compounds
... 1. A food additive that is named as a single ingredient is often a mixture of many compounds. For example, a typical “artificial strawberry flavour” found in a milkshake may contain up to 50 different compounds. A few of these are listed below. For each, write a structural formula and an equation or ...
... 1. A food additive that is named as a single ingredient is often a mixture of many compounds. For example, a typical “artificial strawberry flavour” found in a milkshake may contain up to 50 different compounds. A few of these are listed below. For each, write a structural formula and an equation or ...
Chapter 1-Continue
... predictable way. • composed of an atom or group of atoms. • groups that replace a hydrogen atom in the corresponding alkane. • a way to classify families of organic compounds. ...
... predictable way. • composed of an atom or group of atoms. • groups that replace a hydrogen atom in the corresponding alkane. • a way to classify families of organic compounds. ...
This is the first exam with targeted syntheses that you
... The oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds is the reverse of nucleophilic addition (below). Most oxidants accept the alcohol oxygen as a nucleophile followed by loss of the acidic hydrogen. The process is completed by an E2-like elimination of hydrogen from the proto-carbonyl carbon in concert ...
... The oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds is the reverse of nucleophilic addition (below). Most oxidants accept the alcohol oxygen as a nucleophile followed by loss of the acidic hydrogen. The process is completed by an E2-like elimination of hydrogen from the proto-carbonyl carbon in concert ...
Functional Groups 2
... -Higher B.P’s than non-polar molecules -Lower than alcohols that can H-bond w/ each other -Can not H-bond between each other but can H-bond to solvents like water - Lower MW compounds are appreciably soluble in water ...
... -Higher B.P’s than non-polar molecules -Lower than alcohols that can H-bond w/ each other -Can not H-bond between each other but can H-bond to solvents like water - Lower MW compounds are appreciably soluble in water ...
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Preparation of Aldehydes and
... Jones Oxidation uses chromic acid (Jones Reagent) to carry out the oxidation. Jones reagent is prepared by adding CrO3 (or Na2Cr2O7) to sulphuric acid (H2SO4). The oxidation is performed in aqueous acetone solutions. Jones oxidation will not selectively oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes. Instead ...
... Jones Oxidation uses chromic acid (Jones Reagent) to carry out the oxidation. Jones reagent is prepared by adding CrO3 (or Na2Cr2O7) to sulphuric acid (H2SO4). The oxidation is performed in aqueous acetone solutions. Jones oxidation will not selectively oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes. Instead ...
ch12 by dina
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
01. Structure and properties of organic compounds. Aldehydes fnd
... Saturated — compounds that contain only bonds and nо - bonds (simple – C – C – bonds). Alkanes — saturated hydrocarbons that contain only – C – C – and – C – H – bonds. Unsaturated — compounds that contain bonds and - bonds (double bonds (– C = C –) or triple (– C C – ) bonds, and simple – ...
... Saturated — compounds that contain only bonds and nо - bonds (simple – C – C – bonds). Alkanes — saturated hydrocarbons that contain only – C – C – and – C – H – bonds. Unsaturated — compounds that contain bonds and - bonds (double bonds (– C = C –) or triple (– C C – ) bonds, and simple – ...
Molecular Biorefining: A New Strategy for Fungible Biofuels
... This research focuses on the development of a innovative approach for producing biofuels that exhibit superior cost, carbon, and sustainability characteristics compared to conventional biofuels. We have engineered industrially relevant microorganisms to produce desaturated fatty-acids, which will be ...
... This research focuses on the development of a innovative approach for producing biofuels that exhibit superior cost, carbon, and sustainability characteristics compared to conventional biofuels. We have engineered industrially relevant microorganisms to produce desaturated fatty-acids, which will be ...
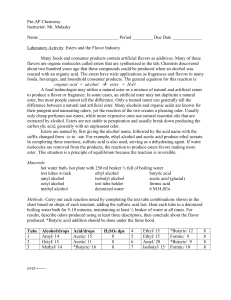
Pre-AP Chemistry
... only cheap perfumes use esters, while more expensive ones use natural essential oils that are extracted by alcohol. Esters are not stable to perspiration and usually break down producing the carboxylic acid, generally with an unpleasant odor. Esters are named by first giving the alcohol name, follow ...
... only cheap perfumes use esters, while more expensive ones use natural essential oils that are extracted by alcohol. Esters are not stable to perspiration and usually break down producing the carboxylic acid, generally with an unpleasant odor. Esters are named by first giving the alcohol name, follow ...
EXP-7
... The Cannizzaro reaction is that of aldehydes that do not contain alpha hydrogens to give carboxylic acids and alcohols (alpha hydrogens cause an Aldol reaction to take place). This occurs in the presence of a strong base. Benzaldehyde, which does not contain alpha hydrogens, was used for this reacti ...
... The Cannizzaro reaction is that of aldehydes that do not contain alpha hydrogens to give carboxylic acids and alcohols (alpha hydrogens cause an Aldol reaction to take place). This occurs in the presence of a strong base. Benzaldehyde, which does not contain alpha hydrogens, was used for this reacti ...
File
... • Alcohols are soluble in organic solvents. • Low molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or less) are soluble in water. • Higher molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or more) are not soluble in water. ...
... • Alcohols are soluble in organic solvents. • Low molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or less) are soluble in water. • Higher molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or more) are not soluble in water. ...
Mild Reduction of Carboxylic Acids to Alcohols
... © 1999ElsevierScienceLtd. All rightsreserved. Keywords: Reduction, Carboxylic acids, Alcohols, Amino acids. ...
... © 1999ElsevierScienceLtd. All rightsreserved. Keywords: Reduction, Carboxylic acids, Alcohols, Amino acids. ...
Section D19: Alkanes, Alkenes and Alcohols
... bromomethane in the presence of UV light. 3.6 recall that alkenes have the general formula CnH2n 3.7 draw displayed formulae for alkenes with up to four carbon atoms in a molecule, and name the straight-chain isomers (knowledge of cis- and transisomers is not required) 3.8 describe the addition reac ...
... bromomethane in the presence of UV light. 3.6 recall that alkenes have the general formula CnH2n 3.7 draw displayed formulae for alkenes with up to four carbon atoms in a molecule, and name the straight-chain isomers (knowledge of cis- and transisomers is not required) 3.8 describe the addition reac ...
Document
... Synthesis Cyclopropanes can be readily prepared by the addition of a carbene to the double bond of an alkene. A carbene has the general structure, R2C:, in which the central carbon is surrounded by six electrons (sextet), and is thus electron deficient. The electron-deficient carbene readily adds to ...
... Synthesis Cyclopropanes can be readily prepared by the addition of a carbene to the double bond of an alkene. A carbene has the general structure, R2C:, in which the central carbon is surrounded by six electrons (sextet), and is thus electron deficient. The electron-deficient carbene readily adds to ...
Functional Groups
... shown by a number inserted before the functional group ending. The number refers to the carbon atom to which the functional group is attached when the chain is numbered starting at the end that will give the smallest number to the group. ...
... shown by a number inserted before the functional group ending. The number refers to the carbon atom to which the functional group is attached when the chain is numbered starting at the end that will give the smallest number to the group. ...
Carbon Compounds
... – Higher boiling points than hydrocarbons with a similar number of carbons – Alcohol methanol – CH3OH ...
... – Higher boiling points than hydrocarbons with a similar number of carbons – Alcohol methanol – CH3OH ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.