Addition of Alcohols to Form Hemiacetals and Acetals
... Amines and aldehydes or ketones react to form hemiaminals, the nitrogen analogs of hemiacetals. The hemiaminals of primary amines then lose water to form an imine (previously, Schiff base). This is the nitrogen analog of the carbonyl group. ...
... Amines and aldehydes or ketones react to form hemiaminals, the nitrogen analogs of hemiacetals. The hemiaminals of primary amines then lose water to form an imine (previously, Schiff base). This is the nitrogen analog of the carbonyl group. ...
Document
... D. Urea is obtained from nitrogen dioxide and ammonia in acidic catalysis E. Urea can be obtained from ammonium cyanate 29. In a 1L volumetric flask 0.25 moles of hydrochloric acid and 820 mL of distilled water are found. 10 g of sodium hydroxide are added, mixed, and the flask is filled to the line ...
... D. Urea is obtained from nitrogen dioxide and ammonia in acidic catalysis E. Urea can be obtained from ammonium cyanate 29. In a 1L volumetric flask 0.25 moles of hydrochloric acid and 820 mL of distilled water are found. 10 g of sodium hydroxide are added, mixed, and the flask is filled to the line ...
Review 3 - Bonham Chemistry
... 21. Industrially, we often need ethanoic acid. The starting material for this product is usually ethane. Show below a series of reactions that would transform ethane to ethanoic acid. ...
... 21. Industrially, we often need ethanoic acid. The starting material for this product is usually ethane. Show below a series of reactions that would transform ethane to ethanoic acid. ...
Document
... Oxidation of Alcohols • Recall that the oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds is typically carried out with Cr6+ oxidants, which are reduced to Cr3+ products. • CrO3, Na2Cr2O7, and K2Cr2O7 are strong, nonselective oxidants used in aqueous acid (H2SO4 + H2O). • PCC is soluble in CH2Cl2 (dichlor ...
... Oxidation of Alcohols • Recall that the oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds is typically carried out with Cr6+ oxidants, which are reduced to Cr3+ products. • CrO3, Na2Cr2O7, and K2Cr2O7 are strong, nonselective oxidants used in aqueous acid (H2SO4 + H2O). • PCC is soluble in CH2Cl2 (dichlor ...
IC.29.3 Alcohol as fuel
... • Ethanol produces carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, as it burns. • Carbon dioxide is also added to the atmosphere as a result of making fertilisers for the crops, and during the manufacture of ethanol from the crops. • Some people say this means ethanol fuel is not carbon neutral. © Oxford Universi ...
... • Ethanol produces carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, as it burns. • Carbon dioxide is also added to the atmosphere as a result of making fertilisers for the crops, and during the manufacture of ethanol from the crops. • Some people say this means ethanol fuel is not carbon neutral. © Oxford Universi ...
Slide 1
... ~ Methanol & its toxicity ~ Methanol itself may cause inebriation but by itself is almost completely non-toxic. The problem you see is methanol is metabolized by liver alcohol dehydrogenase also; to formaldehyde then to formic acid. It is these two metabolites that cause toxicity, with formic acid b ...
... ~ Methanol & its toxicity ~ Methanol itself may cause inebriation but by itself is almost completely non-toxic. The problem you see is methanol is metabolized by liver alcohol dehydrogenase also; to formaldehyde then to formic acid. It is these two metabolites that cause toxicity, with formic acid b ...
Chemistry of alcohols (powerpoint)
... from either side of the carbocation. This gives a mixture of alkenes from unsymmetrical alcohols... ...
... from either side of the carbocation. This gives a mixture of alkenes from unsymmetrical alcohols... ...
Chapter 20 - people.vcu.edu
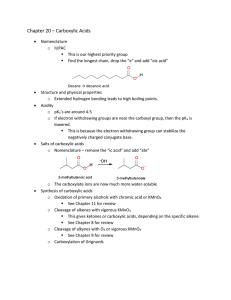
... Structure and physical properties o Extended hydrogen bonding leads to high boiling points. Acidity o pKa’s are around 4-5 o If electron withdrawing groups are near the carboxyl group, then the pK a is lowered. This is because the electron withdrawing group can stabilize the negatively charged con ...
... Structure and physical properties o Extended hydrogen bonding leads to high boiling points. Acidity o pKa’s are around 4-5 o If electron withdrawing groups are near the carboxyl group, then the pK a is lowered. This is because the electron withdrawing group can stabilize the negatively charged con ...
Organic Functional Groups: Aldehydes, Ketones, Acids, Esters
... • Aldehydes and ketones with the same number of carbons are isomers of one another. You will verify this for yourself later. ...
... • Aldehydes and ketones with the same number of carbons are isomers of one another. You will verify this for yourself later. ...
3. Alkanes
... In bicycloalkanes, we name the compound according to the total number of carbons encompassed by the two rings. Numbering starts at one of the bridgehead carbons and proceeds along the longest bridge to the other bridgehead, then along the next longest bridge back to the fist bridgehead. The shortest ...
... In bicycloalkanes, we name the compound according to the total number of carbons encompassed by the two rings. Numbering starts at one of the bridgehead carbons and proceeds along the longest bridge to the other bridgehead, then along the next longest bridge back to the fist bridgehead. The shortest ...
Ch. 09 Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides
... more stable carbocation. • Rearrangements are not unique to dehydration reactions. • Rearrangements can occur whenever a carbocation is formed as a reactive intermediate. • 2° carbocation A rearranges to the more stable 3° carbocation by a 1,2-hydride shift, whereas carbocation B does not rearrange ...
... more stable carbocation. • Rearrangements are not unique to dehydration reactions. • Rearrangements can occur whenever a carbocation is formed as a reactive intermediate. • 2° carbocation A rearranges to the more stable 3° carbocation by a 1,2-hydride shift, whereas carbocation B does not rearrange ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... • Cyclic hydrocarbons. • Molecule is planar. • Many aromatic hydrocarbons are known by their common names. ...
... • Cyclic hydrocarbons. • Molecule is planar. • Many aromatic hydrocarbons are known by their common names. ...
C3 3.1-3.4 part 1 Alcohols, carboxlic acids and esters progress ticket
... Organic compounds such as ethyl propanoate are used in perfumes. Give two properties of these compounds that make them suitable for use in perfumes. ...
... Organic compounds such as ethyl propanoate are used in perfumes. Give two properties of these compounds that make them suitable for use in perfumes. ...
- professional publication
... Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions Effect of Substituent Groups, Determination of Orientation, Determination of Relative Reactivity, Classification of Substituent Groups, Mechanism of Nitration, Sulphonation, Halogenation, Friedel Craft’s Alkylation and Friedel Craft’s Acylation, Reactivity and Or ...
... Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions Effect of Substituent Groups, Determination of Orientation, Determination of Relative Reactivity, Classification of Substituent Groups, Mechanism of Nitration, Sulphonation, Halogenation, Friedel Craft’s Alkylation and Friedel Craft’s Acylation, Reactivity and Or ...
Alkanes CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl CH3CH3 + Cl2 → CH3CH2Cl +
... Alcohols can be dehydrated to form alkenes. The reactions can be classified as dehydration or elimination. Reagents and conditions are heat under reflux at 170oC with excess conc. H2SO4, or heat at 300oC over Al2O3. You should be able to predict the alkenes that would form from a typical alcohol, su ...
... Alcohols can be dehydrated to form alkenes. The reactions can be classified as dehydration or elimination. Reagents and conditions are heat under reflux at 170oC with excess conc. H2SO4, or heat at 300oC over Al2O3. You should be able to predict the alkenes that would form from a typical alcohol, su ...
Evaporation and
... 3. Wrap Probe 1 and Probe 2 with a 3cm by 3cm square pieces of filter paper and secure with a small rubber band. You are trying to manke a paper skirt and not a paper sock. The paper should be even with the probe end. Suspend these probes from an iron ring so that they hang freely. 4. Find your gogg ...
... 3. Wrap Probe 1 and Probe 2 with a 3cm by 3cm square pieces of filter paper and secure with a small rubber band. You are trying to manke a paper skirt and not a paper sock. The paper should be even with the probe end. Suspend these probes from an iron ring so that they hang freely. 4. Find your gogg ...
04_01_03.html
... Overview of Chapter This chapter introduces chemical reactions and their mechanisms by focusing on two reactions that yield alkyl halides. (1) alcohol + hydrogen halide ROH + HX RX + H2O (2) alkane + halogen RH + X2 RX + HX Both are substitution reactions ...
... Overview of Chapter This chapter introduces chemical reactions and their mechanisms by focusing on two reactions that yield alkyl halides. (1) alcohol + hydrogen halide ROH + HX RX + H2O (2) alkane + halogen RH + X2 RX + HX Both are substitution reactions ...
Organic Chemistry: Chemistry that involves Carbon
... Task: Write out the balanced equations for the combustion of Ethane Propane and Butane, assuming Oxygen is present. ...
... Task: Write out the balanced equations for the combustion of Ethane Propane and Butane, assuming Oxygen is present. ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.