Products From Oil
... ETHANOL C2H5OH Ethanol can be produced in two ways: by the fermentation of sugars by the hydration of ethene. 1. Fermentation of Sugars Fermentation is used to produce ethanol as an industrial chemical. The raw material, usually glucose, is dissolved in water to make a solution containing about ...
... ETHANOL C2H5OH Ethanol can be produced in two ways: by the fermentation of sugars by the hydration of ethene. 1. Fermentation of Sugars Fermentation is used to produce ethanol as an industrial chemical. The raw material, usually glucose, is dissolved in water to make a solution containing about ...
Revision
... when treated with KOH in ethanol, gives Y ( an isomer of X ). Ozonolysis of X (H2O2 workup) produces two compounds: a two carbon Aldehyde, and a four carbon ketone. What is X? ...
... when treated with KOH in ethanol, gives Y ( an isomer of X ). Ozonolysis of X (H2O2 workup) produces two compounds: a two carbon Aldehyde, and a four carbon ketone. What is X? ...
CAPE CHEMISTRY UNIT TWO REVISION PAPER MODULE 1 (a
... dioxide. [4 marks] Residence time refers to the average time that a molecule of a particular gas spends in the atmosphere from its introduction by a source to its removal by a sink. Residence time is affected by the concentration of the gas that is naturally present and the rate by which it is remov ...
... dioxide. [4 marks] Residence time refers to the average time that a molecule of a particular gas spends in the atmosphere from its introduction by a source to its removal by a sink. Residence time is affected by the concentration of the gas that is naturally present and the rate by which it is remov ...
alcohol - Haverford Alchemy
... often referred to by the common name glycols. • This is preferably reserved for two compounds, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. • Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary according to the number of carbon substituents bonded to the hydroxyl-bearing carbon. • This classificatio ...
... often referred to by the common name glycols. • This is preferably reserved for two compounds, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. • Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary according to the number of carbon substituents bonded to the hydroxyl-bearing carbon. • This classificatio ...
Unit 2 Content Statements
... To meet market demand ethanol is made by means other than fermentation. Direct catalytic hydration of alkenes is another way of making alkanols. Alkanols can be converted to alkenes by dehydration. The benzene ring resists addition reactions. (ii) Oxidation Alcohols burn in oxygen and air to produce ...
... To meet market demand ethanol is made by means other than fermentation. Direct catalytic hydration of alkenes is another way of making alkanols. Alkanols can be converted to alkenes by dehydration. The benzene ring resists addition reactions. (ii) Oxidation Alcohols burn in oxygen and air to produce ...
organic chemistry i
... Industrial source o hydration of alkenes o oxo process o Fermentation of carbohydrates Fuel from carbohydrates. Carbon dioxide balance Ethanol Preparation of alcohol o hydrolysis of alkyl halides o grignard synthesis Reactions of alcohol o reaction with hydrogen halide o reaction with phosphorus tri ...
... Industrial source o hydration of alkenes o oxo process o Fermentation of carbohydrates Fuel from carbohydrates. Carbon dioxide balance Ethanol Preparation of alcohol o hydrolysis of alkyl halides o grignard synthesis Reactions of alcohol o reaction with hydrogen halide o reaction with phosphorus tri ...
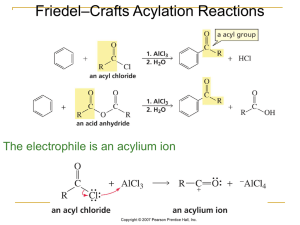
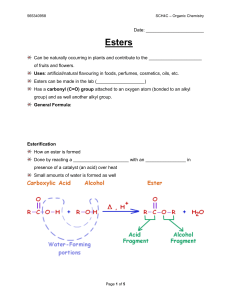
Esterification
... formation of phenyl benzoate from benzyl chloride and phenol including a detailed explanation of recrystallization. ...
... formation of phenyl benzoate from benzyl chloride and phenol including a detailed explanation of recrystallization. ...
Word Version of Answer Key
... In order to answer this question, first you must know what makes alcohol different from other foods and beverages. The answer? It’s the chemical makeup of alcohol! All types of alcohol contain ethanol, or C2H5OH. The picture to the left shows what the actual compound looks like. The ethanol molecule ...
... In order to answer this question, first you must know what makes alcohol different from other foods and beverages. The answer? It’s the chemical makeup of alcohol! All types of alcohol contain ethanol, or C2H5OH. The picture to the left shows what the actual compound looks like. The ethanol molecule ...
9- alcohol_dehydrogenase_mechanism
... • Ethanol binds to the hydrophobic core lined by nine amino acids, which surround the substrate • After binding NAD+, the 100 rotation makes the protein go from its apo "open" form to the halo "closed". This narrows the cleft, brings the substrate binding site closer and excludes water from the acti ...
... • Ethanol binds to the hydrophobic core lined by nine amino acids, which surround the substrate • After binding NAD+, the 100 rotation makes the protein go from its apo "open" form to the halo "closed". This narrows the cleft, brings the substrate binding site closer and excludes water from the acti ...
Chpt. 22: Some Families of Organic Compounds
... • The higher boiling points are due to the fact that the highly polar –OH group gives rise to hydrogen bonding between the alcohol molecules. Oxygen, being more electronegative, has a partial negative charge, and hydrogen has a partial positive charge. The oxygen in the hydroxyl group in one molecul ...
... • The higher boiling points are due to the fact that the highly polar –OH group gives rise to hydrogen bonding between the alcohol molecules. Oxygen, being more electronegative, has a partial negative charge, and hydrogen has a partial positive charge. The oxygen in the hydroxyl group in one molecul ...
Chapter 10
... An organic compound containing at least one halogen attached to an sp3 hybridized carbon ...
... An organic compound containing at least one halogen attached to an sp3 hybridized carbon ...
Name / Functional Group
... 2. You need a water bath of approximately 60°C. Fill a 400 mL beaker about 1/3 full of tap water and heat it to boiling by turning on the hot plate to “10”. 2. Place one spatula-tip of solid salicylic acid into the test tube (about ¼ tsp). 3. Add 20 drop of methanol (methyl alcohol). Be careful, the ...
... 2. You need a water bath of approximately 60°C. Fill a 400 mL beaker about 1/3 full of tap water and heat it to boiling by turning on the hot plate to “10”. 2. Place one spatula-tip of solid salicylic acid into the test tube (about ¼ tsp). 3. Add 20 drop of methanol (methyl alcohol). Be careful, the ...
Esters - Mr. Lee`s Science
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
... Uses: artificial/natural flavouring in foods, perfumes, cosmetics, oils, etc. Esters can be made in the lab (___________________) Has a carbonyl (C=O) group attached to an oxygen atom (bonded to an alkyl group) and as well another alkyl group. General Formula: ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.